Global Environment Outlook 2025 | 10 Dec 2025
For Prelims: United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), Global Environment Outlook, Biodiversity, Greenhouse Gas (GHG), Unemployment, Malnutrition, Critical Mineral, Global Environment Outlook.
For Mains: Key Findings of the Global Environment Outlook 2025, Current state of global environmental degradation and its consequences, Five key areas requiring transformation to prevent environmental degradation and way forward.
Why in News?
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) has released the 7th edition of Global Environment Outlook 2025 (GEO-7) during the 7th session of the UNEP in Nairobi.
What are the Key Highlights of Global Environment Outlook Report 2025?
- Rising Greenhouse Gas: Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions have increased by 1.5% annually since 1990, reaching record highs (1.55°C) in 2024 and intensifying climate impacts.
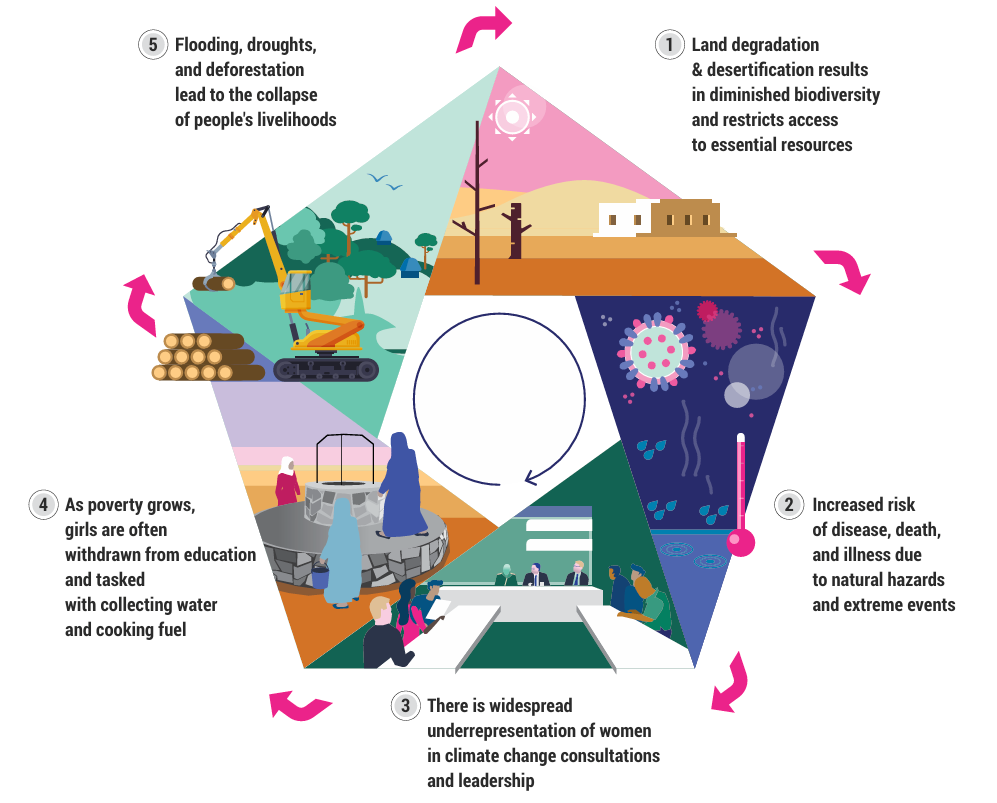
- Biodiversity Loss: One million species out of an estimated eight million are threatened with extinction. 20–40% of the global land area is degraded, affecting over 3 billion people.
- Economic Costs: Climate-related extreme weather events cost approximately USD 143 billion annually over the last two decades; air pollution induced health damages alone cost USD8.1 trillion in 2019 (6.1% of global GDP).
- 9 million deaths occur annually from pollution-related causes.
- The report states that strategic investments in climate stability, biodiversity, and pollution reduction could yield USD 20 trillion annually by 2070, whereas inaction risks devastating both economies and ecosystems.
- Plastic Crisis: 8,000 million tonnes of plastic waste pollute the planet, with toxic chemical exposure causing USD1.5 trillion in annual health-related economic losses.
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- About UNEP: The UNEP, founded on 5th June, 1972, is the foremost global environmental authority. It defines the international environmental agenda, advances sustainable development across the UN, and acts as a leading voice for planetary protection.
- Notable Publications: Emission Gap Report, Adaptation Gap Report, Global Environment Outlook, Frontiers, Invest into Healthy Planet.
- Signature Initiatives: Beat Pollution, UN75, World Environment Day, Wild for Life.
- Head Office: Nairobi, Kenya.
What can be the Various Impacts of Environmental Degradation?
- Crossing Dangerous Tipping Points: Likely to exceed 1.5°C by the early 2030s and 2.0°C by the 2040s, causing irreversible ecosystem collapse and mass displacement.
- Global Economies Collapse: Annual global GDP could fall 4% by 2050 and 20% by 2100, leading to mass unemployment, poverty, and systemic instability.
