Central Bank Digital Currency | 22 Jan 2026
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recommended placing a proposal to link BRICS countries' central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) on the agenda for the 2026 BRICS summit (host-India).
- The RBI’s proposal builds on a 2025 declaration at a BRICS summit in Rio de Janeiro, which pushed for interoperability between members’ payment systems to make cross-border transactions more efficient.
What is Central Bank Digital Currency?
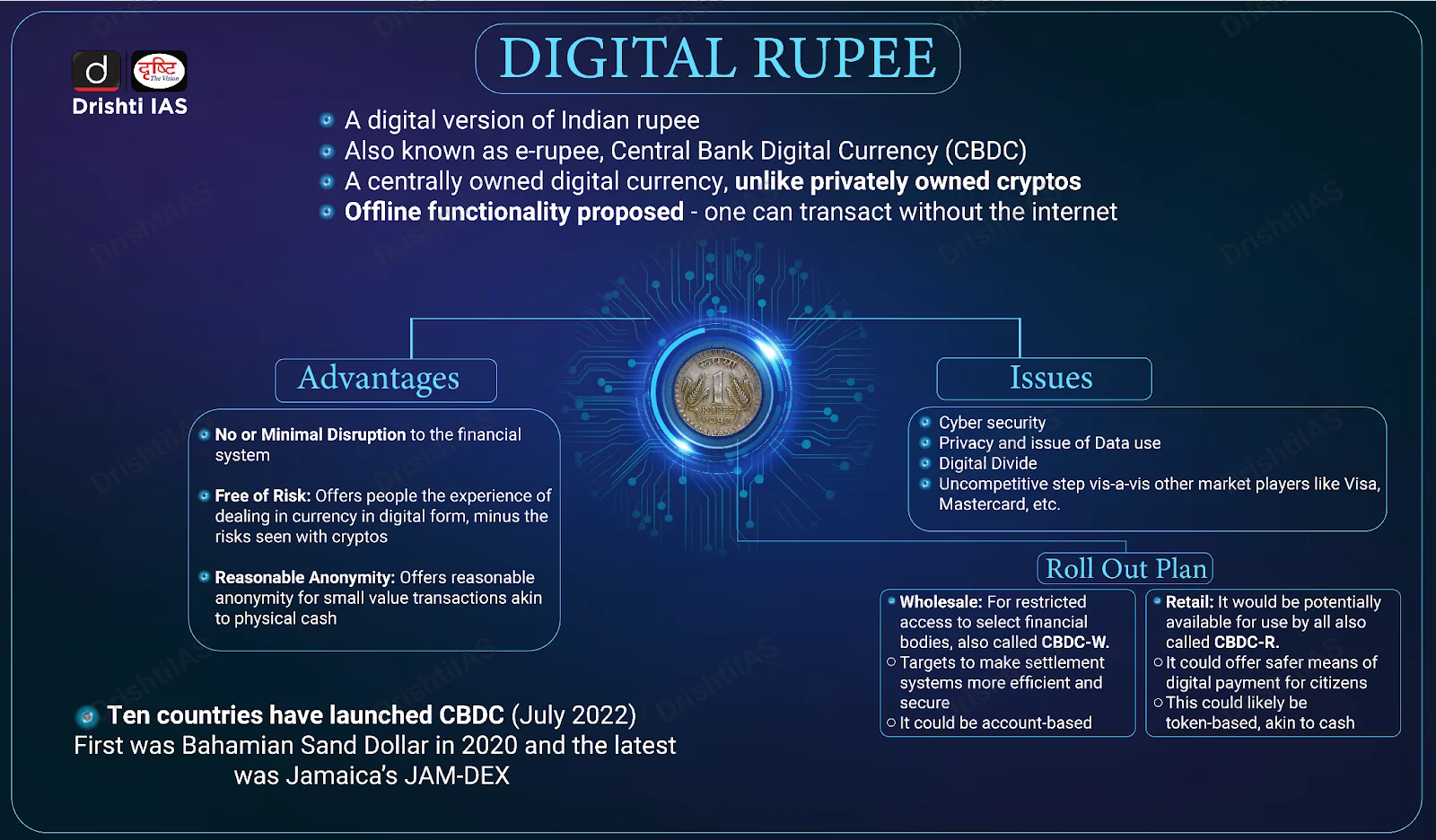
- About: A CBDC is a digital form of a country's fiat currency, issued and backed directly by its central bank. It represents a liability of the central bank, similar to physical cash (banknotes and coins) or reserves held by commercial banks at the central bank.
- Unlike cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, which are decentralized and typically volatile, a CBDC is centralized, stable in value (pegged to the national currency), and functions as legal tender.
- Functioning: CBDCs use cryptography for security, integrity, and authentication.
- Techniques include encryption for data protection and digital signatures to authorize transactions.
- Privacy-enhancing methods like zero-knowledge proofs balance anonymity with regulation.
