SRVAs and Internationalization of Rupee | 18 Aug 2025
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India, Special Rupee Vostro Accounts, Treasury Bills, G-secs, Unified Payments Interface
For Mains: Internationalization of Indian Currency benefits and challenges, Growth & Development
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has allowed non-residents holding Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs) to invest surplus balances in government securities, while also removing prior approval for banks to open SRVAs, these steps aimed at boosting rupee trade and internationalising the Indian Rupee.
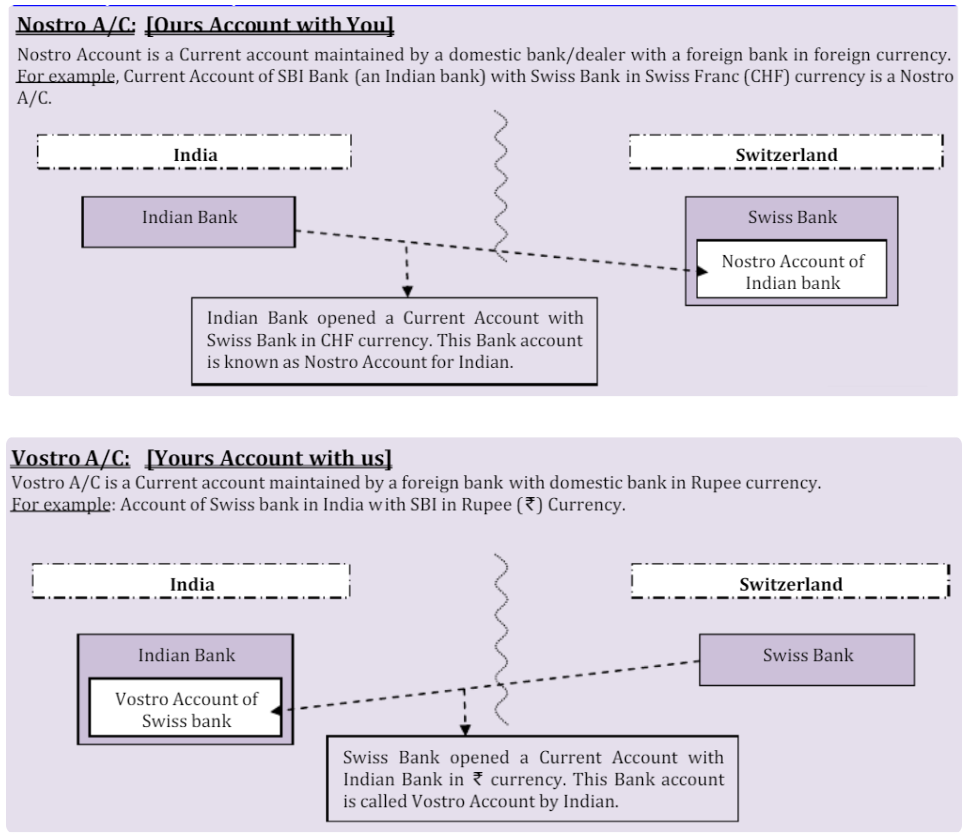
What are Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVAs)?
- About: SRVAs are accounts opened by foreign entities with Indian banks. They facilitate settlement of international trade transactions in Indian Rupees.
- SRVAs introduced in 2022, the mechanism allows exporters and importers to invoice and settle trade directly in rupees.
- RBI Measures to Promote Rupee through SRVAs: Non-resident entities with SRVAs can now invest their rupee surplus balances in Central government securities (G-secs) and Treasury Bills.
- Earlier authorised dealer (AD) banks required RBI’s prior approval before opening SRVAs for overseas correspondent banks. Now AD banks can open SRVAs independently without seeking RBI permission.
- This aims to quicken the operationalisation of rupee-based trade settlements.
- Earlier authorised dealer (AD) banks required RBI’s prior approval before opening SRVAs for overseas correspondent banks. Now AD banks can open SRVAs independently without seeking RBI permission.
- Significance: Promotes internationalisation of the Indian Rupee. Reduces dependence on hard currencies like the US dollar in bilateral trade.
- Encourages surplus rupee funds to be productively deployed in Indian government securities.
What is Internationalization of Rupee?
