Shaping India’s AI-Driven Economy | 19 Nov 2025
Why in News?
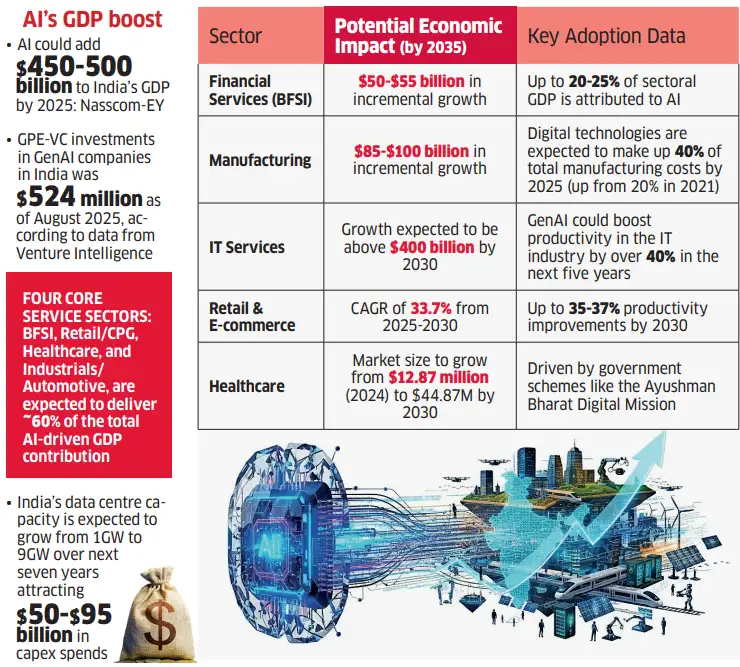
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is set to drive India’s next phase of economic growth, with NITI Aayog estimating that AI could add USD 500–600 billion to GDP by 2030.
What does NITI Aayog Reports Say about AI’s Impact on the Indian Economy??
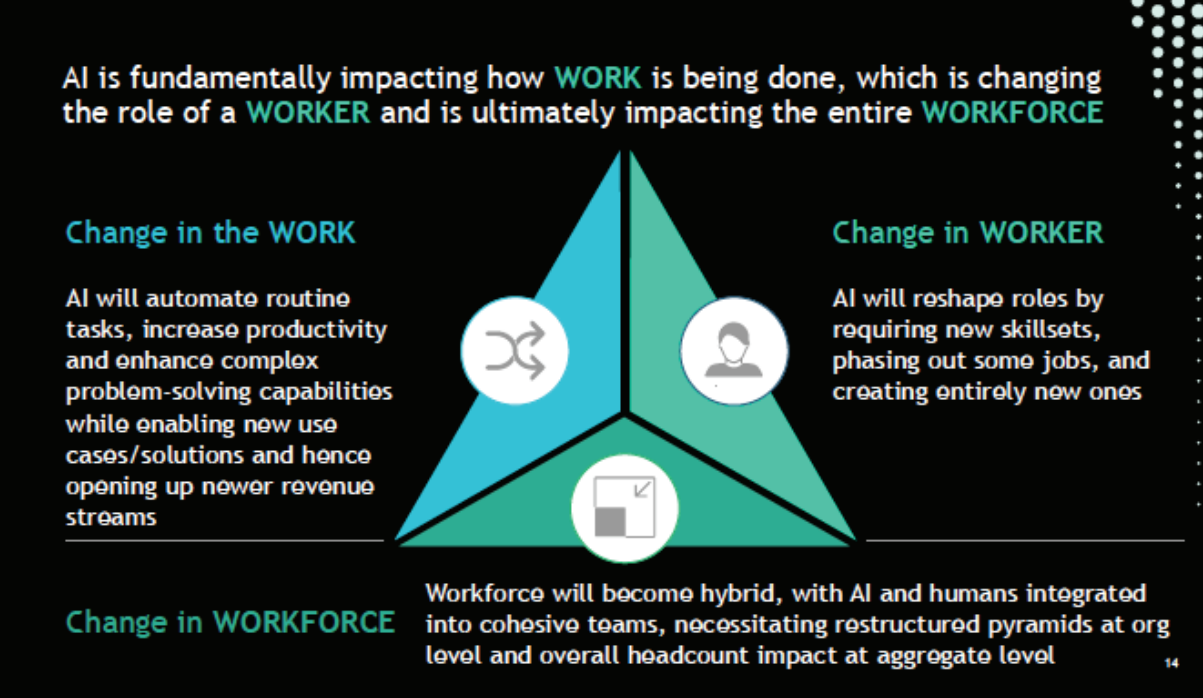
- Roadmap for Job Creation in the AI Economy: This report presents India’s strategic plan to address the disruptions caused by AI, aiming to position the country as the global hub for AI-driven workforce development.
