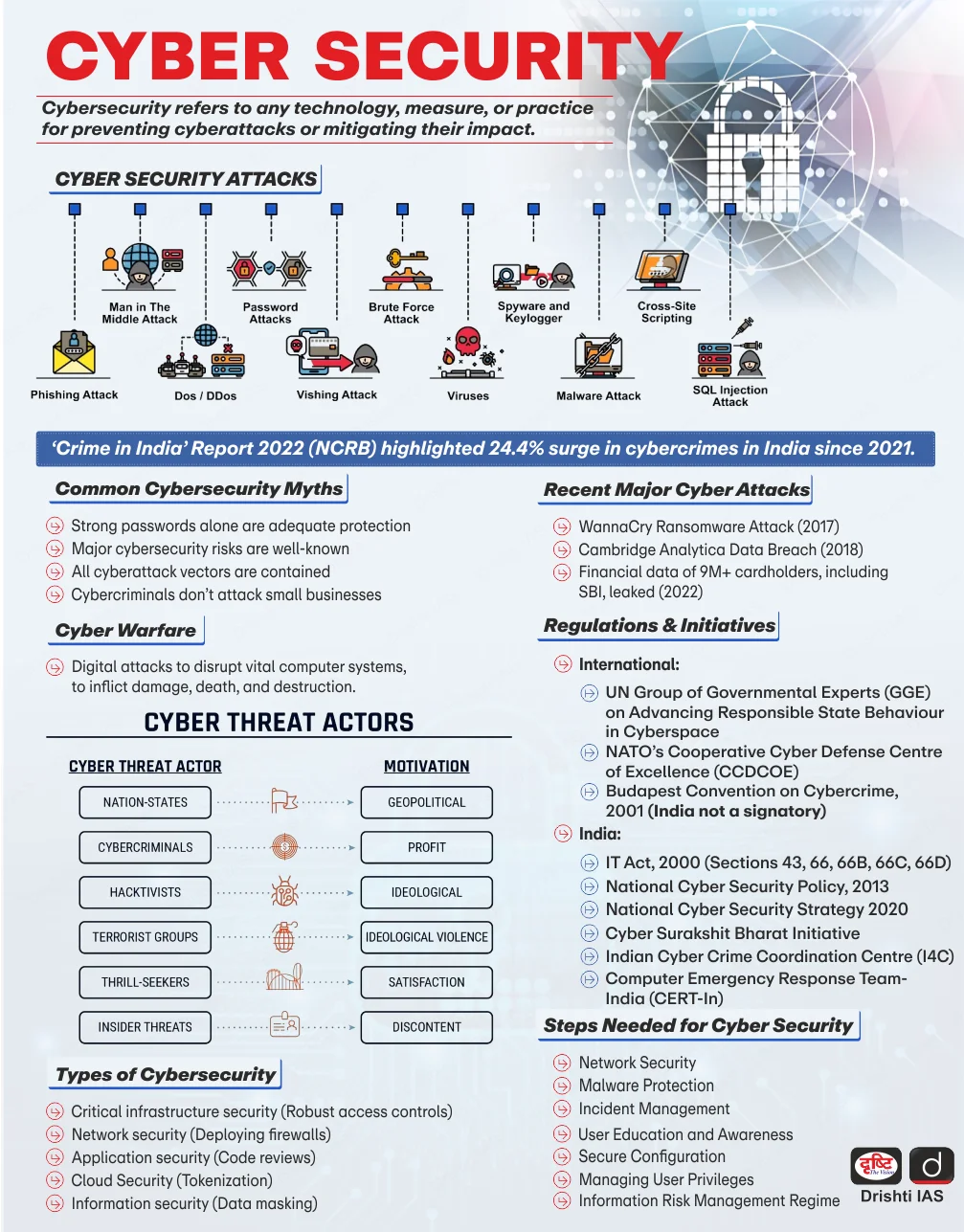
Rising Cyber Frauds in India | 19 Jul 2025
For Prelims: Cybercrime, Digital arrest, Information Technology Act, Digital Personal Data Protection Act, Indian Computer Emergency Response Team, National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre, Cyber Swachhta Kendra, Ransomware attack, Budapest Convention on Cybercrime.
For Mains: Current Framework for Cyber Security in India, Key Emerging Cyber Threats Affecting India's Digital Landscape.
Why in News?
The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C), a unit under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), has reported a sharp surge in financial cyber frauds targeting Indian citizens, primarily originating from Southeast Asian countries.