- Loss of Fertile Land: Equivalent to a Colombia or Ethiopia of fertile land lost each year, threatening agriculture and water availability, destroying livelihoods, fueling conflict, and eroding biodiversity.
- Nutritional Decline: Per-person food availability could drop 3.4% by 2050, intensifying hunger, malnutrition, famine, and social unrest.
- Financial Drain: Already trillions annually, these costs will grow, diverting vital resources and trapping societies in perpetual crisis.
What Transformative Actions are Recommended by GEO-7 to Prevent Environmental Collapse?
- Economy and Finance: Transition to comprehensive wealth metrics and price externalities to reflect the true value of GDP. Reform policies to incentivize decarbonization, sustainable agriculture, and ecosystem restoration.
- Achieving net-zero by 2050 and funding biodiversity needs approximately USD 8 trillion in annual investment until 2050—a fraction of the cost of inaction.
- Global benefits could reach USD 20 trillion per year by 2070, booming thereafter to a potential USD 100 trillion per year.
- Materials and Waste: Implement transparent, traceable circular design, shift investments to circular and regenerative models, and reshape consumption through circular mindsets.
- Energy: Decarbonize the energy supply, improve energy efficiency across sectors, ensure sustainable critical mineral value chains, and address global energy access and energy poverty.
- 9 million premature deaths could be avoided by 2050 via measures like cutting air pollution. By 2050.
- Food Systems: Promote healthy, sustainable diets, increase agricultural circularity and efficiency, and sharply cut food loss and waste.
- Almost 200 million people could be lifted out of undernourishment. Over 100 million people could escape extreme poverty.
- Environment: Accelerate ecosystem conservation and restoration, enhance climate adaptation via Nature-based Solutions, and enforce strong climate mitigation strategies.
- Collaboration: Requires co-development of solutions by governments, private sector, civil society, academia, and Indigenous Peoples, whose knowledge is crucial.
- Integrated Action: Policies across the five key areas must be implemented in parallel, not in isolation, to ensure a just transition for all.
What Should be India's Strategic Priorities to Prevent Environmental Degradation?
- Green GDP Framework: Develop and implement an "Inclusive Wealth Index" or "Green GDP" that accounts for the depreciation of natural capital (forests, soil, water, air quality) alongside economic growth.
- Transition to Circular Economy: Launch a National Circular Economy Mission with sector-specific (construction, plastic, electronics, textiles) roadmaps. Mandate recycled content in packaging, and create strong markets for secondary raw materials.
- Subsidy Reforms: Gradually phase out petrol, diesel, and coal subsidies, redirecting them to renewable energy, electric mobility, organic farming, and sustainable public transport.
- Scale Up Nature-Based Solutions (NbS): Mainstream Nature-Based Solutions into public infrastructure budgets. Treat mangrove restoration as coastal defense, wetland rejuvenation as water security, and urban green spaces as public health infrastructure.
Conclusion
GEO-7 presents humanity with a defining choice: embrace systemic transformation across the economy, energy, food, materials, and environment to unlock USD 20 trillion annually by 2070, or face catastrophic GDP losses, ecosystem collapse, and mass displacement. Whole-of-government approaches, Indigenous knowledge integration, and USD 8 trillion annual investment until 2050 are critical to securing planetary and human well-being.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyse the current state of global environmental degradation as highlighted in the GEO-7 report. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What is the GEO-7 report?
GEO-7 is the 7th Global Environment Outlook by UNEP, assessing planetary environmental health and economic transformation pathways.
Q. What are the projected economic benefits of environmental transformation by 2070?
Transformation pathways could deliver USD 20 trillion annually by 2070, expanding to USD 100 trillion thereafter, while avoiding 9 million premature deaths and lifting 200 million from undernourishment by 2050.
Q. What are the five key systems requiring transformation as per the report?
The five key areas are: Economy and Finance, Materials and Waste, Energy, Food Systems, and the Environment, all of which require parallel and integrated policy actions.
Summary
- The UN's GEO-7 report states that investing in climate, nature, and pollution control can yield up to USD 100 trillion annually in long-term economic benefits, while inaction risks cutting global GDP by 20% and causing irreversible damage.
- Current degradation is severe, with record emissions, 1 million species at risk, 9 million pollution-related deaths yearly, and trillions in annual economic costs.
- Averting crises requires sweeping, parallel transformations across five key systems: Economy, Materials/Energy use, Food production, and Environmental management.
- Success hinges on massive collaborative investment (~USD 8 trillion/year), integrating Indigenous knowledge, and moving 'Beyond GDP' to value natural and human capital.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q. The ‘Common Carbon Metric’, supported by UNEP, has been developed for
(a) assessing the carbon footprint of building operations around the world
(b) enabling commercial fanning entities around the world to enter carbon emission trading
(c) enabling governments to assess the overall carbon footprint caused by their countries
(d) assessing the overall carbon foot-print caused by the use of fossil fuels by the world in a unit time
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Discuss global warming and mention its effects on the global climate. Explain the control measures to bring down the level of greenhouse gases which cause global warming, in the light of the Kyoto Protocol, 1997. (2022)