Speciality Fertilisers | 07 Nov 2025
India is bracing for higher fertiliser prices ahead of the crucial Rabi crop season due to China's suspension of Urea and Speciality Fertiliser exports.
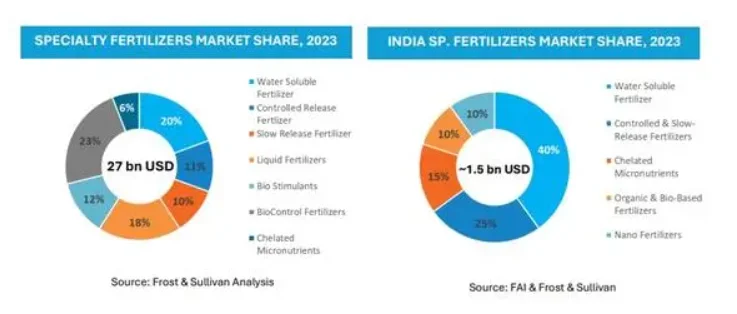
Speciality Fertilisers
- About: Speciality fertilisers are advanced formulations beyond basic NPK (Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sulphur), including water-soluble, slow or controlled-release, and micronutrient-based products that enhance nutrient efficiency and crop-specific performance.
- Examples: Chelated micronutrients (Fe-EDTA, Zn-EDTA, Fe-EDDHA), water-soluble fertilisers (WSFs) such as monoammonium phosphate (MAP) and potassium nitrate (KNO₃); and stabilised nitrogen fertilisers with urease inhibitors (NBPT).
- Uses:
- For high‐value crops (fruits, vegetables, flowers) and horticulture.
- For soils with specific deficiencies or in micro‐nutrient‐deficient zones (zinc, boron, etc).
- For precision agriculture and improved nutrient-use efficiency.
- India & Speciality Fertilisers:
- India currently imports about 95% of its speciality fertilisers-mainly water-soluble and advanced formulations, due to limited domestic R&D, raw material shortages, and China’s market dominance.
- India has recently initiated its first indigenous water-soluble fertiliser production and secured supply contracts with Russia, Jordan, Israel, and Morocco to curb excessive dependence on China.
- Market Size: The global speciality fertilisers market is projected to reach $63 billion by 2035, while India’s market is expected to grow to $5–6 billion by 2030, backed by sustainable agricultural practices.
| Read More: Fertiliser Sector in India |