World Bioproduct Day 2025 and BioE3 Policy | 10 Jul 2025
Why in News?
The Department of Science & Technology (DST), along with BIRAC and iBRIC+, organized World Bioproduct Day 2025, focusing on Equity, Environment, and Economy to highlight the importance of inclusive public participation in biotechnology.
- The event also reiterated the government's goal of achieving a USD 300 billion bioeconomy by 2030 under the BioE3 framework.
World Bioproduct Day
- Launched in 2021 by the World Bioeconomy Forum, the day aims to promote awareness about the potential of bio-based products in advancing environmental sustainability, climate action, and green innovation by reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
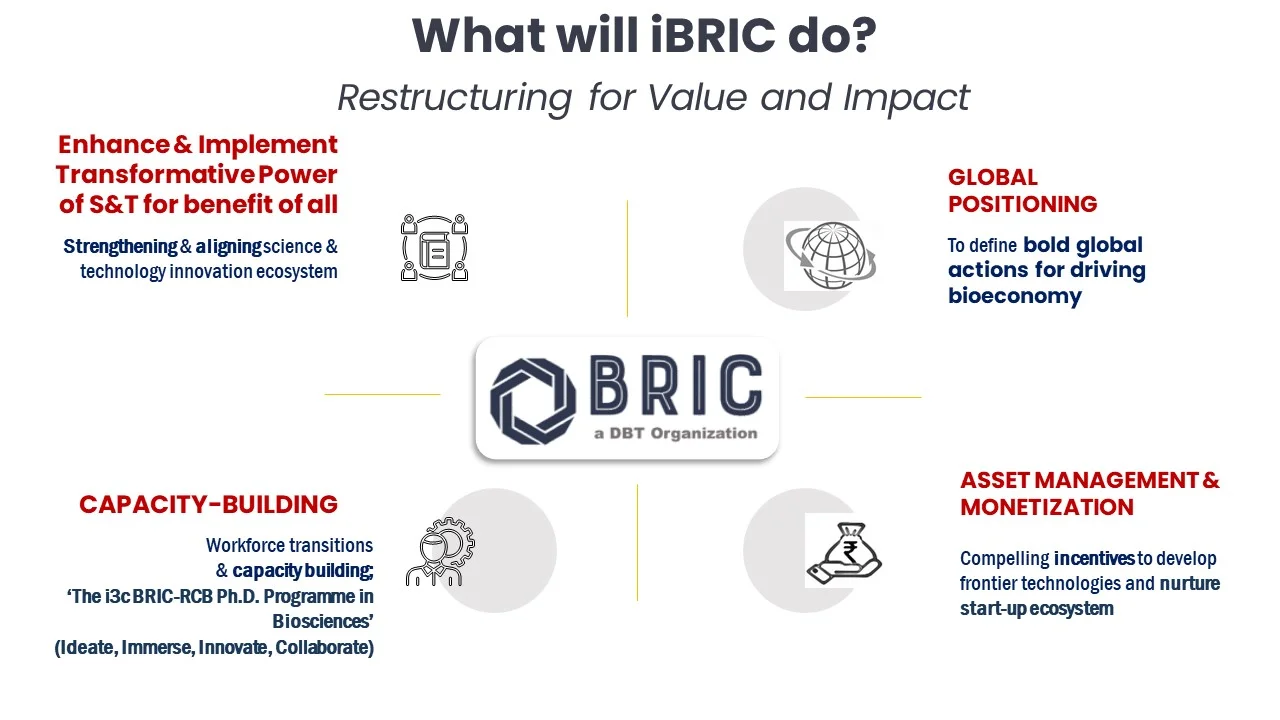
iBRIC+
- iBRIC+ (Indian Bioeconomy Research and Innovation Consortium Plus) is a strategic initiative by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) aimed at accelerating India’s bioeconomy through a collaborative, multi-stakeholder platform.
- Building on the iBRIC foundation, it expands focus to strengthen regional innovation ecosystems and support a sustainable, high-performing bioeconomy.
- It complements BRIC, which integrates 13 DBT institutions under one framework to improve governance, ensure HR parity, promote NEP-aligned research, enable interdisciplinary collaboration, and align R&D with national missions for enhanced socio-economic impact.
