Satellite Internet | 19 Aug 2025
Why in News?
Starlink has received a Unified Licence to provide satellite internet services in India.
How Does Satellite Internet Work?
- About: Satellite internet uses orbiting satellites or mega-constellations- hundreds to thousands of satellites at varying altitudes to transmit data between user terminals on Earth and space-based infrastructure.
- Working Mechanism: Satellite internet operates through a two-segment system: the space segment and the ground segment.
- Space Segment: It comprises satellites in different orbits equipped with communication payloads for data transmission.
- Satellites receive data signals from user terminals or ground stations, process or relay them, and transmit them back to Earth.
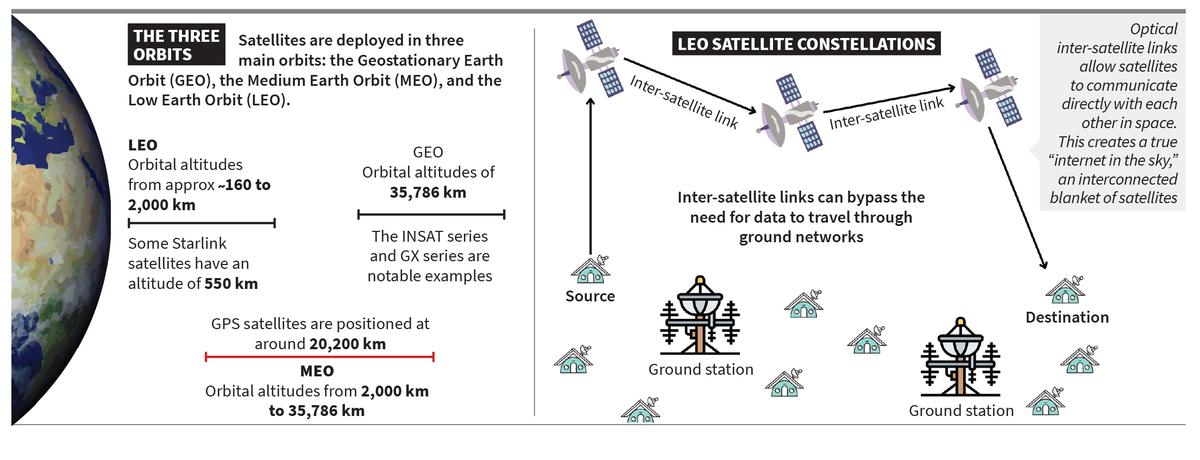
- LEO mega-constellations incorporate on-board signal processing and optical inter-satellite links, allowing direct satellite-to-satellite communication and reducing reliance on ground stations.
- Ground Segment: It consists of user terminals (antennas, modems) and ground stations that communicate with the satellites.
- Terminals send requests to satellites, which route the data through the constellation or ground infrastructure to reach the internet backbone.
- Space Segment: It comprises satellites in different orbits equipped with communication payloads for data transmission.
- Orbital Deployment: Satellites are deployed in 3 main orbits:
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): Lies around 35,786 km above the equator. A single GEO satellite covers nearly one-third of Earth’s surface.
- It has broad coverage, but high latency, so unsuitable for real-time applications. Example: Viasat Global Xpress.
- Medium Earth Orbit (MEO): Lies at 2,000–35,786 km altitude. It has lower latency than GEO but requires constellations for global coverage. Example: O3b MEO.
- Low Earth Orbit (LEO): Lies at less than 2,000 km altitude. Very low latency, smaller satellites, and rapid deployment, but smaller coverage per satellite.
- LEO satellites form “mega-constellations” for global reach. Example: Starlink with over 7,000 satellites.
- Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO): Lies around 35,786 km above the equator. A single GEO satellite covers nearly one-third of Earth’s surface.
What are the Key Potential Applications of Satellite Internet?
- Connectivity & Communications: Provides internet in remote areas via compact user terminals.
- Future direct-to-smartphone services aim to integrate connectivity into smart devices, enabling the Internet of Everything (IoE).
- Transport, Logistics & Public Services: Enhances navigation, supports autonomous vehicles, improves logistics, powers smart cities, provides early warning systems, and enables coordinated disaster response.
- Healthcare & Agriculture: Facilitates telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, and supports precision farming, crop health monitoring, and optimized resource use.
- Strategic, Industrial & Environmental Uses: Aids defence operations, environmental monitoring, energy exploration, and tourism, while its dual-use nature requires integration into national resilience plans, bridging the digital divide, and shaping international governance for strategic advantage.
- Disaster Response & Emergency Communication: It allows rapid deployment of connectivity in disaster-affected regions, supporting emergency management.
- During Hurricane Harvey (2017), satellite internet enabled rescue operations when terrestrial networks failed.
Note:
- Starlink: A satellite internet constellation by SpaceX, providing high-speed, low-latency internet globally.
- Commercial satellite internet services are not yet operational in India.
- Eutelsat OneWeb, Reliance Jio-SES, and Starlink have obtained necessary permits & government is finalizing spectrum allocation for its commercial rollout.
Key Satellite Internet Projects:
- Project Kuiper (Amazon): Plans to deploy over 3,200 advanced LEO satellites to provide affordable, high-speed broadband globally.
- Starlink (SpaceX): Launched in 2019, aims for a 42,000-satellite LEO mega-constellation.
- OneWeb (Eutelsat, France): Operates the world’s second-largest satellite constellation after Starlink.
- Qianfan or G60 Starlink Constellation (China): Planned LEO mega-constellation by Shanghai Spacecom Satellite Technology (SSST) to provide global internet coverage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. For the measurement/estimation of which of the following are satellite images/remote sensing data used? (2019)
- Chlorophyll content in the vegetation of a specific location
- Greenhouse gas emissions from rice paddies of a specific location
- Land surface temperatures of a specific location
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q. With reference to Web 3-0, consider the following statements: (2022)
- Web 3.0 technology enables people to control their own data.
- In Web 3.0 world, there can be blockchain based social networks.
- Web 3.0 is operated by users collectively rather than a corporation.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Q. Has digital illiteracy, particularly in rural areas, coupled with lack of Information and Communication Technology(ICT) accessibility hindered socio-economic development? Examine with justification. (2021)