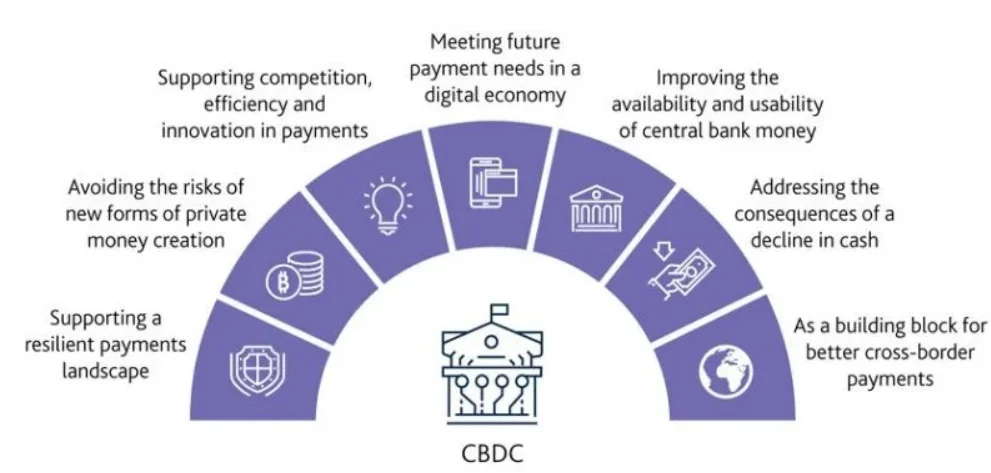
- Objective: It aims to modernize payment systems amid the rise of private digital currencies (e.g., stablecoins) and declining cash, focusing on efficient and inclusive financial systems.
- Benefits:
- Key Characteristics:
- Issuer and Backing: Issued exclusively by the central bank, ensuring full faith and credit of the government. It is not issued by private entities or commercial banks.
- Digital Nature: Exists solely in electronic form, recorded on centralized ledgers, distributed ledger technology, or hybrid systems. It enables seamless digital payments without relying on intermediaries for core settlement.
- Purpose and Availability: Designed as a complement to (not a replacement for) physical cash and existing bank deposits. It serves as a means of payment, unit of account, and store of value.
- Types: A retail CBDC (rCBDC) is for the general public’s daily payments like transfers and purchases. A wholesale CBDC (wCBDC) is limited to banks and institutions for interbank settlements and large transactions.
- Distinction from Existing Digital Money: While most money today is already digital (e.g., bank account balances or mobile payments), those are liabilities of commercial banks. A CBDC is a direct claim on the central bank, offering the highest level of safety and liquidity comparable to cash.
- Global Context: The Bahamas became the first country to launch a nationwide CBDC named Sand Dollar in 2020, followed by Nigeria’s eNaira, also launched in 2020. Over 90% of the world’s central banks are exploring CBDCs, and around 60% are already conducting tests or proofs of concept.
- While no BRICS member has fully launched a digital currency, all five are running pilot projects.
- The main national CBDCs are Brazil’s Drex (advanced pilot), Russia’s Digital Ruble (ongoing pilot with limited commercial use), India’s e-Rupee (7 million retail users), and China’s e-CNY (most widespread pilot), while South Africa remains in the research stage.
Digital Currency
- Digital Currency: Digital currency is a form of currency that exists only in electronic form, also referred to as digital money, electronic money, or cybercash, with transactions conducted via computers or internet-connected wallets.
- It is possible to make payments in a digital currency without using the US dollar or SWIFT. A digital currency can also be programmed with conditions, such as a time-frame for spending.
- Key Features: It can be centralized, like fiat currency issued by a central bank, or decentralized, such as cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which use cryptography to secure transactions.
- Types of Digital Currency: Broadly, digital currencies are categorized into three types:
- Cryptocurrencies (e.g., Bitcoin)
- Virtual currencies (e.g., gaming tokens)
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs).
- CBDCs vs. Fiat Currency: Unlike physical currencies, digital currencies have no tangible form, with CBDCs existing purely digitally, serving as a supplement or replacement to traditional fiat currency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)?
A CBDC is a digital form of a country’s fiat currency, issued and backed by the central bank, functioning as legal tender and a secure claim on the central bank.
2. How does a CBDC differ from cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin?
CBDCs are centralized, stable, and government-backed, whereas cryptocurrencies are decentralized, volatile, and not legal tender.
3. Which BRICS countries are piloting CBDCs?
Brazil (Drex), Russia (Digital Ruble), India (e-Rupee), China (e-CNY) are piloting CBDCs, while South Africa remains in the research stage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to Central Bank digital currencies, consider the following statements : (2023)
- It is possible to make payments in a digital currency without using US dollar or SWIFT system.
- A digital currency can be distributed with condition programmed into it such as a time-frame for spending it.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)