India’s Sugar Exports | 20 Mar 2023
Why in News?
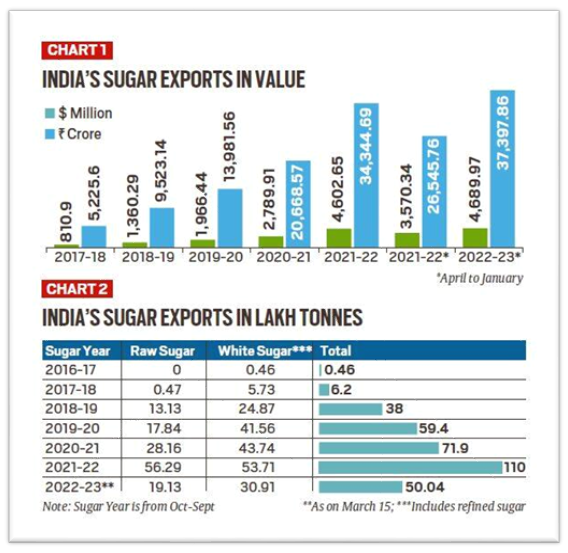
India has gone from being a marginal sugar exporter five years ago to No. 2 in the world, behind only Brazil. Between 2017-18 and 2021-22, exports have soared from USD 810.9 million to USD 4.6 billion.
- Sugar exports may cross USD5.5 billion in the current fiscal year.
What is the Status of the Sugar Industry in India?
- About:
- Sugar industry is an important agro-based industry that impacts the rural livelihood of about 50 million sugarcane farmers and around 5 lakh workers directly employed in sugar mills.
- In (Oct-Sep) 2021-22 India emerges as the world’s largest producer and consumer of sugar and world’s 2nd largest exporter of sugar.
- Distribution:
- Sugar industry is broadly distributed over two major areas of production- Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana and Punjab in the north and Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh in the south.
- South India has a tropical climate which is suitable for higher sucrose content giving a higher yield per unit area as compared to north India.
- Sugar industry is broadly distributed over two major areas of production- Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana and Punjab in the north and Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu and Andhra Pradesh in the south.
- Geographical Conditions for the Growth of Sugar:
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C with hot and humid climate.
- Rainfall: Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type: Deep rich loamy soil.
What is the Status of Sugar Exports?
- Background:
- Till 2017-18, India hardly exported any raw sugar (produced after the first crystallisation of cane juice).
- It mainly shipped plantation white sugar (produced by refining of raw sugar) with 100-150 ICUMSA value (International Commission for Uniform Methods of Sugar Analysis). This was referred to as low-quality whites or LQW in international markets.
- ICUMSA is a measure of purity. The lower the value, the more the whiteness.
- Current Status:
- Out of India’s total 110 lakh tonnes(lt) sugar exports in 2021-22, raws alone accounted for 56.29 lt.
- The biggest importers of Indian raw sugar were Indonesia (16.73 lt), Bangladesh (12.10 lt), Saudi Arabia (6.83 lt), Iraq (4.78 lt) and Malaysia (4.15 lt).
- Out of India’s total 110 lakh tonnes(lt) sugar exports in 2021-22, raws alone accounted for 56.29 lt.
- Reasons for Rising Exports:
- Free of Bacterial Compound: Indian raw sugar is free of dextran, a bacterial compound formed when sugarcane stays in the sun for too long after harvesting.
- Indian cane is crushed within 12-24 hours of harvesting while it takes around 48 hours in Brazil.
- High Sucrose Content: Indian raw sugar has a higher polarization (98.5-99.5%) compared to other producers like Brazil, Thailand, and Australia, making it easier and cheaper to refine.
- Polarisation is the percentage of sucrose present in a raw sugar mass.
- Free of Bacterial Compound: Indian raw sugar is free of dextran, a bacterial compound formed when sugarcane stays in the sun for too long after harvesting.
- Cap on Exports:
- Lower stocks and production dipping in 2021-22 has led the government to cap India’s exports in the current sugar year to 61 lakh tonnes to ensure domestic availability.
- The government did it to ensure domestic availability and contain food inflation but overseas markets once lost aren’t easy to regain.
- Lower stocks and production dipping in 2021-22 has led the government to cap India’s exports in the current sugar year to 61 lakh tonnes to ensure domestic availability.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the current trends in the cultivation of sugarcane in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- A substantial saving in seed material is made when ‘bud chip settlings’ are raised in a nurse, and transplanted in the main field.
- When direct planting of setts is done, the germination percentage is better with singlebudded setts as compared to setts with many buds.
- If bad weather conditions prevail when setts are directly planted, single-budded setts have better survival as compared to large setts.
- Sugarcane can be cultivated using settlings prepared from tissue culture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Tissue culture is a technique in which fragments of plants are cultured and grown in a laboratory.
- It provides a new way to rapidly produce and supply disease-free seed cane of existing
- commercial varieties.
- It uses meristem to clone the mother plant.
- It also preserves genetic identity.
- The tissue culture technique, owing to its cumbersome outfit and physical limitation, is turning out to be uneconomical.
- Bud Chip Technology
- As a viable alternative of tissue culture, it reduces the mass and enables quick multiplication of seeds.
- This method has proved to be more economical and convenient than the traditional method of planting two to three bud setts.
- The returns are relatively better, with substantial savings on the seed material used for planting. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The researchers have found that the setts havingbuds are giving germination about 65 to 70% with better yield. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Large setts have better survival under bad weather but single budded setts also give 70% germination if protected with chemical treatment. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Tissue culture can be used to germinate and grow sugarcane settlings which can be transplanted later in the field. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Do you agree that there is a growing trend of opening new sugar mills in the Southern states of India? Discuss with justification. (2013)