India-UK Vision 2035 and CETA | 25 Jul 2025
For Prelims: Free Trade Agreement, Bilateral Investment Treaty, Artificial Intelligence, International Solar Alliance, "NET Zero" Innovation Virtual Centre
For Mains: India-UK bilateral relations and evolving strategic partnership, Significance of Free Trade Agreements (FTAs)
Why in News?
The Indian Prime Minister's visit to London marked the unveiling of the India–UK Vision 2035 roadmap and the formalisation of the Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA), a Free Trade Agreement (FTA), with the goal of pushing bilateral trade beyond USD 100 billion by 2030.
What are the Key Features of the India-UK Vision 2035?
- Trade and Economic Cooperation: The newly signed CETA is central to the Vision 2035, aiming to increase bilateral trade and create jobs.
- The Joint Economic and Trade Committee (JETCO) will oversee its implementation, with plans to advance a Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT).
- Technology and Innovation: A major focus is the Technology Security Initiative, targeting advancements in next-generation technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), quantum computing, telecom, and critical minerals.
- Defense:The two countries have agreed on a 10-year defence industrial roadmap, focusing on joint research and manufacturing in areas like jet engine technology, maritime security, and directed energy weapons.
- The UK will also rely on India for logistics in the Indian Ocean Region and work with India under the Indo-Pacific Oceans’ Initiative (IPOI) to set up a Regional Maritime Security Centre of Excellence (RMSCE) to tackle non-traditional maritime security threats.
- Climate and Sustainability: India and the UK will work together to mobilize green finance, collaborate on offshore wind and nuclear technologies, and build joint supply chains in green goods.
- Platforms like the International Solar Alliance and Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure will facilitate these efforts.
- Education and Skills: The UK will encourage the establishment of university campuses in India, and both countries will focus on Mutual Recognition of Qualifications and climate-linked job creation through a Green Skills Partnership.
- Global Governance: Reinforces commitment to multilateralism and advocating for reforms in institutions like the United Nations, WTO, IMF, and the World Bank.
What are the Key Highlights of the India-UK CETA?
- Key Features:
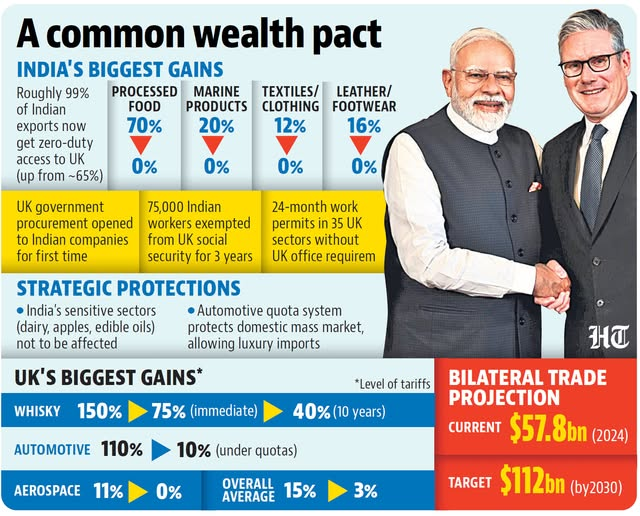
- Duty-Free Access: India will have 99% duty-free access to the UK market, benefiting labor-intensive sectors such as textiles, leather, marine products, electric and hybrid vehicles and auto components.
- India to cut or eliminate duties on 90% of tariff lines, covering 92% of imports from the UK (includes cars, alcohol).
- India will eliminate tariffs on UK electric vehicles in the sixth year of the agreement, with no duties on EVs priced below GBP 40,000.
- Services Sector: Indian professionals and companies will enjoy expanded market access in IT, financial services, education, and more, with simplified visa processes for sectors like engineering, architecture, and hospitality.
- Double Contribution Convention: Under Double Contribution Convention, India-UK CETA will exempt Indian professionals and their employers from UK social security contributions for three years, improving the competitiveness of Indian talent.
