Human Development Report 2025 | 07 May 2025
For Prelims: Human Development Report, United Nations Development Programme, Artificial Intelligence, National Health Mission, Multidimensional poverty
For Mains: Human Development Index and its implications for India, Role of Artificial Intelligence in addressing human development challenges
Why in News?
India has been ranked 130th out of 193 countries and territories in the 2025 Human Development Report (HDR), titled "A Matter of Choice: People and Possibilities in the Age of AI", released by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
- The report noted that while India has made steady strides, inequality continues to undercut its human development achievements.
What are the Key Highlights of Human Development Report 2025?
Global
- Stalled Human Development Progress: The global HDI saw its smallest increase since 1990 (excluding the 2020-2021 crisis years).
- If pre-Covid trends had continued, most countries could have reached very high human development by 2030, this is now likely to be delayed by decades.
- Top and Bottom Ranks: Iceland ranked first with an HDI of 0.972, while South Sudan ranked last with an HDI of 0.388.
- Growing Inequality: The disparity between the richest and poorest nations has been widening, with high-HDI countries continuing to make progress while low-HDI countries face stagnation.
- AI and Future of Work: The report notes that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is rapidly spreading, with 1 in 5 people globally already using AI tools.
- While 60% served people believe AI will create new job opportunities, half fear it could replace or transform their current roles.
- The 2025 Human Development Report emphasizes the need for inclusive, human-centered AI policies to ensure AI contributes positively to human development, rather than exacerbating inequalities or displacing jobs.
India
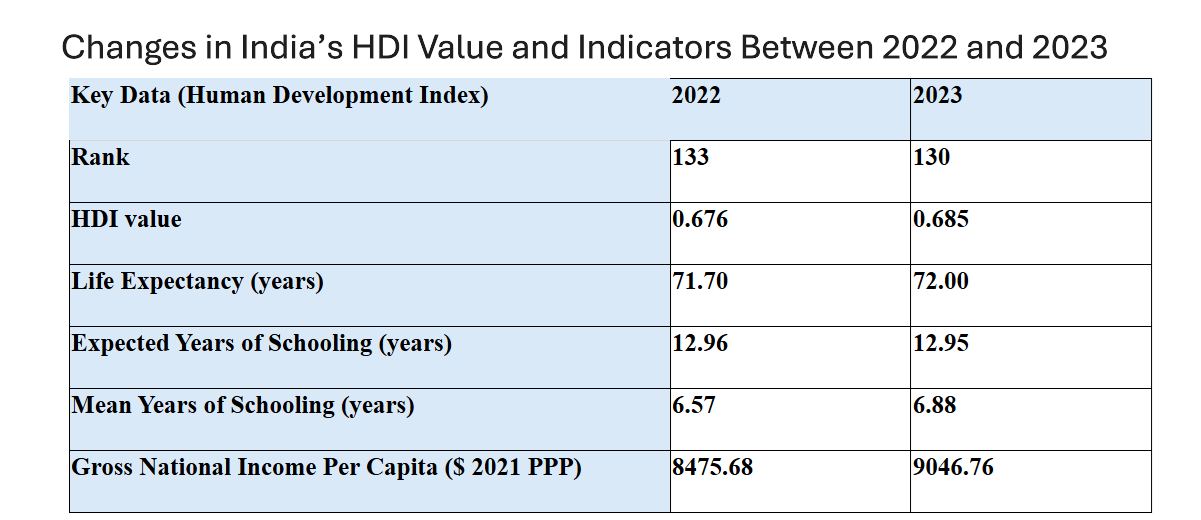
- India’s HDI Ranking: India ranked 133rd in 2022 and improved to 130th in 2023, with its HDI value rising from 0.676 to 0.685.
- The country remains in the "medium human development" category, though it is approaching the threshold for "high human development" (HDI ≥ 0.700).
- Regional Comparison: Among India’s neighbors, China (78th), Sri Lanka (89th), and Bhutan (125th) rank above India, while Bangladesh (130th) is on par. Nepal (145th), Myanmar (150th), and Pakistan (168th) are ranked below India.
- Progress in Key Areas:
- Life Expectancy: India’s life expectancy rose from 58.6 years in 1990 to 72 years in 2023, the highest ever, reflecting a strong post-pandemic recovery.
- This progress is attributed to national health programs like National Health Mission, Ayushman Bharat, Janani Suraksha Yojana, and Poshan Abhiyaan.
- Education: India's mean years of schooling have increased, with children now expected to stay in school for 13 years, up from 8.2 years in 1990.
- Initiatives like the Right to Education Act 2009, National Education Policy 2020, and Samagra Shiksha Abhiyan have improved access, though quality and learning outcomes still require attention.
- National Income: India’s Gross National Income per capita rose over fourfold, from USD 2,167 in 1990 to USD 9,046 in 2023 based on 2021 Purchasing Power Parity (PPP).
