Semaglutide for Fatty Liver Treatment | 12 May 2025
Why in News?
A new study found that semaglutide (used in weight-loss and diabetes drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy) is also effective in treating fatty liver disease, also known as Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH).
What is Semaglutide?
- About: Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist. It is primarily used to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity.
- Semaglutide mimics the action of GLP-1, a hormone that helps lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin secretion in response to meals, inhibiting glucagon release, and delaying gastric emptying.
- Side Effects: Semaglutide is associated with common side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal discomfort.
- It is contraindicated (not medically advised) for individuals with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid cancer or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2.
What is Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease?
- About Fatty Liver Disease: Fatty liver disease (hepatic steatosis) is the buildup of excess fat in liver cells.
- It becomes unhealthy when fat exceeds 5% of liver cells (hepatocytes), affecting liver function and metabolism.
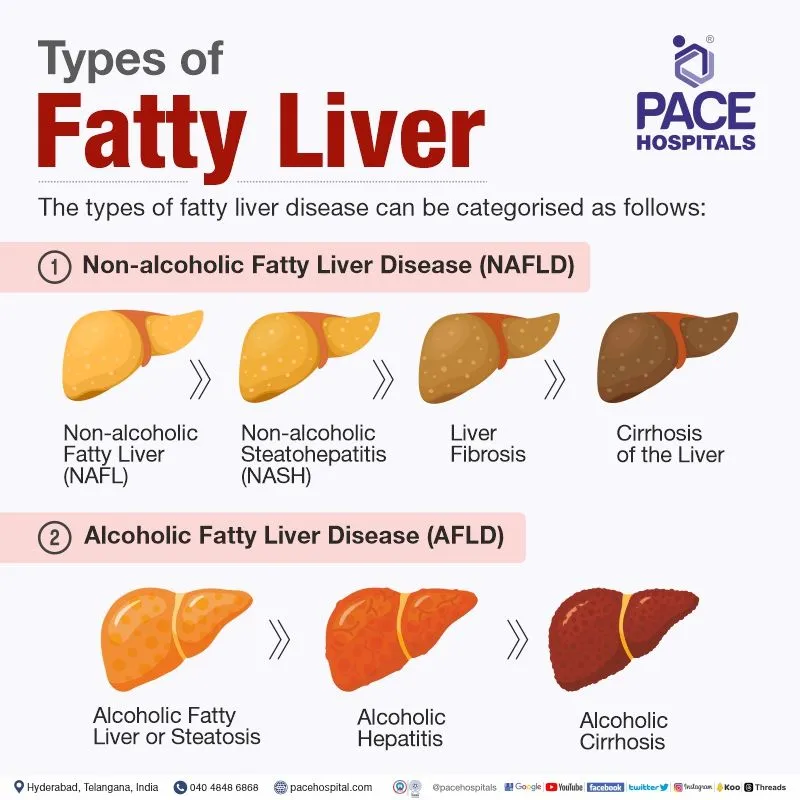
- It is of 2 types- NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) & Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD).
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) or Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) (earlier known as NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver without excessive alcohol intake and may cause serious liver damage over time.
- Its prevalence in India is estimated at 9–32%.
- 4 Stages of MASLD:
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFL): Fat builds up in the liver without causing damage or inflammation, usually leading to mild discomfort from an enlarged liver.
- Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) or Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH): A more serious form with liver inflammation, scarring, and links to heart and kidney issues. Around 25% may progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
- Fibrosis: Long-term inflammation creates scar tissue in the liver, which affects its ability to function.
- Cirrhosis: The most severe stage with permanent liver scarring, shrinking, and possible liver failure or cancer.
- Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD): AFLD, or alcoholic steatohepatitis, is caused by excessive alcohol intake (≥ 40g/day in males, ≥ 20g/day in females), leading to fat accumulation in the liver.
- Alcohol metabolism in the liver generates toxic compounds that damage liver cells, trigger inflammation, and impair natural defences.
- Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease: The primary treatment is weight loss through diet, exercise, or medication.
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: These medications aid in weight loss by regulating gut hormones that control appetite and fat storage.
- Resmetirom: A thyroid hormone-based drug that specifically targets liver fat, though it is costly.
- FGF21 Drugs: These drugs focus on adipose tissue to reduce fat accumulation and enhance metabolic health.
- Tirzepatide: A dual-action medication that promotes weight loss, assists in diabetes management, and shows potential benefits in treating sleep apnea.
What are India's Key Initiatives to Promote Healthy Lifestyle?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Hepatitis B virus is transmitted much like HIV.
(b) Hepatitis B unlike Hepatitis C, does not have a vaccine.
(c) Globally, the number of people infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses arc several times more than those infected with HIV.
(d) Some of those infected with Hepatitis B and C viruses do not show the symptoms for many years.
Ans: (b)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)