GPS Spoofing | 18 Oct 2025
An Air India flight operating from Vienna to Delhi was forced to divert after a suspected GPS signal spoofing over the Middle East disrupted its navigation. The spoofing of signals caused severe degradation of the aircraft’s flight control systems, including failures in autopilot, autothrust, flight director, and autoland functions.
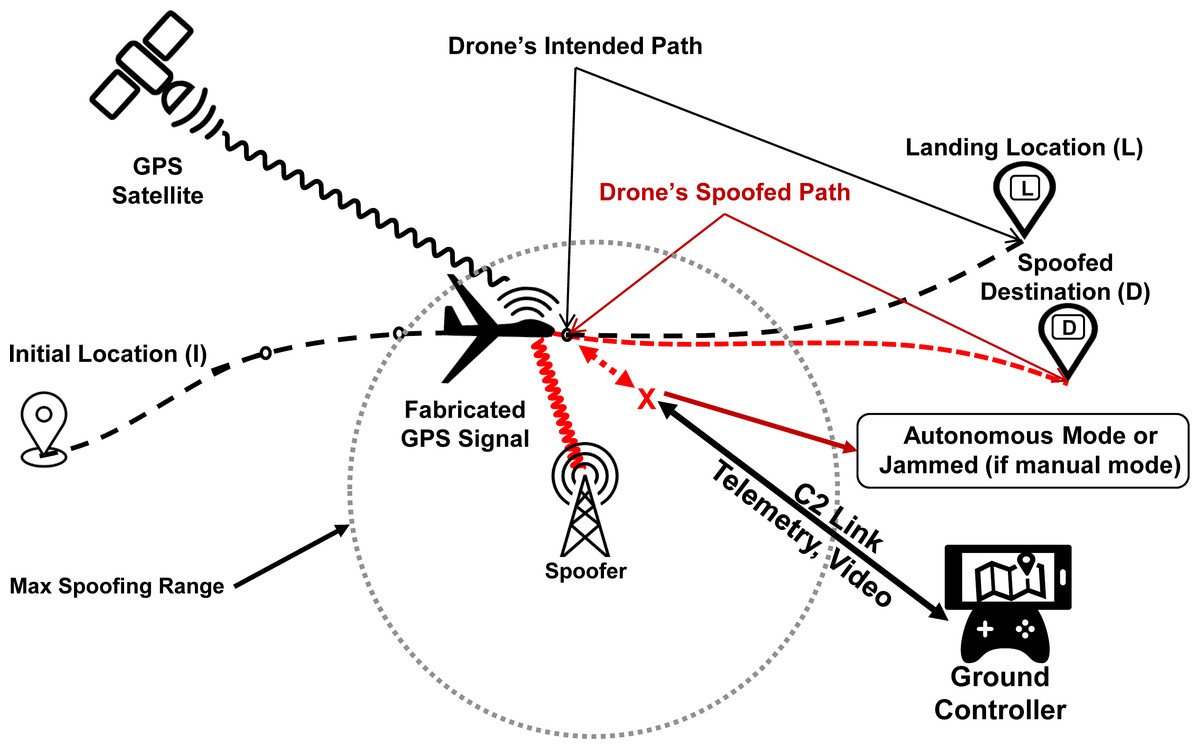
- GPS Spoofing: It is a cyberattack in which fake or counterfeit GPS signals are sent to receivers, causing them to compute incorrect position, navigation, or time information.
- Working Mechanism: Attackers use ground-based transmitters to broadcast strong counterfeit GPS signals that override genuine satellite signals.
- The GPS receiver locks onto these fake signals, producing incorrect location or time readings.
- Effects on Aviation: Spoofing can cause aircraft navigation systems including autopilot, flight director, and autoland, to malfunction, leading to misrouting, cockpit confusion, false warnings, and risks of entering restricted airspace or collisions.
- Difference from Jamming: Unlike jamming, which blocks or disrupts signals, spoofing feeds false data, making detection and response more difficult.
- Mitigation Measures: Robust backup navigation systems like Inertial Reference Systems (IRS) offer alternative location data during spoofing.
- Anti-spoofing technologies, multi-constellation GNSS, advanced signal processing, and pilot training are essential to enhance resilience.
- Working Mechanism: Attackers use ground-based transmitters to broadcast strong counterfeit GPS signals that override genuine satellite signals.
| Read more: Global Cybersecurity Outlook 2025 |