- Additionally, 135 million Indians escaped multidimensional poverty between 2015-16 and 2019-21, contributing to HDI improvement.
- AI Skills Growth: India is emerging as a global AI leader with the highest self-reported AI skills penetration.
- 20% of Indian AI researchers now remain in the country, a significant rise from nearly zero in 2019.
- Life Expectancy: India’s life expectancy rose from 58.6 years in 1990 to 72 years in 2023, the highest ever, reflecting a strong post-pandemic recovery.
- Challenges Impacting India’s HDI:
- Inequality Reduces HDI: Inequality has reduced India’s HDI by 30.7%, one of the highest losses in the region.
- Gender Disparities: Female labour force participation (at 41.7% and political representation continue to lag.
- Steps like the 106th constitutional amendment reserving one-third of legislative seats for women show promise for transformative change.
How can Artificial Intelligence Contribute to Human Development?
- Enhancing Productivity and Economic Growth: AI is expected to significantly boost productivity, with 70% of global respondents optimistic about its impact. By automating routine tasks, AI allows focus on innovation in sectors like manufacturing, services, and agriculture.
- A Google report estimates AI could add Rs 33.8 lakh crore to India's economy by 2030, playing a key role in reaching the USD 1 trillion digital economy target by 2028 and contributing 20% to GDP.
- Improving Access to Healthcare: In radiology, AI improves accuracy, detecting abnormalities that may be missed by human eyes, while in oncology, it helps create personalized treatment plans based on patient data.
- AI also streamlines clinical workflows, optimizes resource allocation, and supports remote monitoring and telemedicine, particularly in underserved areas.
- Furthermore, AI is revolutionizing medical education with virtual reality (VR) and adaptive learning, enhancing healthcare professionals' skills.
- Transforming Education: AI enables personalized learning through adaptive platforms, with real-time support from AI tutors and chatbots, especially in underserved areas.
- It also helps educators track student progress and identify learning gaps more effectively.
- Empowering Governance: AI is streamlining public service delivery in India by improving efficiency, enhancing transparency, and detecting fraud in welfare schemes.
- Tools like MuleHunter.AI, developed by the Reserve Bank of India, help combat digital fraud involving mule bank accounts.
- The government’s Bhashini project boosts multilingual communication, aiding policy outreach across linguistic groups.
- Addressing Inequality and Promoting Inclusion: AI tools can identify and bridge gaps in service delivery, particularly for marginalized communities. When guided by human-centered design, AI can ensure equitable access to opportunities.
How can India Address its Human Development Challenges?
- Gender Equality: To advance gender equity, India must effectively implement the 106th Constitutional Amendment ensuring one-third reservation for women in legislatures and strengthen their decision-making roles.
- Expanding access to financial schemes like PM Mudra Yojana, Stand-Up India, and digital freelancing platforms can boost women’s entrepreneurship. Increasing female workforce participation requires flexible jobs, skilling, crèche support, and promotion of STEM participation through initiatives like Vigyan Jyoti.
- Legal reforms must include stricter enforcement against gender-based violence, child marriage, and workplace discrimination
- Strengthening the Nirbhaya Fund and One Stop Centres is also essential for comprehensive support to women facing violence.
- Address Inequality: To tackle rising inequality (as reflected in India’s 2023 Gini coefficient of 0.410), the government should strengthen inclusive initiatives such as Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, Prime Minister's Employment Generation Programme, and Jan Dhan Yojana.
- These programs help address income inequality, but long-term strategies should also include reforms in land rights, healthcare, and education.
- Promote Sustainable Development Goal 10 for inclusive development policy measures and leverage Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) for equitable development.
- Improve Health and Education: India needs to increase investment in primary healthcare, prioritizing universal access to nutrition through schemes like Poshan Abhiyaan.
- Additionally, improving teacher training, curriculum reforms under NEP 2020, and tech-enabled education tools are key to improving learning outcomes.
- Leverage AI for Digital and Financial inclusion: The government should ensure AI is utilized for inclusive services like e-health monitoring, e-learning, and agriculture advisories, ensuring ethical governance through transparent policies.
- Job creation should focus on manufacturing, green economy, and infrastructure, with skilling programs for emerging sectors.
- Digital and financial inclusion must be enhanced through initiatives like Jan Dhan, Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and digital literacy campaigns.
Conclusion
India’s steady rise in HDI reflects its long-term investments in people-centric development. However, to truly realize its human potential, India must confront inequality head-on not just as a moral imperative but as a strategic priority for sustainable progress. The 2025 HDR makes it clear that inclusion is not optional - it is essential.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Assess India's position in the global human development context. What are the challenges and opportunities for India in improving its HDI ranking? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The Multi-dimensional Poverty Index developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative with UNDP support covers which of the following? (2012)
- Deprivation of education, health, assets and services at household level
- Purchasing power parity at national level
- Extent of budget deficit and GDP growth rate at national level
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Despite consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (2016)