Climate Change Threatens Caspian Sea | 03 May 2025
The Caspian Sea is rapidly shrinking from climate-driven evaporation, endangering biodiversity, livelihoods, and regional stability.
- Projected Decline in Water Levels: Even if global warming stays below 2°C, the Caspian Sea is projected to drop 5–10 m, and up to 21 m by 2100 if temperatures rise further.
- Impacts:
- Biodiversity Loss: It threatens endemic species like the Caspian seal (IUCN Endangered) and Beluga sturgeon (an ancient family of large fish, critically endangered).
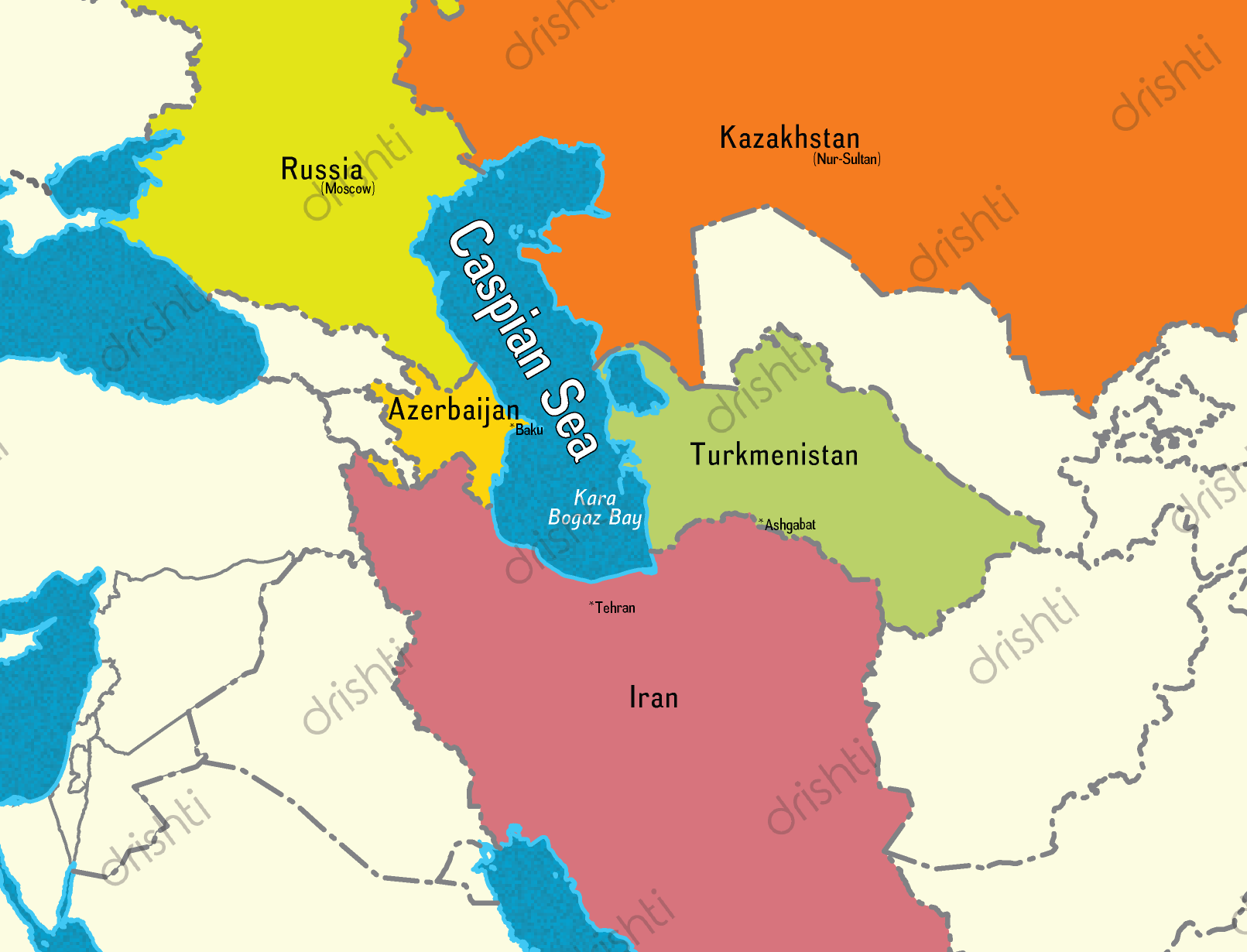
- Industry: Ports like Baku (Azerbaijan), Anzali (Iran), Aktau (Kazakhstan), Turkmenbashi (Turkmenistan), and Lagan (Russia) could be stranded inland.
- The Volga river, the Caspian’s sole maritime link to the outside world, could become nonviable.
- Hydrocarbon production sites like Kashagan (Kazakhstan) and Filanovsky (Russia) will become landlocked.
- Public Health Risks: Dry seabeds could release dust contaminated with industrial pollutants and salt, akin to the Aral Sea disaster.
- About Caspian Sea: It is a tectonic lake and the world's largest inland water body.
- Three major rivers Volga, Ural, and Terek empty into the Caspian.
- It is bordered by Russia, Azerbaijan, Iran, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan.
| Read More: Caspian Sea |