RBI's Gold Reserves | 10 May 2023
For Prelims: Forex and Gold reserve with RBI, Bank of International Settlements (BIS), SDR, IMF.
For Mains: India’s forex reserve and role of central bank in its management.
Why in News?
As per RBI’s Half Yearly Report on Management of Foreign Exchange Reserves: October 2022 - March 2023, its gold reserves touched 794.64 metric tonnes in FY 22-23, an increase of nearly 5% over FY 21-22(760.42 metric tonnes)
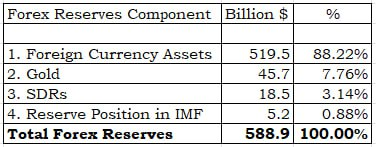
- Gold reserves along with foreign currency assets, special drawing rights and reserve tranche position in the International Monetary Fund make up India’s forex reserves.
How Much Gold has RBI Bought?
- Total Reserves:
- As per RBI, 437.22 tonnes of gold are held overseas are held with the Bank of England and the Bank of International Settlements (BIS), and 301.10 tonnes of gold is held domestically.
- As on March 31, 2023, the country’s total forex reserves stood at $578.449 billion, and gold reserves were pegged at $45.2 billion.
- In value terms (USD), the share of gold in the total forex Eserves increased to about 7.81% at the end of March 2023.
- Recent Purchase:
- The RBI bought 34.22 tonnes of gold in FY 23 (65.11 tonnes of gold in fiscal 2022).
- Between FY 2019 – FY 2021, RBI’s gold reserves were 228.41 tonnes.
- According to the World Gold Council's regional CEO (India), the RBI is among the top five central banks that are buying gold.
- The RBI bought 34.22 tonnes of gold in FY 23 (65.11 tonnes of gold in fiscal 2022).
Which Other Banks are Buying Gold?
- According to the World Gold Council (WGC), gold is being bought mainly by central banks of emerging market economies.
- The WGC report said that in 2022, the People’s Bank of China reported the first increase in its gold reserves since September 2019.
- China has been historically a large buyer of gold.
- During 2022, the central banks from the Middle East, including Egypt, Qatar, Iraq, the UAE, and Oman significantly boosted their gold reserves.
- By the end of 2022, the Central Bank of Uzbekistan became a net purchaser of gold, with its gold reserves rising by 34 tonnes.
- In January-March 2023, the Monetary Authority of Singapore was the largest single buyer of gold after it added 69 tonnes to its gold reserves
Why is RBI Hoarding the Gold?
- Counter Strategy against Negative Interest Rate:
- When the RBI has foreign currency (USD) in its reserves then it invests these dollars to purchase US Govt. bonds on which it earns interest.
- The real interest, however, on these bonds has turned negative due to the rise in inflation in the US.
- The real interest rate is the rate of interest an investor, saver or lender receives (or expects to receive) after allowing for inflation (real interest = nominal interest minus inflation rate).
- The real interest, however, on these bonds has turned negative due to the rise in inflation in the US.
- At the time of such inflation, the demand for gold has increased and RBI being its holder can earn a good return even in stressed economic situations.
- When the RBI has foreign currency (USD) in its reserves then it invests these dollars to purchase US Govt. bonds on which it earns interest.
- Good Hedge in Geopolitical Uncertainty: Due to the uncertainties arising amid the Russia-Ukraine war and US’ conflicts with China, there has been a decline in the acceptance of Dollar by some of the prominent global supplier of Goods like Russia and China.
- If RBI holds dollars and it depreciates/weakens with respect to other currencies, then it's a loss for RBI.
- However, due to the intrinsic value of gold and its limited supply, gold is able to retain its value much longer than other forms of currency.
- Diversify Forex Reserves: Gold is a safer, more secure and more liquid asset and it performs better during times of crisis, and as a long-term store of value.
- Gold has an international price which is transparent, and it can be traded anytime.
How is Gold Significant in the Economy?
- Gold as a Reserve Currency: For most of the 20th century, gold served as the world's reserve currency. The US used the gold standard until 1971 where it was required to have equivalent reserves of gold to back up the paper money.
- Due to the volatility of the US dollar and other currencies, some economists advocate returning to the gold standard since it has been discontinued.
- Intrinsic Value: Due to its inherent value and limited supply, inflationary periods see an increase in demand for gold. Gold is able to keep its value much longer than other forms of currency because it cannot be diluted.
- Gold to Boost Value of Currency: The value of a nation's currency starts depreciating when its imports exceed its exports. A country that is a net exporter, on the other hand, will see an increase in the value of its currency.
- As this raises the value of the country's total exports, a nation that exports gold or has access to gold reserves will see an increase in the strength of its currency when gold prices rise.
- Gold as a Substitute to G-Sec: The central bank of a country can use Gold as a medium to sterilize the market from the influence of foreign currency (in case of FDI) or use as a medium for open market operations (OMO).
- In both of these operations Gold can be used in place of G-Sec.
Note:
- The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 provides the overarching legal framework for deployment of reserves in different foreign currency assets and gold within the broad parameters of currencies, instruments, issuers and counterparties.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. What is/are the purpose/purposes of Government’s ‘Sovereign Gold Bond Scheme’ and ‘Gold Monetization Scheme’? (2016)
- To bring the idle gold lying with Indian households into the economy.
- To promote FDI in the gold and jewellery sector.
- To reduce India’s dependence on gold imports.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. Which one of the following groups of items is included in India’s foreign-exchange reserves? (2013)
(a) Foreign-currency assets, Special Drawing Rights (SDRs) and loans from foreign countries
(b) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and SDRs
(c) Foreign-currency assets, loans from the World Bank and SDRs
(d) Foreign-currency assets, gold holdings of the RBI and loans from the World Bank
Ans: (b)