Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Summit 2025 | 04 Nov 2025
For Prelims: Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation, Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), Gyeongju Declaration (2025),
For Mains: India’s foreign policy in the Indo-Pacific, Role of APEC in shaping regional trade
Why in News?
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Summit 2025, held in Gyeongju, South Korea, concluded with the adoption of the APEC Leaders’ Gyeongju Declaration (2025), reaffirming regional cooperation, digital transformation, and inclusive economic growth.
What are the Key Outcomes of APEC Summit 2025?
- Adoption of the Gyeongju Declaration (2025): The declaration reaffirmed APEC leaders’ commitment to inclusive economic growth, recognising the transformative impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and demographic shifts on labour markets.
- It outlined three priorities:
- Building the world’s most dynamic and interconnected regional economy.
- Preparing the region for digital and AI transformation
- Addressing shared challenges and ensuring growth benefits all
- It outlined three priorities:
- APEC Artificial Intelligence (AI) Initiative (2026-2030): The AI initiative seeks to drive inclusive, resilient growth by boosting innovation, cooperation, capacity building, and sustainable, energy-efficient AI development.
- Framework for Demographic Changes: Adopted by APEC, it addresses the region’s challenges of ageing populations, declining birth rates, and rapid urbanisation.
- It urges people-centred, intergenerational policies for resilient and inclusive growth, and promotes shared policy responses, social innovation, stronger employment, fiscal resilience, and a “silver economy” for ageing populations.
- Strengthened Economic and Technological Cooperation: China–South Korea renewed a currency swap and signed a cybersecurity MoU, US–China talks on the sidelines of the summit signaled easing tensions with plans to restart trade talks and cut select tariffs.
- Support for Inclusive, Rules-Based Multilateralism: Leaders reaffirmed the Putrajaya Vision 2040, stressing free and fair trade, predictable investment, and cooperation through multilateralism over fragmentation.
- Putrajaya Vision 2040 is a long-term strategic plan adopted by the APEC in 2020 to foster an open, dynamic, resilient, and peaceful Asia-Pacific community.
What is Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)?
- About: APEC founded in 1989, is a regional forum of 21 economies that promotes balanced, inclusive, sustainable, and innovative growth while advancing regional economic integration across the Asia-Pacific.
- It uses the term “economies” instead of “countries” to stress economic cooperation over political representation.
- APEC works to ease the movement of goods, services, investments, and people by streamlining customs, improving business conditions, and aligning regional regulations and standards to boost trade and integration.
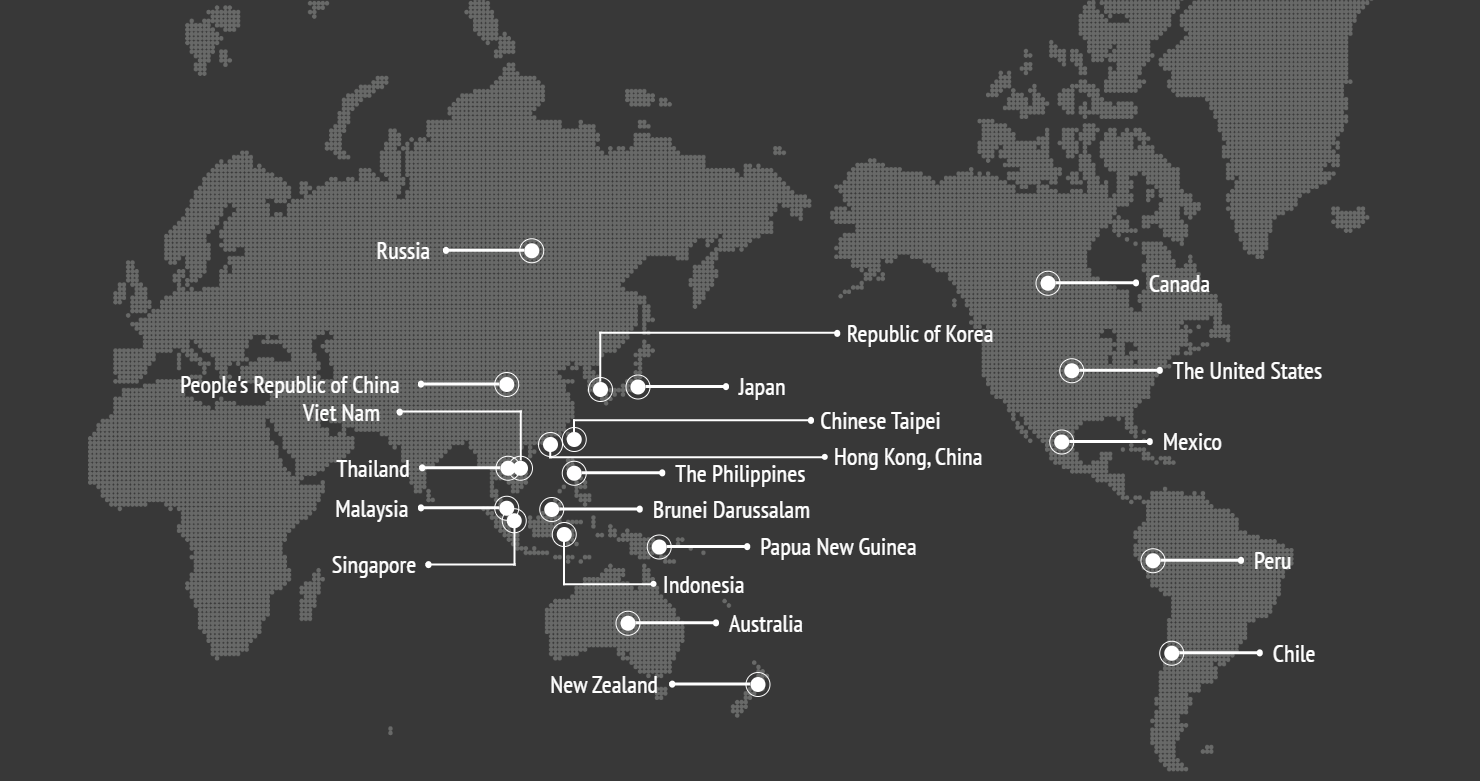
- Members: Australia, Brunei Darussalam, Canada, Chile, China, China, Indonesia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Peru, the Philippines, Russia, Singapore, Chinese Taipei, Thailand, US, and Viet Nam.