- Inclusive Growth: The agreement will promote participation from women, youth, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME), farmers, and innovators, encouraging access to global value chains and supporting sustainable practices.
- Agricultural Benefits: Indian agricultural products like processed foods, edible oils, and seafood will see tariff reductions, boosting exports to the UK.
- Duty-Free Access: India will have 99% duty-free access to the UK market, benefiting labor-intensive sectors such as textiles, leather, marine products, electric and hybrid vehicles and auto components.
- Impact:
- Trade Expansion: The CETA aims to double bilateral trade by 2030, reaching nearly USD 112 billion in goods and services combined. The agreement is projected to increase UK exports to India by 60% by 2040.
- Job Creation: The agreement will stimulate job creation in both countries by expanding economic activities, especially in sectors like manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
- Increased Investment: The inclusion of provisions that benefit MSMEs, startups, and entrepreneurs will encourage investment flows between India and the UK.
How India-UK Relations Evolved Over Time?
- Trade and Investments: Bilateral trade reached USD 21.34 billion in 2023–24. India’s exports to the UK rose by 12.6% to USD 14.5 billion in 2024–25. Imports from the UK grew by 2.3% to USD 8.6 billion.
- Technology and Innovation: The India–UK Technology Security Initiative (TSI), launched in 2024, focuses on key emerging sectors like AI, semiconductors, and cybersecurity.
- The UK is now India’s second-largest research partner after the US. India-UK "NET Zero" Innovation Virtual Centre will focus on green hydrogen and decarbonisation.
- The UK also named India a partner in its International Science Partnership Fund.
- Defence and Security: India and the UK have strengthened defence ties through joint exercises like Konkan, Cobra Warrior, and Ajeya Warrior, focusing on Indo-Pacific cooperation and defence tech.
- Health: India and the UK collaborated during the Covid-19 pandemic, notably with the AstraZeneca-Serum Institute vaccine partnership. Over 60,000 Indians work in the UK’s National Health Service.
- Indian Diaspora: The UK is home to 1.86 million people of Indian origin, contributing significantly to science, arts, business, and politics.
What are the Key Areas of Friction Between India- UK?
- Extradition Issues: India accuses the UK of sheltering fugitives (e.g., Vijay Mallya). The UK's reluctance on extradition strains legal and diplomatic trust.
- Russia-Ukraine War: India's neutral stance clashes with the UK’s strong support for Ukraine, causing strategic discomfort.
- Climate Tariffs: The UK’s planned Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) may hurt Indian exports like steel. India sees this as protectionism.
- Khalistani Activities: Pro-Khalistani protests in the UK strain ties. India wants stronger UK action against such groups.
- Intellectual Property Rights: UK’s push for strict IP protection clashes with India’s need for affordable medicines and flexible innovation rules.
What Steps Can India Take to Strengthen India- UK Ties?
- Deepen Security Ties: Leverage forums like AUKUS and expand cooperation on Indo-Pacific, counterterrorism, and cyber defense.
- Joint Climate Action: Collaborate on clean energy, sustainable agriculture, and green innovation through shared research platforms.
- Trade & Investment Diplomacy: Expand market access to push investment and promote India as a Global Capability Centre (GCC) hub.
- Leverage the Indian Diaspora: Engage the 1.86 million-strong Indian community in the UK for political, cultural, and economic outreach.
Conclusion
- The India-UK Vision 2035 and CETA deepen strategic, economic, and technological ties, offering opportunities in trade, innovation, defence, and climate. Careful handling of policy differences and focused diplomacy will help build a stronger, future-ready partnership.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the strategic significance of the India–UK Vision 2035 and how it redefines bilateral relations in a post-Brexit world. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Prelims:
Q1. We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model? (2021)
- As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the Parliament to legislate is limited.
- In India, matters related to the constitutionality of Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as(2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q1. The judicial systems in India and the UK seem to be converging as well as diverging in recent times. Highlight the key points of convergence and divergence between the two nations in terms of their judicial practices. (2020)