- It introduces the 3W framework for AI and outlines its potential impact on work, workers, and the workforce.
- Roadmap on AI for Inclusive Societal Development: This report focuses on utilizing cutting-edge technologies to transition informal workers into a more formal, empowered, and future-ready labor force.
- It emphasizes AI’s potential to enhance inclusivity and foster sustainable development.
- AI as Both a Challenge and Opportunity for India: AI presents both challenges and opportunities for India’s economy.
- While it disrupts traditional formal jobs, it simultaneously provides a unique opportunity to formalize and significantly improve the productivity of the vast informal workforce.
What Potential does AI Hold for India's Economic Transformation?
- Job Creation in New, High-Value Sectors: India could create up to 4 million new jobs by 2031, especially in tech and customer service, with jobs ranging from Prompt Engineers to Quantum ML Engineers and advanced AI model developers.
- Enhanced Global Economic Standing: India can become the “AI workforce capital of the world” by shifting from traditional IT services to AI-driven work and innovation, using its strong digital talent base.
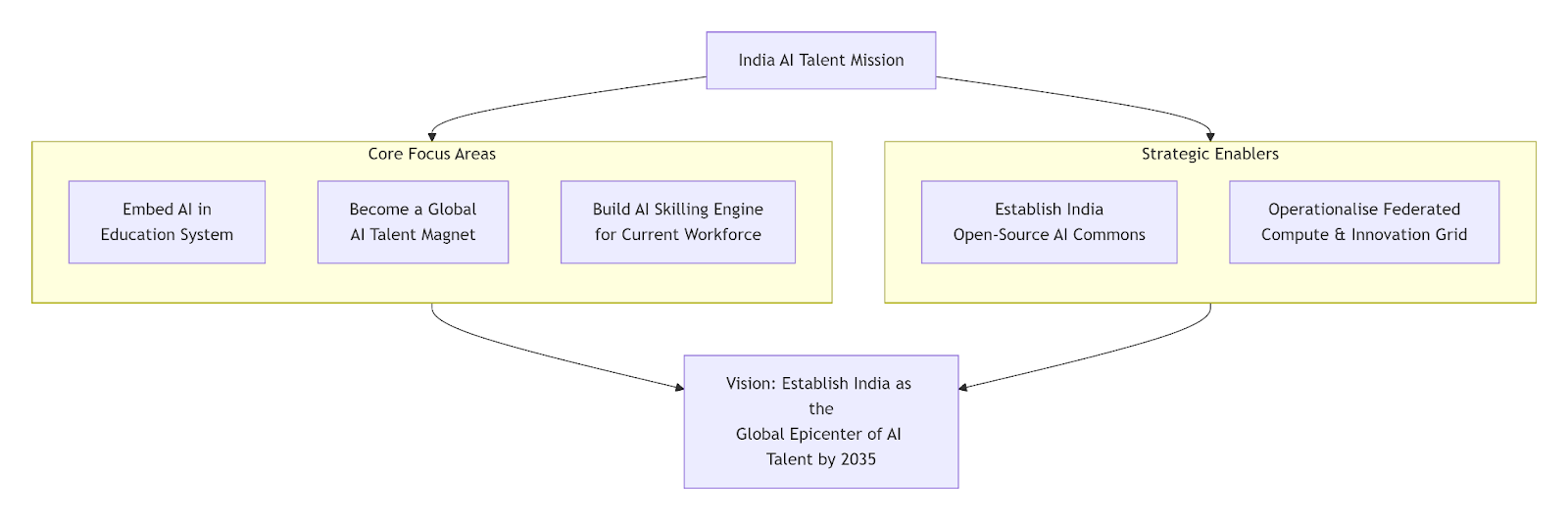
- The proposed India AI Talent Mission can also help reverse brain drain, similar to efforts in Singapore and the UAE.
