India’s SDG 3 Progress | 26 Sep 2025
Why in News?
India has achieved its best-ever position in the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Index 2025, ranking 99th out of 167 countries, up from 109 in 2024. The rise reflects progress in infrastructure and basic services.
- However, challenges remain in achieving SDG 3-Good Health and Well-being, with persistent health disparities, especially in rural and tribal areas.
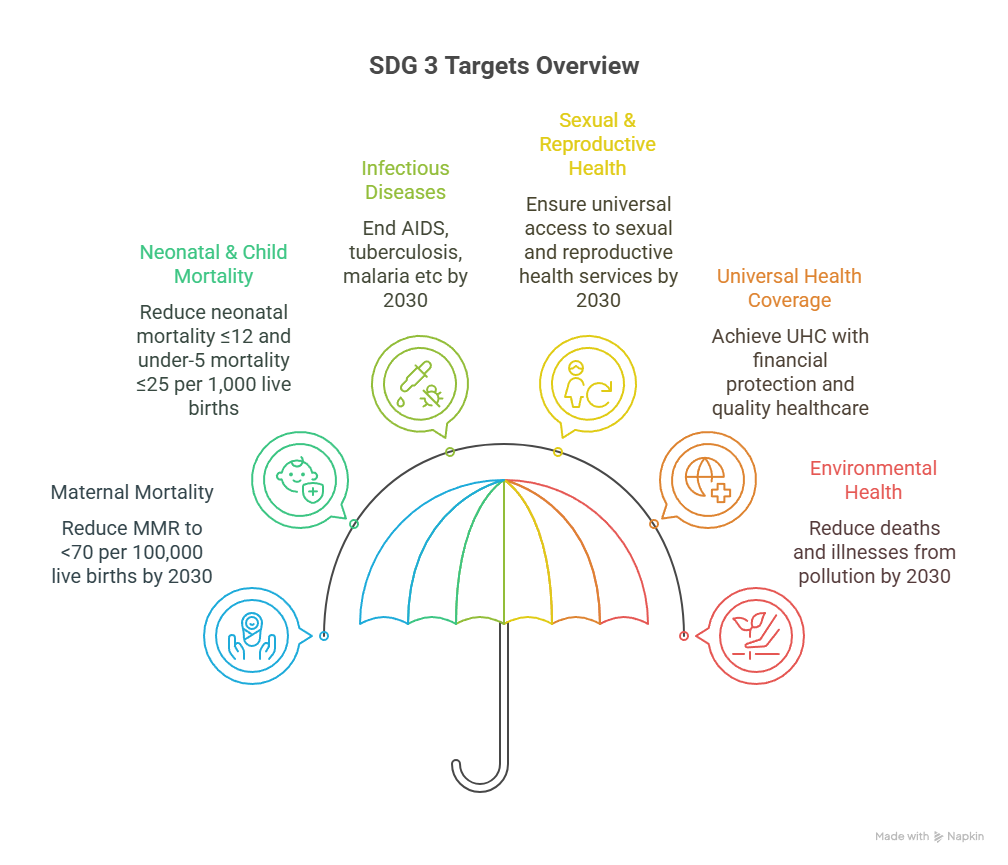
What is the Status of India’s Progress on SDG 3?
- Maternal Health: The maternal mortality ratio (MMR) stands at 97 deaths per 100,000 live births, far from the target of 70.
- Child Mortality: The under-five mortality rate is 32 deaths per 1,000 live births, against a target of 25.
- Life Expectancy: The average life expectancy is currently 70 years, falling short of the 73.63-year target.
- Financial Burden: Out-of-pocket healthcare expenditure remains a heavy burden at 13% of total consumption, nearly double the target of 7.83%.
- Immunisation: While high at 93.23%, immunisation coverage has not yet achieved the universal target of 100%.
What are the Reasons for Gaps in Achieving SDG 3 Targets?
- Access Issues: Poor health infrastructure, especially in rural areas, and economic barriers prevent many from accessing quality healthcare.
- Non-Economic Factors: Challenges such as poor nutrition, inadequate sanitation, and unhealthy lifestyle choices contribute significantly to the disease burden.
- Socio-Cultural Barriers: Cultural practices and stigma, particularly around mental and reproductive health, often deter communities from seeking available medical services.
- Double Burden of Disease: India continues to battle communicable diseases such as Malaria, Dengue, and Leprosy, while the rise of non-communicable diseases (NCDs)—including diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, places additional strain on the health system.
- Covid-19 Pandemic Disruption: It diverted resources from immunization, maternal care, and disease control, leading to delayed diagnoses, interrupted treatment, fewer institutional deliveries, and setbacks in vaccine coverage.
What Measures Should India Adopt to Enhance SDG 3 Progress?
- Universal Health Insurance: Implement universal health insurance to cut out-of-pocket costs and enhance equitable healthcare access.
- Strengthening PHCs & Digital Health: Strengthen Primary Health Centres (PHCs) for early disease detection and use telemedicine and digital records to expand access in remote areas.
- School Health Education: Introduce a structured health education curriculum in schools covering nutrition, hygiene, reproductive health, road safety, and mental well-being.
- E.g., Finland reduced cardiovascular deaths, and Japan improved hygiene and longevity through school health education.
- Cross-Sectoral Convergence: Strengthen coordination among Ministry of Health, Women and Child Development, Jal Shakti, and Environment for integrated nutrition, water and sanitation, environmental health, and healthcare.
- Empower Panchayati Raj Institutions and Urban Local Bodies to manage health initiatives and conduct social audits for accountability.
- Accelerating the implementation of Schemes: Accelerate the implementation of schemes like Ayushman Bharat (Rs 5 lakh health cover per family); Poshan Abhiyaan (reduce stunting, under-nutrition), Mission Indradhanush (child immunization), and LaQshya (improve labour room and maternity care quality).
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine India’s progress under SDG 3 (“Good Health and Well-being”) and discuss the key challenges in achieving maternal and child health targets by 2030 |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Sustainable development is described as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In this perspective, inherently the concept of sustainable development is intertwined with which of the following concepts? (2010)
(a) Social justice and empowerment
(b) Inclusive Growth
(c) Globalization
(d) Carrying capacity
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).” Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)