Green Hydrogen | 25 Aug 2025
Why in News?
A new report has positioned India as a potential global leader in the green hydrogen economy, with the capacity to capture 10% of the worldwide market and export 10 million tonnes annually by 2030.
What is Green Hydrogen (GH2)?
- About: Green Hydrogen refers to hydrogen produced through electrolysis, where renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydro are used to split water molecules (H₂O) into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂).
- It can also be produced via biomass gasification, a process that converts biomass into hydrogen-rich gas.
- Applications: Its uses include a wide range of applications such as Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs), aviation and maritime transport, and various industrial sectors like fertilizers, refineries, and steel.
- It also holds potential in road and rail transport, shipping, and power generation.
- India’s Green Hydrogen Ambitions: Through policies like the National Green Hydrogen Mission, Green Hydrogen Certification Scheme, and development of Green Hydrogen Hubs at Kandla, Paradip, and Tuticorin, India MAPS its Green Hydrogen Ambitions as follows:
- M – Market Leadership: Capture 10% of the global GH2 market by 2030, projected to cross 100 MMT.
- A – Abatement of Emissions: Enable ~50 MMT CO₂ reduction annually, aligning with India’s NDC and net-zero goals.
- P – Powering Production: Develop 5 MMT per annum of GH2 production capacity by 2030.
- E – Employment Creation: Generate 6 lakh+ green jobs across the GH2 value chain, from R&D to production, storage, and export.
- Other Types of Hydrogen:
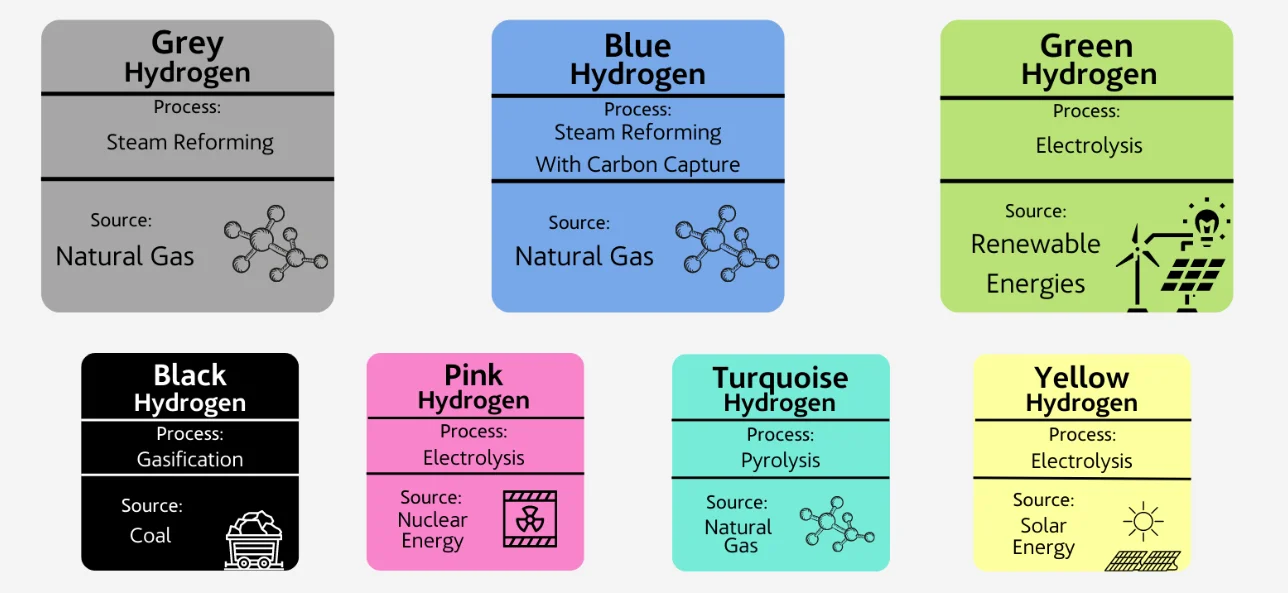
What are the Key Challenges in India’s Green Hydrogen Ecosystem?
India’s Green Hydrogen journey is hindered by a CAGE that restricts its scaling potential:
C – Cost Barrier: Early-stage Green Hydrogen costs nearly $4–4.5/kg, much higher than grey hydrogen, limiting competitiveness.
A – Access to Capital: High upfront investments in electrolysers and renewable capacity deter private players.
G – Gaps in Infrastructure: Lack of transport pipelines, storage, and refuelling networks slows adoption.
E – Economic Viability Issues: Delayed carbon pricing mechanism makes fossil fuel-based hydrogen artificially cheaper, undercutting Green Hydrogen.
What Measures can India Adopt to Boost Green Hydrogen Adoption?
To break free from the CAGE, India must step on the POWER pedal:
P – Pricing Carbon: Accelerating the introduction of a carbon tax/market mechanism to level the field with fossil fuels.
O – Obligation Mandates: Enforce Green Hydrogen Purchase Obligations in hard-to-abate sectors (steel, fertilisers, refining).
W – Widen Infrastructure Base: Build electrolyser capacity, storage, transport pipelines, and export corridors with partners like EU, Japan, S. Korea.
E – Economic Reallocation: Shift subsidies from fossil fuels to GH2, and provide tax incentives & viability gap funding.
R – Risk Pooling through Demand Aggregation: Create pooled procurement platforms with payment security mechanisms to ensure bankable contracts and competitive pricing.
Keywords for Mains
- “Hydrogen is the New Oil” – Fuel of the future.
- “Act Green, Trade Clean” – Export corridors for sustainable growth.
- “Sustainability is the Truest Dharma” – Green energy as ethical responsibility.
- “Green Hydrogen is India’s Tryst with Clean Destiny.”

