PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) | 30 Oct 2025
Why in News?
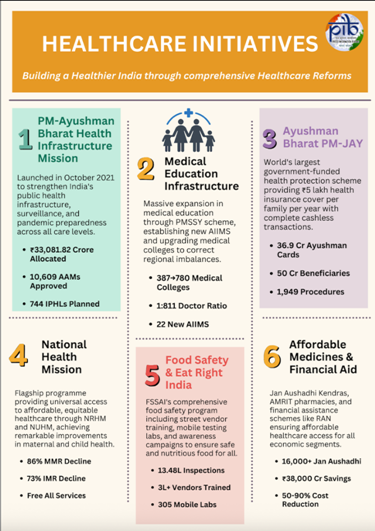
The Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission ) was launched in October 2021 to address the gaps in India’s healthcare system exposed by the COVID-19 pandemic and to enhance preparedness for future health crises.
- The mission advances universal health coverage goals and aligns with SDG-3 targets.
What is PM-ABHIM?
- About: The PM-ABHIM is one of the largest nationwide health initiatives, aims to build a resilient, accessible, and self-reliant public health system capable of responding effectively to current and future health emergencies.
- Aim & Implementation: It aims to bridge the service delivery gaps between urban and rural areas.
- It operates under a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) component, and focuses on strengthening health infrastructure at all levels- from primary and secondary to tertiary - during FY 2021–22 to FY 2025–26.
- One Health Approach: It emphasises disease surveillance, research, and the adoption of the One Health approach, which recognises the interconnection between human, animal, and environmental health.
- Major Components of PM-ABHIM:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs): upgrading Sub-Health and Primary Health Centres into rural (R-AAMs) and urban (U-AAMs) units for comprehensive care.
- Block Public Health Units (BPHUs): strengthen local health administration and services.
- Integrated Public Health Laboratories (IPHLs): district-level labs for advanced diagnostics and disease tracking.
- Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs): New tertiary-care units in high-population districts.
- Health Surveillance & IT Systems: real-time digital network connecting labs nationwide.
- Health Research & Innovation, support for studies on infectious diseases and One Health initiatives.
- Significance:
- Comprehensive Healthcare System Strengthening: By upgrading and establishing AAMs, IPHLs, and CCBs, the mission ensures that healthcare services are accessible to all, especially in underserved areas.
- Expansion of Surveillance Systems: PM-ABHIM strengthens India’s disease surveillance network, providing real-time data integration from block, district, regional, and national levels.
- Support for Universal Health Coverage (UHC): By building infrastructure and improving service delivery, PM-ABHIM aligns with India’s commitment to achieving Universal Health Coverage and advancing the Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG-3), ensuring access to quality healthcare for all citizens.
- Decentralized Healthcare Delivery: PM-ABHIM emphasizes local healthcare delivery by upgrading Sub-Health Centres and establishing Urban Health and Wellness Centres (U-AAMs) in slum and underserved urban areas, improving access to primary care services.
What are India’s Various Health Care Initiatives?
- National Health Mission:
- The National Health Mission aimed to create community-owned and decentralised healthcare systems to make services accessible, affordable, and equitable, particularly for vulnerable groups.
- National Health Policy (2017):
- The National Health Policy (2017) laid the groundwork for transforming India’s healthcare delivery system.
- It emphasised the importance of community-based health systems, highlighting the role of trained first responders, local self-government institutions, and community organisations in improving healthcare access and disaster preparedness.
- Ayushman Bharat Scheme (2018):
- Building on NHM’s success, the Ayushman Bharat Scheme (2018) marked a major leap in India’s journey towards Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- It integrates preventive, promotive, and curative health interventions through four major pillars:
- Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Aarogya Yojana (AB–PMJAY)
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAMs)
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
- PM–Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM–ABHIM)
WHO’s Global Pandemic Agreement
- The World Health Organization (WHO) adopted the first Global Pandemic Agreement at its 78th World Health Assembly under Article 19 of the WHO Constitution.
- It aims to strengthen global health security and ensure equitable pandemic responses.
- Adopted on 20th May 2025, it promotes international cooperation for timely access to diagnostics, vaccines, and therapeutics.
- It is the second global legal instrument after the 2003 Framework Convention on Tobacco Control.
Conclusion
Four years after its launch, the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission has transformed India’s health landscape by investing in pandemic preparedness, infrastructure modernisation, and disease surveillance. PM-ABHIM serves as a cornerstone of the country’s efforts to build a safer, healthier, and more equitable future for all citizens.
| Drishti Mains Question Q. Discuss how the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) enhances India’s health resilience and complements existing national health programs |
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. When was PM-ABHIM launched?
It was launched in October 2021 with an allocation of ₹64,180 crore for implementation during 2021–2026.
Q. What is the main objective of the PM-Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM)?
To strengthen India’s public health infrastructure, improve disease surveillance, and ensure equitable access to affordable, quality healthcare at all levels.
Q. How does PM-ABHIM complement other health initiatives?
It complements the National Health Mission and Ayushman Bharat by focusing on infrastructure, research, and pandemic preparedness across rural and urban areas.
Q. What are the major components under PM-ABHIM?
Key components include Ayushman Arogya Mandirs, Block Public Health Units, Integrated Public Health Labs, Critical Care Blocks, and IT-enabled disease surveillance systems
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the National Rural Health Mission, which of the following are the jobs of ‘ASHA’, a trained community health worker? (2012)
- Accompanying women to the health facility for antenatal care checkup
- Using pregnancy test kits for early detection of pregnancy
- Providing information on nutrition and immunization.
- Conducting the delivery of baby
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. The public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that the private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? (2015)