Perseverance Rover Captures Eclipse on Mars
For Prelims: Solar Eclipse, Perseverance Rover, Mars Missions, Planet Mars, NASA
For Mains: Space Technology, Perseverance Rover, Phobos, Mars
Why in News?
Recently, NASA’s (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) Perseverance Rover has captured a solar eclipse on Mars.
- Perseverance Mars rover captured an eclipse featuring Phobos, one of Mars' two moons. Phobos is moving very slowly towards Mars, and millions of years from now, they will collide.
- These observations can help scientists better understand the moon’s orbit and how its gravity pulls on the Martian surface, ultimately shaping the Red Planet’s crust and mantle.
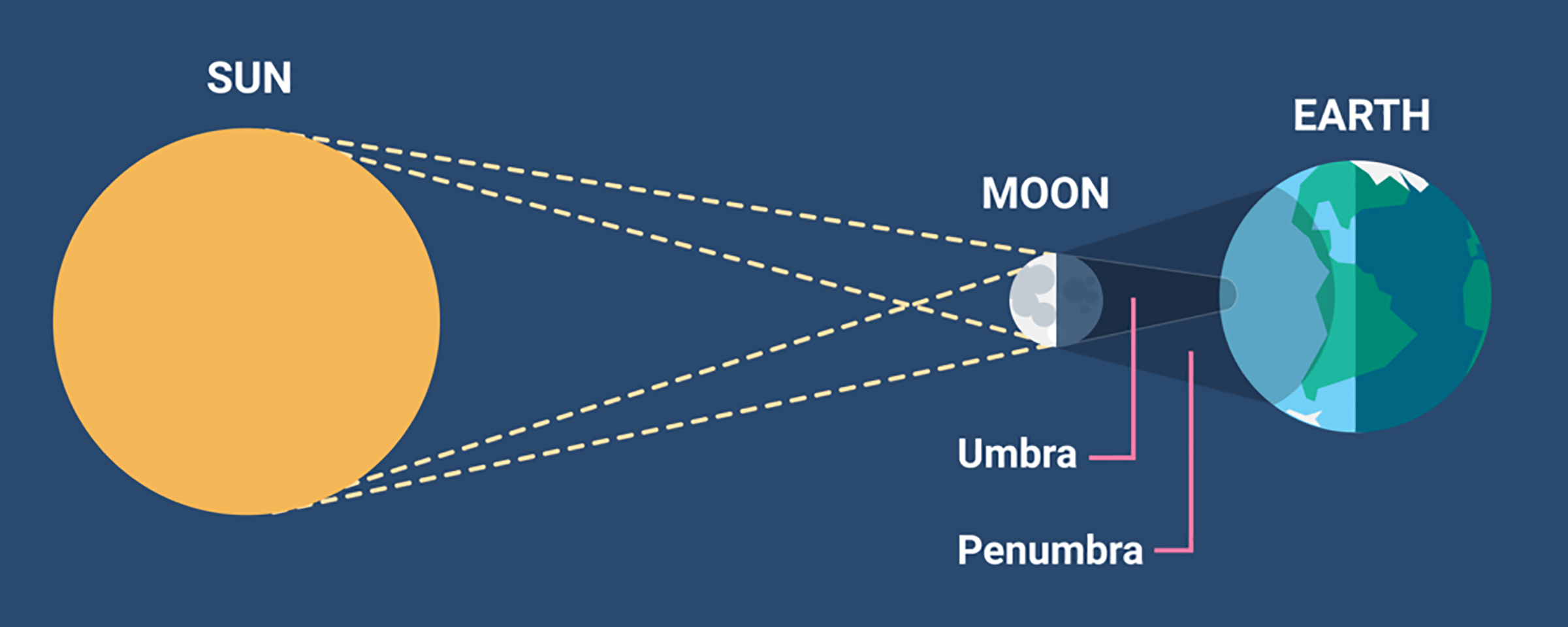
What is Solar Eclipse?
- A solar eclipse is a phenomenon that occurs when the moon comes in the way of the sun’s light. The moon's shadow casts itself on Earth, blocking out the sun's light (as seen from Earth).
- The moon's shadow has two parts: a central region (umbra) and an outer region (penumbra). Depending upon which part of the shadow passes over the Earth, one of three types of solar eclipses could be observed:
- Total Solar Eclipse- The entire central portion of the sun is blocked out by the moon.
- Partial Solar Eclipse- Only part of the sun's surface is blocked out.
- Annular Solar Eclipse- The sun is covered in such a way that only a small ring-like sliver of light is seen from the sun's disc. This ring is known as the ring of fire.
- An annular eclipse happens when the moon is farthest from Earth. As the moon is farther away from Earth, it seems smaller and is unable to block the entire view of the sun, because of which the ring-like structure could be observed.
What is Perseverance Rover?
- About:
- Perseverance is the most advanced, most expensive and most sophisticated mobile laboratory sent to Mars.
- It is different from previous missions because it is capable of drilling and collecting core samples of the most promising rocks and soils and setting them aside in a "cache" on the surface of Mars.
- It is the centerpiece of NASA's Mars 2020 mission which also included the small robotic and coaxial helicopter Ingenuity.
- Launch: 30th July 2020
- Landing: 18th February 2021
- Power Source:
- A Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) which converts heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium (Plutonium Dioxide) into electricity.
- Objectives:
- Perseverance’s primary objective is looking for signs of ancient microbial life.
- The rover is studying and analyzing the Red Planet's regolith, rock and dust, and is the first rover to collect and cache samples.
What is Mars?
- Size and Distance:
- It is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System.
- Mars is about half the size of Earth.
- Similarity to the Earth (Orbit and Rotation):
- As Mars orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 24.6 hours, which is very similar to one day on Earth (23.9 hours).
- Mars' axis of rotation is tilted 25 degrees with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. This is similar with Earth, which has an axial tilt of 23.4 degrees.
- Like Earth, Mars has distinct seasons, but they last longer than seasons on Earth since Mars takes longer to orbit the Sun (because it's farther away).
- Martian days are called sols—short for ‘solar day’.
- Surface:
- It has colors such as brown, gold and tan. The reason Mars looks reddish is due to oxidation or rusting of iron in the rocks, and dust of Mars. Hence it is also called Red Planet.
- Mars has the largest volcano in the solar system i.e. Olympus Mons. It's three times taller than Earth's Mt. Everest with a base the size of the state of New Mexico.
- Atmosphere:
- Mars has a thin atmosphere made up mostly of carbon dioxide, nitrogen and argon gases.
- Magnetosphere:
- Mars has no magnetic field till date, but areas of the Martian crust in the southern hemisphere are highly magnetized, indicating traces of a magnetic field.
- Moons:
- Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, that may be captured asteroids.
What are the other Mars Missions?
- ExoMars rover (2021):
- The European Space Agency and Russian space agency planned to send a joint mission to Mars in September 2022.
- It has since been suspended after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- The European Space Agency and Russian space agency planned to send a joint mission to Mars in September 2022.
- Tianwen-1: China's Mars Mission (2021):
- China’s first Mars mission will search for pockets of water beneath the surface that could host life.
- UAE’s Hope Mars Mission (UAE’s first-ever interplanetary mission) (2021):
- The UAE Hope Mars Mission is building a complete picture of Mars' climate.
- India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan (2013):
- Mangalyaan is India’s Mars orbiter that has been observing the planet since September 2014.
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971):
- The identical Soviet Mars 2 and Mars 3 spacecraft, launched in 1971, each released descent craft 4.5 hours prior to their arrivals at Mars. But the landers had the misfortune of arriving at Mars during one of the greatest dust storms in recorded history.