Double Helix Model of DNA | 14 Nov 2025
Why in News?
James Watson, one of the co-discoverers of the double-helix structure of Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), recently passed away.
What is Double Helix Model of DNA?
- Discovery: The DNA double helix model was discovered by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, revolutionized the field of biology, laying the foundation for modern genetics, biotechnology, and medical research.
- This milestone remains a cornerstone in the understanding of heredity, evolution, and genetic diseases.
- Watson and Crick deciphered DNA’s structure as a double helix based on Rosalind Franklin’s critical X-ray crystallography (Photo 51).
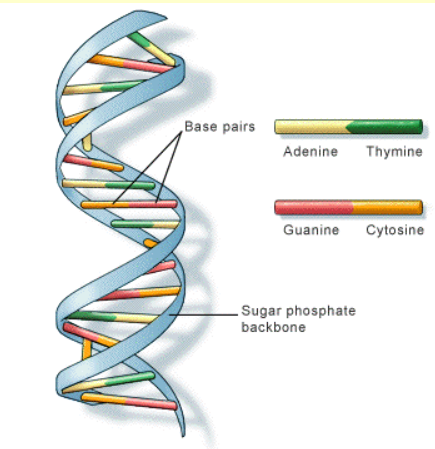
- Structure: DNA consists of two long strands that twist around each other to form a helical shape, creating the "double helix."
- Each strand is made up of sugar and phosphate molecules, which form the backbone of the structure.
- The majority of DNA is found in the cell nucleus so it is called nuclear DNA.
- Base Pairs: The two strands are connected by nitrogenous base pairs, with Adenine (A) always pairing with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) pairing with Guanine (G). These base pairs form the "rungs" of the helical ladder.
- Antiparallel Strands: The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions, a feature known as "antiparallel," which ensures that the base pairs align correctly for complementary bonding.
- Core Features:
- Complementary Base Pairing: The two strands are noted as being connected through specific base-pairing rules where Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine. This pairing is highlighted as a fundamental principle of DNA stability.
- Mechanism of Accurate Replication: This complementary pairing is emphasized for explaining how DNA replicates with high accuracy, ensuring faithful transmission of genetic information across generations.
- Significance of Discovery:
- It gave rise to fields such as Molecular Biology, Biotechnology, and Genetic Engineering.
- Awarded the Nobel Prize (1962) in Physiology or Medicine (Watson, Crick, and Maurice Wilkins) for their DNA model, highlighting its foundational importance.
- Paved the way for the Human Genome Project (2003), CRISPR gene editing tool, and personalized medicine.
- In agriculture, DNA analysis reshaped farming practices by enabling the creation of genetically modified crops and pest-resistant plant varieties.
- DNA has also become indispensable in forensic science, assisting in crime-solving.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why was the discovery of the DNA double helix historically significant?
It revealed how genetic information is stored and replicated, transforming heredity studies, launching molecular biology, and enabling advances like genetic engineering, genome sequencing, CRISPR, and personalised medicine.
2. What is the core idea of Watson and Crick’s double-helix model?
The model shows two antiparallel DNA strands forming a spiral staircase, stabilized by complementary base pairing (A–T, G–C), ensuring structural stability and accurate genetic replication.
3. What makes DNA central to heredity and evolution?
DNA stores genetic instructions in nucleotide sequences, passes traits across generations, mutates to create variation, and thus drives evolutionary change, adaptation, and species diversification.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: DNA Barcoding can be a tool to:(2022)
- assess the age of a plant or animal.
- distinguish among species that look alike.
- identify undesirable animal or plant materials in processed foods.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Q: With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
(b) Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
(c) A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
(d) Cells taken out from plants and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Ans: (a)