Weather Balloons | 24 May 2025
The US has reduced its weather balloon launches following budget cuts by the administration, causing concerns globally among meteorologists about the impact on weather forecasting accuracy.
Weather Balloons:
- About: Léon Teisserenc de Bort, a French meteorologist, pioneered weather balloon use in 1896 and discovered the tropopause and stratosphere.
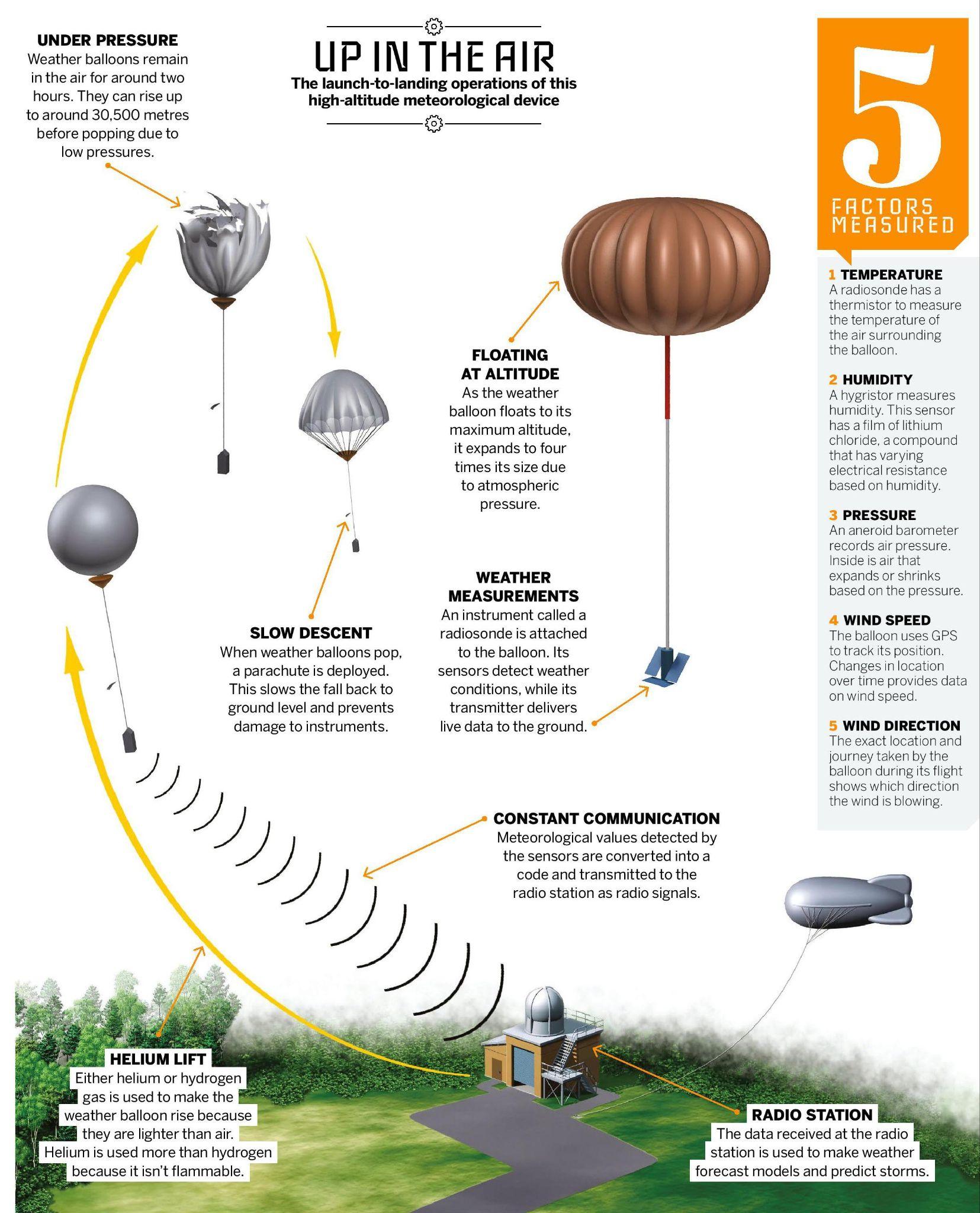
- Weather balloons are large latex balloons filled with helium or hydrogen, used by meteorologists to study the upper atmosphere (above 5,000 feet).
- Modern weather balloons can rise up to 1,15,000 feet (35 km) in about 2 hours.
- Key Components: They carry a radiosonde, a small battery-powered radio-transmitter suspended about 66 feet below, which collects and transmits real-time data on temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind to ground stations via radio signals.
- High-tech radiosondes are lighter, more energy-efficient, and use Global Positioning System (GPS) for accurate tracking and wind measurement, though they are still launched using weather balloons.
- Significance: Helps fill the gap between surface observations and satellite data, offering detailed vertical profiles of the atmosphere essential for accurate weather prediction.
- India’s Scenario: The National Balloon Facility (NBF), Hyderabad, was established in the 1960s as a collaborative initiative between the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) and the ISRO to enable high-altitude scientific balloon launches for atmospheric and space research.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) and over 900 global weather stations launch balloons twice daily to maintain forecasting accuracy.
| Read More: Weather Monitoring by IMD, Surveillance Balloon |