Digital Banking Units: Progress & Challenges | 14 May 2025
For Prelims: Digital Banking Units (DBUs), Financial Inclusion, Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY), Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Direct Benefit Transfers(DBT), Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), Atal Pension Yojana (APY), Payment banks, Small Finance Banks, Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
For Mains: Significance of Financial Inclusion for Inclusive Growth and Upliftment of Vulnerable Sections, Challenges Related to Digital Banking Units (DBUs), Measures to Make DBUs more Effective.
Why in News?
Digital Banking Units (DBUs), launched in 2022 to extend digital financial services to the remotest parts of the country, have seen limited expansion due to challenges like high operational costs, low digital adoption etc. raising questions about their effectiveness and long-term sustainability.
What is a Digital Banking Units (DBUs)?
- About: A DBUs is a specialised fixed point business unit or hub, housing a certain minimum digital infrastructure for delivering digital banking products entirely through self-service, anytime.
- They were launched in 2022, across 75 remote districts of India, commemorating India’s 75th year of Independence.
- DBUs are set up by scheduled commercial banks (SCBs) (excluding Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), payment banks, and local area banks) with digital banking experience, without prior Reserve Bank of India (RBI) approval in Tier 1 to Tier 6 centres, except where specifically restricted.
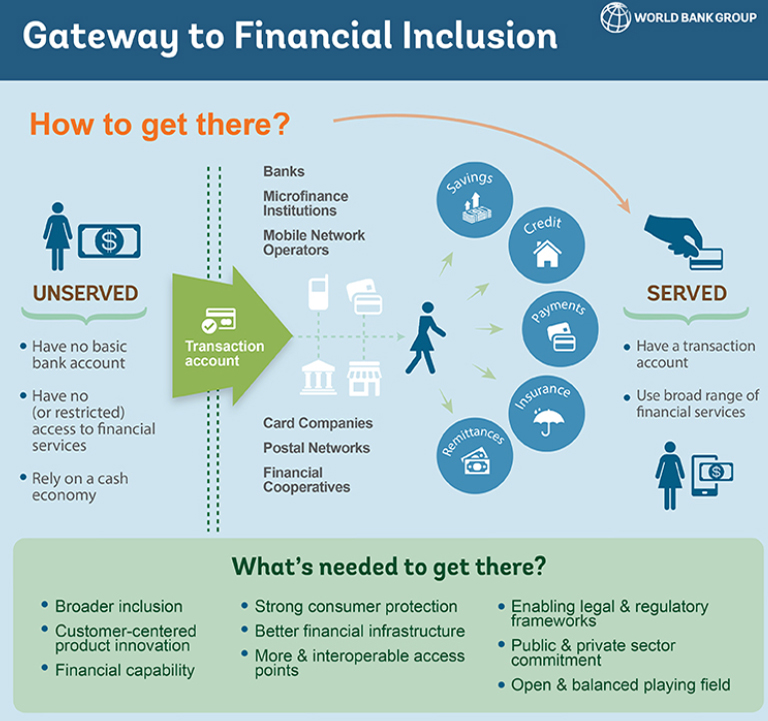
- Benefits: It aims to boost financial inclusion by enhancing access to digital banking for underserved and unbanked populations.
- Services Offered: ATMs, cash deposit machines, passbook and internet kiosks, bill payments, and account opening via e- KYC (Know Your Customer)
- RBI Mandate for DBUs: The RBI mandates that DBUs must be physically separate from existing branches, with distinct entry and exit points.
- They should be designed to serve digital users, featuring advanced technologies like Interactive Teller Machines, Service Terminals, and Cash Recyclers.
- Additionally, each DBU must be overseen by a senior, experienced executive.
Difference Between Digital Banks and DBUs
- Digital banks are licensed under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949, with a balance sheet and legal personality, promoting innovation and competition.
- DBUs are extensions of traditional banks, offering digital services within the bank's regulations, with limited scope for competition and innovation.
- Digital Banks offer a broader range of banking services, including deposits, loans, and other financial products, all digitally.
- DBUs focus on delivering digital banking products and services in a specific location but do not offer full-fledged banking services like digital banks.
What are the Challenges Faced by Digital Banking Units (DBUs)?
- Ineffective Planning: At the time of implementation of DBUs, banks were given just 45 days to set them up at centrally chosen locations, without considering local needs, digital readiness, or regional differences in demand and banking habits, which impacted the initiative's effectiveness.
- High Operational Costs: RBI requires DBUs to be separate from branches with costly infrastructure like interactive teller machines and video KYC. In low-traffic areas, high costs deter banks from expanding DBUs.
- Low Digital & Financial Literacy: Limited digital skills, especially among senior citizens, and the lack of cash counters in tier-II, tier-III towns, and rural areas hinder DBU effectiveness, limiting financial inclusion.
- Connectivity & Strategic Integration Issues: Remote areas lack stable internet and power, disrupting DBU operations.
What are Government Initiatives for Financial Inclusion?
What Steps Should be Taken to Enhance the Effectiveness of Digital Banking Units?
- Decentralised, Demand-Based Expansion: Instead of a top-down rollout, DBUs should be established based on local demand, digital literacy levels, and banking penetration.
- A decentralised, data-driven model can ensure sustainability and avoid underutilisation.
- Strengthening Digital Literacy Programs: Leverage the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA), aimed at digitally empowering rural citizens, to improve digital literacy in areas with low engagement.
- Banks should collaborate with local governments and community organizations to conduct training sessions for citizens, especially senior citizens and women, on using digital services effectively.
- Infrastructure Support: Invest in improved connectivity infrastructure, especially in remote and underserved areas.
- The BharatNet Project can play a crucial role in ensuring that stable internet access is available to remote areas.
- Establish backup power solutions like solar power to mitigate frequent power outages that affect DBU operations.
- Enhancing Customer Support: DBUs should include human support for digital onboarding, problem resolution, and financial advice to enhance customer engagement.
- Additionally, offering multilingual interfaces and local language assistance can improve comfort and accessibility in diverse regions.
- Focus on Financial Products and Services: DBUs should ensure easy access to Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY), Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), and Atal Pension Yojana (APY), particularly in rural areas where insurance penetration is low.
- Facilitate quick access to digital loans, such as those under PM Mudra Yojana, e-Mudra, and other MSME schemes.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. What are Digital Banking Units (DBUs)? Discuss the challenges in implementing them and suggest measures to optimize their effectiveness in rural areas. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to India, consider the following: (2010)
- Nationalization of Banks
- Formation of Regional Rural Banks
- Adoption of village by Bank Branches
Which of the above can be considered as steps taken to achieve the “financial inclusion” in India?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana (PMJDY) is necessary for bringing unbanked to the institutional finance fold. Do you agree with this for financial inclusion of the poorer section of the Indian society? Give arguments to justify your opinion.