- About: Internationalization of the rupee refers to promoting its usage in cross-border trade, investments, and financial transactions without mandatory conversion to a dominant foreign currency like the USD.
- Benefits:
- Reduces Vulnerability: Less reliance on foreign currencies like the dollar shields the economy from global crises and currency shortages.
- Settling trade in INR lowers hedging costs and protects businesses from currency volatility, boosting competitiveness.
- Eases Forex Reserve Pressure: Reduces the need to hold large USD/EUR reserves, freeing resources for other priorities.
- Enables Deficit Financing: Global acceptance of INR allows the government to raise funds abroad through rupee-denominated bonds.
- Strengthens Markets: More foreign demand for INR assets deepens Indian bond and equity markets, attracting long-term capital.
- Reduces Vulnerability: Less reliance on foreign currencies like the dollar shields the economy from global crises and currency shortages.
- Negative Impacts: Increases exposure to global volatility and complicates monetary management.
- Large foreign participation could destabilize equity or debt markets if not regulated properly.
What are the Challenges in the Internationalisation of Rupee?
- Limited Global Acceptance: INR is not fully convertible on the capital account, which restricts its usage in global financial markets.
- The absence of INR in major platforms like CLS (Continuous Linked Settlement) limits settlement efficiency.
- INR Liquidity Constraints Abroad: Lack of readily available INR liquidity in overseas financial systems hampers the ease of settlement in INR.
- Regulatory and Documentation Complexities: Stringent KYC norms, inconsistent across RBI and SEBI, act as a deterrent for foreign portfolio investors (FPIs).
- Insufficient Trade Invoicing in INR: A major portion of India’s external trade is still invoiced and settled in USD or other convertible currencies.
- Lack of INR-based Payment Infrastructure Globally: Limited integration of UPI, Real Time Gross Settlement System (RTGS), and RuPay with foreign payment systems restricts cross-border transactions.
- Geopolitical and Currency Dominance: The USD's dominance as the global reserve and trade currency poses a structural limitation.
- Countries may hesitate to adopt INR unless India becomes a major trading and financial hub.
Major Steps Taken for Internationalisation of Rupee
- SVRAs: Operationalized with 22 countries to facilitate rupee trade settlements.
- MoUs with Central Banks: Signed with UAE, Indonesia, Maldives, etc., to settle bilateral trade in local currencies.
- UPI Global Expansion: As of July 2025 Unified Payments Interface is operational in seven countries (UAE, Singapore, Bhutan, Nepal, Sri Lanka, France, and Mauritius).
- Strategic Action Plan 2024–25 (RBI): Includes allowing persons resident outside India (PROI) to open INR accounts abroad, permitting Indian banks to lend in INR to PROIs, and enabling FDI and portfolio investment through Special Non-Resident Rupee Accounts (SNRR) and SRVAs.
- The RBI has liberalized Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 to promote the internationalization of the rupee for cross-border trade settlement.
- Currency Swap Agreements: Singed with more than 20 countries it facilitates liquidity support and trade settlement in local currencies.
- Masala Bonds: Issuance of rupee-denominated bonds to attract global investors.
What are RBI’s Recommendations for Internationalisation of Rupee?
- Boost Cross‑Border Settlement Mechanisms: Develop and standardize Local Currency Settlement (LCS) frameworks supported by sufficient INR liquidity, to reduce dependency on USD.
- Strengthening Financial Market Infrastructure: Build a global 24×5 INR forex market, enabling interbank trades via overseas branches and extended CCIL platform hours.
- Facilitate G‑sec inclusion in indices like JPMorgan, to attract stable passive flows.
- Simplify KYC and Onboarding: Harmonize KYC norms across RBI, SEBI, and global custodians. Accept digital signatures, and scanned documents with Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT) confirmations to reduce processing delays.
- Include INR in IMF’s SDR Basket: Position INR as a global reserve currency by aiming for inclusion in the International Monetary Fund (IMF) Special Drawing Rights basket.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Internationalisation of the rupee reduces dollar dependence but risks external shocks. How can India strike a balance between ambition and stability? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Convertibility of rupee implies (2015)
(a) being able to convert rupee notes into gold
(b) allowing the value of rupee to be fixed by market forces
(c) freely permitting the conversion of rupee to other currencies and vice versa
(d) developing an international market for currencies in India
Ans: (c)