What is the State of Financial Cyber Frauds in India as per I4C Analysis?
- Rising Financial Losses: In the first half of 2025, India lost an average of Rs 1,000 crore per month to cyber frauds, totaling Rs 7,000 crore.
- According to the I4C,the projected annual loss may exceed Rs 1.2 lakh crore (Rs 1.2 trillion) in 2025, amounting to 0.7% of India’s GDP.
- Origin & Nature of Scams: Over 50% of cyber frauds targeting Indians originated from Southeast Asian countries such as Cambodia, Myanmar, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand, operated from high-security compounds allegedly run by Chinese handlers.
- These primarily involve stock trading/investment scams, digital arrest scams & task-based and investment-based scams.
- Indian intelligence has identified 45 scam centres in Cambodia, 5 in Laos, and 1 in Myanmar.
- Modus Operandi: Victims, including Indians, are being trafficked via fake job offers and routed through countries like Dubai, China, and Thailand to operate cyber scams.
- Recruitment agents are active across Indian states (Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, J&K, Uttar Pradesh, and Delhi).
- Systemic Gaps & Enforcement Action: India’s cyber fraud ecosystem is exploited due to loopholes in digital banking transactions, issuance of ghost SIM cards by PoS agents in the telecom sector, and weak verification processes in immigration, enabling anonymous and cross-border cybercrimes.
Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- About: The Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C) was launched by the Ministry of Home Affairs in 2020 to provide a comprehensive and coordinated response to cybercrime, including financial frauds.
- Key Objectives:
- Act as the national nodal agency to monitor, prevent, and investigate cybercrimes, especially those targeting women, children, and critical infrastructure.
- Provide an early warning system and facilitate trend analysis, pattern recognition, and data sharing among law enforcement agencies.
- Enable easy reporting of cybercrime and promote public awareness on cyber hygiene and fraud prevention.
- Assist States/UTs in building capacity of police, prosecutors, and judicial officers in areas like cyber forensics and investigation.
- National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal: A citizen-centric platform under I4C that enables individuals to report cyber frauds online. Reported complaints are forwarded to the relevant law enforcement agencies for necessary legal action.
What are Cyber Frauds?
- About: Cyber frauds are criminal activities conducted using digital technology (internet) to deceive individuals or organizations for financial gain.
- It exploits vulnerabilities in cybersecurity systems, digital platforms, or human behavior to steal money, data, or identities.
- Types of Cyberfrauds:
|
Cyber Fraud/ Threats |
Description |
|
Digital Arrests |
Impersonating authorities (police or income tax officers) to extort money. |
|
Online Job/Task-Based Scams |
Fake work-from-home offers with upfront payments. |
|
Malware |
Malware is used to steal personal information that allows cyber criminals to gain control of a victim's computer. |
|
Ransomware |
Ransomware encrypts a victim's files and demands payment for decryption. E.g., WannaCry attack in 2016 |
|
Phishing |
Phishing involves emails that appear to be from trusted sources, tricking users into clicking links that lead to fake websites and attackers gaining sensitive details e.g., credit card numbers. |
|
Cyberbullying |
Cyberbullying includes any threat to a person’s safety, coercion to say or do anything. |
|
Cyber Spying |
Cyber Spying targets a public or private entity’s network to gain access to classified data, private information, or intellectual property. |
|
Business Email Compromise (BEC) |
Scammers hack legitimate email accounts to impersonate suppliers, employees, or tax office members, considered a white-collar crime. |
|
Dating Hoodwinks |
Hackers use dating websites, chat rooms, and online dating apps to pose as potential partners and gain access to personal data. |
|
ATM/PoS Frauds |
Skimming card details or unauthorized transactions. |
- Consequences of Cyber Fraud:
- Individuals face unauthorised financial transactions, loss of account access, and misuse of personal data for harassment or blackmail.
- Businesses risk legal penalties, regulatory fines, and loss of market value due to compromised client data.
- Governments face threats to national security as cyber breaches target defence and critical information systems.
- Notable Cyberfraud Incidents:
- Aadhaar Data Breach (2018): Personal data of 1.1 billion Aadhaar cardholders was compromised, including Aadhar numbers, PAN and bank details.
- Canara Bank ATM Attack (2018): Hackers used skimming devices on 300 debit cards, leading to a theft of over Rs 20 lakh.
- Pegasus Spyware Case: The Israeli spyware Pegasus was allegedly used to access data from mobile devices without consent, affecting over 300 verified Indian phone numbers.