- New Revenue Pools and Industries: It opens new avenues like AI-driven drug discovery and smart manufacturing, while its convergence with Quantum Computing, IoT, and 5G is creating opportunities in smart cities and logistics optimization.
- Productivity Gains: AI boosts efficiency and global competitiveness, delivering 10–20% productivity gains in software development and reducing costs in customer service through chatbots and real-time translation.
- Foundation for a Future-Ready Economy: Creating an open-source India AI Commons will provide datasets, models, and benchmarks to democratize innovation, while India’s AI Compute Grid will offer shared high-performance computing access to boost local R&D and retain talent.
What are the Challenges Posed by AI to the Indian Economy?
- Job Losses in the Tech Sector: As per Niti Aayog, the IT services workforce may drop from 7.5–8 million (2023) to 6 million by 2031.
- Overall, 60% of formal jobs in India face automation risk by 2030, with the IT and BPO sectors especially vulnerable due to routine, scalable tasks.
- Education System Gaps: India faces gaps in computer science education, with limited access and outdated AI curricula that miss emerging concepts like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
- These weaknesses contribute to low research output, with AI patent shares dropping to under 5%, and fewer than 500 AI-related PhDs produced each year.
- AI Talent Supply-Demand Gap: AI talent demand is rising at 25% CAGR (from 800,000 to 1.25 million by 2026), while supply grows at only 15% CAGR.
- India also faces net negative talent migration, losing top AI researchers at a rate of 1.55 per 10,000.
- Broader Systemic Risks: India risks losing competitiveness and strategic ground to countries like China, Saudi Arabia, the UAE, and Singapore, while socially, limited protection for 400 million informal workers and uneven impacts across regions and groups create major challenges.
What Recommendations has NITI Aayog Made for the Sustainable Use of AI in India?
- Embed AI in the Education System: Integrate AI learning from schools, expand AI-focused higher education, and increase AI PhD fellowships to strengthen research, while ensuring curricula stay updated through faculty–industry collaboration.
- Become a Global AI Talent Magnet: Offer competitive grants, high salaries, and priority access to the national computer grid to retain and bring back Indian AI researchers, and introduce a dedicated AI talent visa to attract global experts.
- Building an AI Skilling Engine: Launch national reskilling programs by scaling NAPS (National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme) and PMKVY (Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana) for widespread AI literacy, and introduce flexible AI master's and doctoral pathways for working professionals to upgrade into high-skill roles.
- Establishing India Open-source AI Commons: Create a central AI commons with high-quality datasets, models, and benchmarks, incentivize data contribution from universities and ministries, and ensure trust and transparency through reliable validation tools.
- Federated National Compute & Innovation Grid: Consolidate fragmented HPC resources into a unified compute grid, and provide tiered, affordable access for students, startups, and researchers to support advanced model training and reduce dependence on foreign infrastructure.
Conclusion
AI offers India a transformative economic opportunity—NITI Aayog estimates USD 500–600 billion GDP boost by 2030—if paired with reskilling, stronger AI education, robust data governance, open-source commons, and national computational infrastructure. Strategic policy, inclusive skilling, and research investments are essential to mitigate job displacement and regional inequality for sustainable growth.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q. Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword for the Indian economy. Critically analyze this statement and suggest a strategic roadmap for India to become a global leader in inclusive AI. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the projected contribution of AI to India’s GDP by 2030?
NITI Aayog estimates that AI could contribute USD 500-600 billion to India’s GDP by 2030 through productivity and innovation gains.
2. How many jobs could AI create in India by 2031?
AI could generate up to 4 million new jobs by 2031, particularly in tech, customer service, and high-value AI roles.
3. How does AI pose a risk to India's formal job sector?
NITI Aayog highlights a risk of large-scale job displacement, with the IT services workforce potentially shrinking from 7.5-8 million to 6 million by 2031, affecting 60% of formal sector jobs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Introduce the concept of Artificial Intelligence (AI). How does Al help clinical diagnosis? Do you perceive any threat to privacy of the individual in the use of AI in healthcare? (2023)