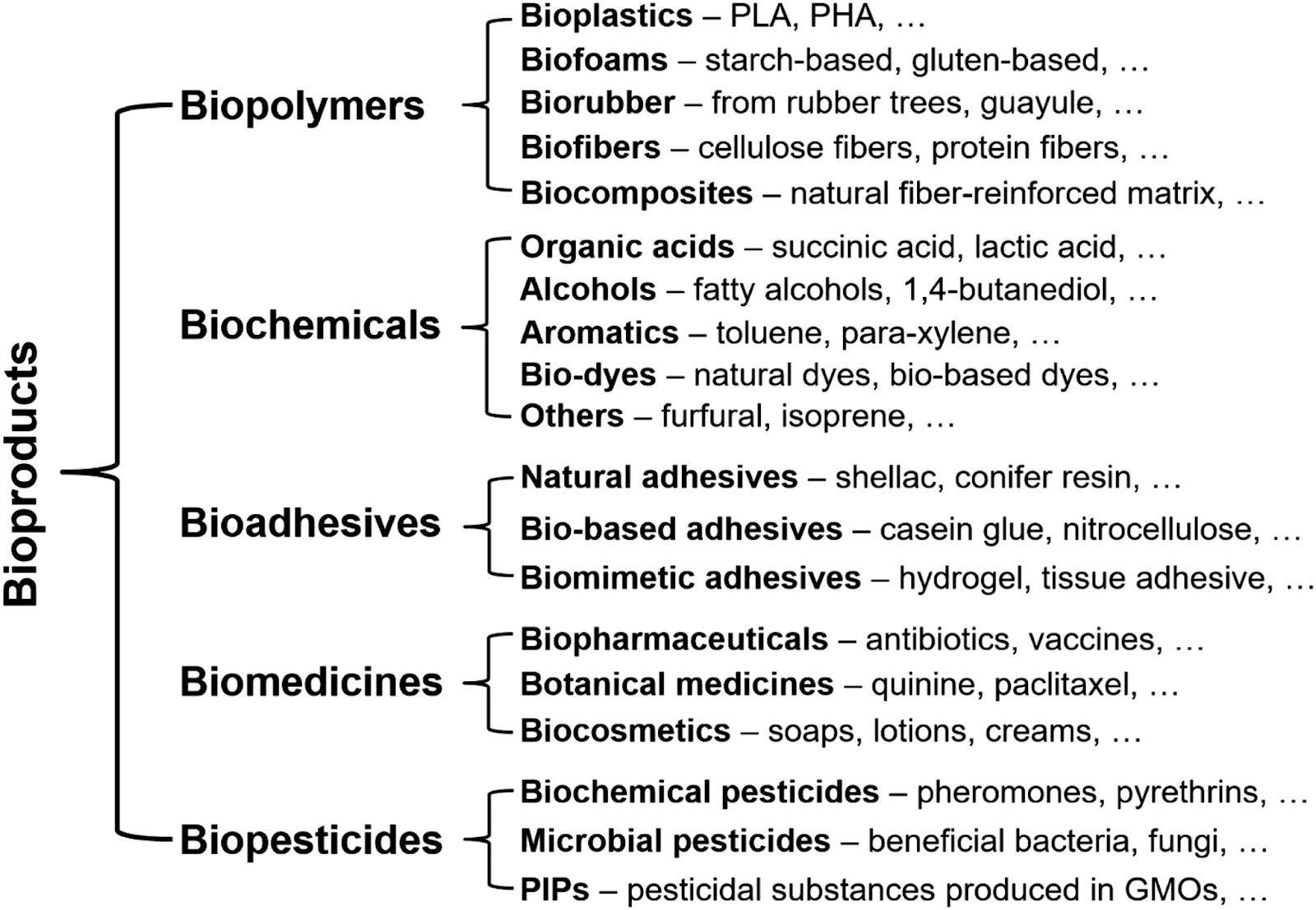
What are Bioproducts?
- About: Bioproducts are fuels, materials, and chemicals made from renewable biomass like crops, trees, algae, and agricultural waste.
- Eg: Biofuels (ethanol, biogas), bioplastics, bio-based cosmetics, and plant-derived medicines.