- Its 21 member economies are home to around 2.95 billion people and represent approximately 62% of world GDP and 48% of world trade in 2021.
- India is not a member of APEC, it does have close political, economic, and strategic ties with many of its members.
- APEC Process: It operates on consensus and voluntary participation, with all members having an equal voice and decisions made through dialogue.
- The APEC process is supported by a permanent secretariat based in Singapore.
- India’s Interest in APEC: India views APEC as a gateway to deeper trade, investment, and regional integration in the Asia-Pacific.
- Membership would help India align with global trade standards, simplify procedures, and attract more foreign investment and complement national initiatives like ‘Make in India’ and ‘Digital India’.
- Reasons for the Decline in India’s Bid for APEC Membership: India’s bid for APEC membership declined due to the forum’s consensus-based admission process, a freeze on new members, and concerns over India’s protectionist trade policies and regulatory complexity.
- Geopolitical factors, including China’s quiet opposition, has kept India out of the forum despite its applications in 1991 and 1997.
- While India has joined APEC meetings as a guest or observer, its membership remains off the table.
How APEC’s Evolving Agenda Aligns with India's Indo-Pacific Vision?
- Shared Vision: Both APEC and India’s Indo-Pacific strategy emphasise a free, open, and inclusive regional order, rooted in transparency, connectivity, and respect for international rules.
- Focus on Connectivity and Integration: APEC’s agenda on supply-chain resilience, infrastructure, and digital connectivity complements India’s efforts under the Act East Policy and initiatives like MAHASAGAR and the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI).
- Digital and Innovation Synergy: APEC’s new emphasis on AI, digital economy, and innovation-driven growth aligns with India’s domestic programmes like Digital India, Startup India, and IndiaAI strengthening India’s role as a digital bridge in the region.
- As APEC expands its agenda beyond trade, it offers India opportunities to engage informally with regional economies and shape the Indo-Pacific’s economic architecture.
Conclusion
The 2025 APEC Summit in Gyeongju marked the convergence of technology and geopolitics in the Asia-Pacific. Through the Gyeongju Declaration and the AI Initiative, it set the course for sustainable and equitable AI-driven growth across the region.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Examine how Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) evolving agenda reflects the transformation of global economic governance. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the APEC Leaders’ Gyeongju Declaration (2025)?
It is the outcome document of the 2025 APEC Summit held in Gyeongju, South Korea, reaffirming leaders’ commitment to inclusive economic growth, digital and AI transformation, and regional economic integration under the Putrajaya Vision 2040.
2. What is the APEC Artificial Intelligence (AI) Initiative (2026–2030)?
A six-year framework adopted at the APEC 2025 Summit to harness AI’s potential for inclusive and resilient economic growth through innovation, and sustainable AI infrastructure.
3. What is the APEC Collaborative Framework for Demographic Changes?
It is a regional plan to address ageing populations, declining birth rates, and rapid urbanisation through intergenerational, people-centred policies promoting “silver economy.”
4. How does APEC operate as an organisation?
APEC functions on consensus and voluntary cooperation, not binding treaties, with all 21 member economies having equal voice and decisions made collectively through dialogue.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following pairs: (2009)
|
Organization |
Location of Headquarters |
|
1. Asian Development Bank |
Tokyo |
|
2. Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation |
Singapore |
|
3. Association of SouthEast Asian Nations |
Bangkok |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Q2. India is a member of which among the following? (2015)
- Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation
- Association of South-East Asian Nations
- East Asia Summit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) India is a member of none of them
Ans: (b)