What are the Key Emerging Cyber Threats Affecting India's Digital Landscape?Click Here to Read: Emerging Cyber Threats in India |
What are the Key Initiatives Related to Cybersecurity?
- Global Initiatives on Cybersecurity:
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is the first international treaty to address cybercrime through legal harmonization, investigative cooperation, and capacity building. It came into force on 1st July 2004.
- India is not a signatory of the Budapest Convention.
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF): IGF is a multi-stakeholder platform under the UN that facilitates dialogue among governments, private sector, academia, and civil society on public policy issues related to Internet governance and cybersecurity.
- UNGA Resolutions on ICT Security: The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) has established 2 key platforms for addressing cybersecurity:
- Open-ended Working Group (OEWG), initiated by Russia, focuses on inclusive dialogue and capacity building in ICT security.
- Group of Governmental Experts (GGE), initiated by the USA, works on developing norms of responsible state behaviour in cyberspace and international legal frameworks.
- Budapest Convention on Cybercrime: It is the first international treaty to address cybercrime through legal harmonization, investigative cooperation, and capacity building. It came into force on 1st July 2004.
- Indian Initiatives:
- Legislative Measures:
- Institutional Framework:
- Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In)
- National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC)
- Indian Cyber Crime Coordination Centre (I4C)
- Cyber Swachhta Kendra
- Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System for real-time monitoring, tracking, and resolution of cyber fraud cases.
- The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) registered FIRs against PoS agents for issuing fraudulent SIMs.
- Strategic Initiatives:
- Bharat National Cybersecurity Exercise 2024
- National Cyber Security Policy, 2013: Provides vision and strategies for securing cyberspace and protecting critical information infrastructure.
- Chakshu & Digital Intelligence Platform by DoT:
- Chakshu, a tool on Sanchar Saathi portal to report fraudulent calls, SMS, or WhatsApp messages related to KYC expiry or bank account updates.
- Digital Intelligence Platform to enable real-time coordination to tackle cyber frauds.
- Sector-Specific Regulations:
- Cybersecurity Framework for SEBI Regulated Entities: Mandates cybersecurity policies for securities markets.
- Telecommunications (Critical Telecommunication Infrastructure) Rules, 2024
What Measures Should be Taken to Strengthen Cybersecurity Frameworks in India?
- Infrastructure & AI-Based Security: Strengthen digital infrastructure through firewalls, regular software/hardware updates, and AI-driven threat detection systems to proactively identify, predict, and neutralize cyber threats.
- AI tools must support ransomware prediction, incident response, and forensic analysis.
- Cyber Awareness & Literacy: Launch nationwide cyber literacy programs in regional languages targeting rural communities, youth, and senior citizens.
- Incorporate cybersecurity education in schools and universities to build digital resilience from an early age, supported by secure infrastructure and staff training.
- Institutional & Audit Reforms: Conduct mandatory cybersecurity audits in critical sectors like banking, healthcare, and utilities, including stress tests and employee preparedness.
- Establish district-level cybersecurity units for localized threat management and coordination with CERT-In.
- Corporate & Banking Safeguards: Enforce two-factor authentication (2FA), data encryption, and monitoring systems in businesses and banks.
- Financial institutions must track suspicious transactions, detect foreign IP logins, and prevent conversion of stolen funds into cryptocurrency.
- Personal Cyber Hygiene: Encourage citizens to adopt secure digital practices, such as avoiding suspicious communications, using strong, unique passwords, and not bypassing security warnings to reduce individual vulnerability to cyber fraud.
Conclusion
The rise of financial cyber frauds in India highlights the urgent need for strengthened cybersecurity measures and enhanced public awareness. While initiatives play a crucial role in combating cyber threats, the evolving nature of cybercrimes demands continuous adaptation of legal, technological, and institutional frameworks. By addressing systemic gaps and fostering digital literacy, India can mitigate the risks associated with cyber fraud and ensure a safer digital ecosystem for its citizens.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key cybersecurity challenges in India? Suggest comprehensive measures to strengthen India's cybersecurity framework? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialised consultant to minimise the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q.2 In India, it is legally mandatory for which of the following to report on cyber security incidents? (2017)
- Service providers
- Data centres
- Body corporate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the different elements of cyber security ? Keeping in view the challenges in cyber security, examine the extent to which India has successfully developed a comprehensive National Cyber Security Strategy. (2022)