- Significance: Bioproducts reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby addressing air pollution, deforestation, and biodiversity loss.
- Through biotechnological innovation, they promote climate-resilient development without compromising product quality or performance.
- Categories of Bioproducts:
- Production Methods: Bioproducts are produced using methods such as fermentation, pyrolysis, enzymatic conversion, and chemical synthesis.
- Biodegradability: Not all bioproducts are biodegradable and it depends on the intended use (e.g., bio-based paint is not biodegradable).
- Feedstocks & Sustainability: Common sources include soybeans, corn, sugarcane, sunflowers, flax, potatoes, algae, and mycelium.
- Many bioproducts use agricultural or forestry waste, minimizing pressure on food supply. For example, sunflower residue after seed removal can be converted into biofuel.
What is the BioE3 Policy?
- About: The BioE3 Policy (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment, and Employment), launched by the Department of Biotechnology in 2024 to promote high-performance biomanufacturing by integrating advanced biotechnological processes across key sectors.
- It aims to strengthen India’s bioeconomy through sustainable practices, innovation, and employment generation.
- It supports India's broader goals of achieving a 'Net Zero' carbon economy and promoting sustainable growth through a circular bioeconomy.
- Key Features:
- Biomanufacturing Infrastructure: The policy focuses on boosting research and development (R&D), entrepreneurship, and the creation of Biomanufacturing & Bio-AI hubs and Biofoundries.
- Supports Sustainable Biomanufacturing: Aligned with the ‘Lifestyle for Environment’ (LiFE) initiative, the policy supports the development of regenerative bioeconomy models that are sustainable and resource-efficient.
- It also emphasizes ethical biosafety and global regulatory alignment to boost India's global competitiveness while ensuring responsible biotechnology development.
- Workforce Expansion: Focuses on building a skilled biotechnology workforce, especially in Tier-II and Tier-III cities, to create new jobs and drive inclusive regional growth using local biomass.
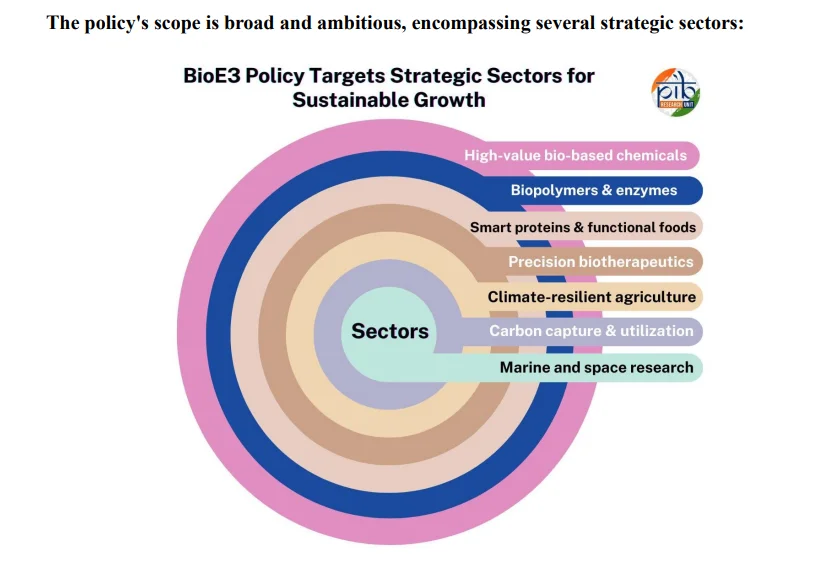
- Core Themes of BioE3 Policy:
- Bio-Based Chemicals & Enzymes: Promote eco-friendly alternatives to petrochemicals.
- Functional Foods & Smart Proteins: Develop nutrient-rich, sustainable food sources.
- Precision Biotherapeutics: Advance targeted medical treatments and diagnostics.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Support farming techniques adapted to climate change.
- Carbon Capture & Utilization (CCU): Encourage technologies to capture and reuse carbon.
- Futuristic Marine & Space Research: Explore marine and space biotech for novel solutions in biomanufacturing.
Government Initiatives Related to Biotechnology
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)