Breakthrough in CAR T-Cell Therapy | 10 Feb 2026
Why in News?
A new study by the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bombay, published in Biomaterials Science, has demonstrated a gentler method for recovering lab-grown T-cells.
- This development in cancer immunotherapy, particularly CAR T-cell therapy, could potentially make advanced cancer care more reliable and affordable in India.
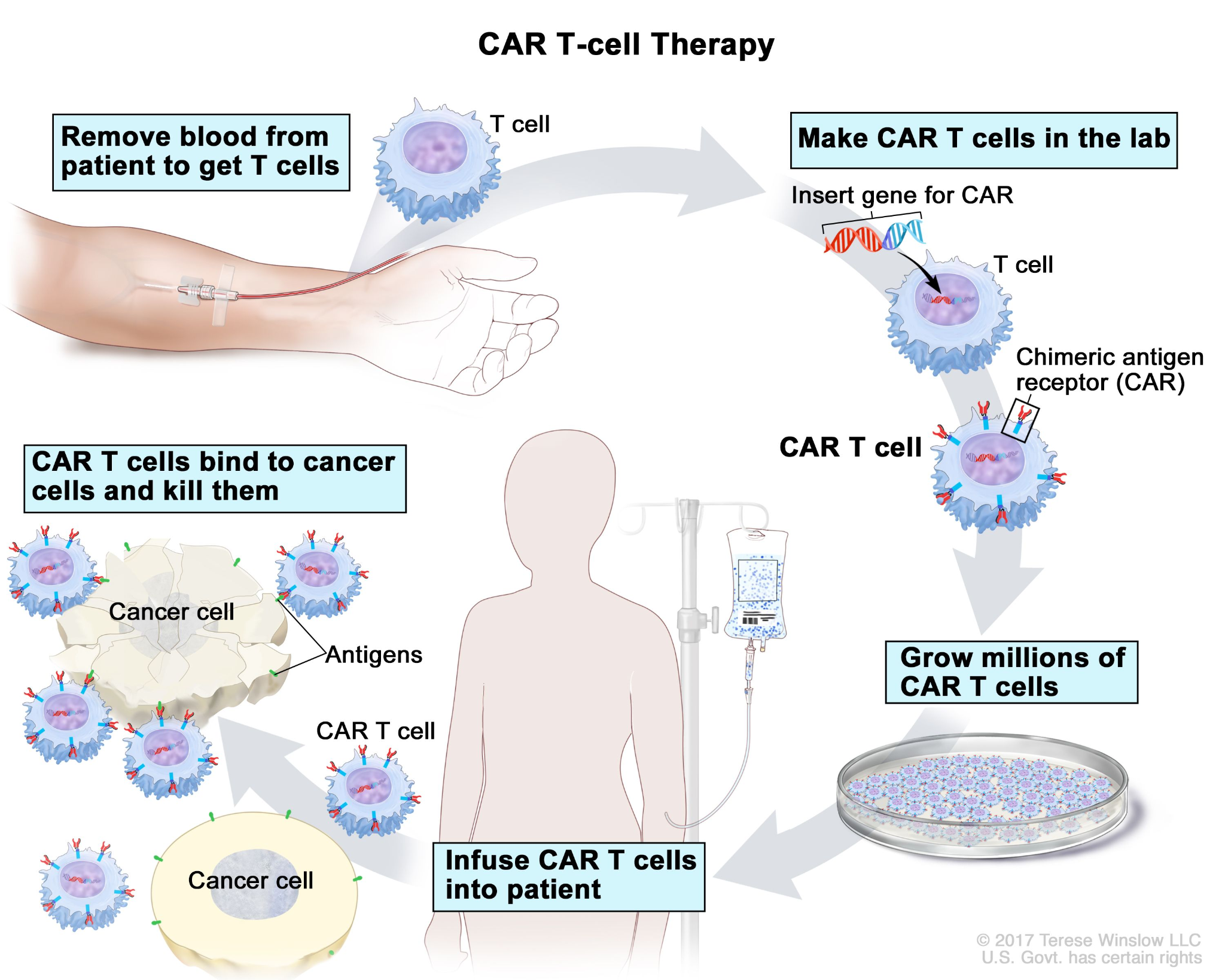
What are T-cells and CAR T-cell Therapy?
- T-Cells: These are a type of white blood cell that act as the body’s frontline soldiers. They patrol the bloodstream to detect infections or abnormal cells like cancer.
- Upon detection, they either destroy the threat directly or signal other immune cells to assist.
- CAR T-cell Therapy: This is a cutting-edge treatment where T-cells are collected from a patient and genetically engineered in a lab.
- Scientists add a gene to equip these cells with Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs).
- These receptors act like trackers, guiding the T-cells to recognize and destroy specific cancer cells.
- It is currently approved for certain blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
- NexCAR19: In 2023, NexCAR19 became India’s first approved indigenous CAR-T cell therapy, developed through a collaboration between IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT (a company incubated at IIT Bombay).
- As the world's most affordable CAR-T therapy, it positions India on the global map for advanced cell and gene therapy.
What are the Key Findings of IIT Bombay Study on CAR T-cell Therapy?
- Cell Recovery: Growing T-cells in 3D scaffolds (which mimic the human body) is effective for cell growth but makes retrieval difficult.
- T-cells grip the fibrous scaffolds tightly, and harsh recovery methods (using trypsin) damage them.
- Traditional extraction methods use harsh enzymes (like Trypsin or TrypLE) which strip the cells of vital proteins, rendering them less effective or killing them.
- Efficient Recovery: IIT Bombay team found that using a commercially available enzyme called Accutase (instead of Trypsin) allows for the gentle detachment of cells.
- Accutase effectively releases the cells from the 3D scaffold without harming their outer membrane.
- Accutase-recovered cells showed higher survival, preserved immune function, and formed healthy clusters, indicating better readiness for cancer therapy.
Significance
- Current CAR T-cell therapies can cost Rs 3-4 crore globally. By reducing the waste of expensive lab-grown cells and improving efficiency, this method helps Indian initiatives (like ImmunoACT) bring the cost down to a fraction of the global price.
- A more consistent supply of healthy T-cells means the therapy is more likely to succeed when infused back into the patient.
- This highlights India's growing capability in biomedical engineering, moving from generic drug manufacturing to novel process innovation in complex therapies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are T-cells?
T-cells are a type of white blood cell that play a central role in immune defence by identifying and destroying infected or cancerous cells
2. What is CAR T-cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is a form of cancer immunotherapy in which a patient’s T-cells are genetically engineered to express Chimeric Antigen Receptors (CARs) that target specific cancer cells
3. Which cancers are currently treated using CAR T-cell therapy?
CAR T-cell therapy is approved for certain blood cancers, mainly leukemia and lymphoma
4. Why is T-cell recovery important in CAR T-cell therapy?
Damaged or non-functional T-cells reduce treatment effectiveness, making safe recovery of lab-grown cells critical.
5. What is NexCAR19?
NexCAR19 is India’s first indigenous CAR T-cell therapy, approved in 2023, developed by IIT Bombay, Tata Memorial Centre, and ImmunoACT
6. Why is CAR T-cell therapy expensive?
High costs arise from complex cell engineering, specialised lab infrastructure, and low recovery efficiency of viable T-cells
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body? (2022)
(a) They protect the environmental allergens. body
(b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
(c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
(d) They protect the body from diseases caused by pathogens.
Ans: (d)