5 Years of NEP 2020 | 02 Aug 2025
For Prelims: National Education Policy (NEP 2020), PM SHRI, Right to Education Act, 2009, PARAKH, NISHTHA, PM e-VIDYA, DIKSHA, Vidya Samiksha Kendra, SDG, Centrally Sponsored Scheme, Multidisciplinary Education and Research Universities (MERUs)
For Mains: Key Achievements & Challenges Related to NEP 2020, Government Policies Related to Education, Measures to Strengthen NEP.
Why in News?
The Union Education Minister inaugurated the Akhil Bharatiya Shiksha Samagam (ABSS) 2025 to mark the 5th anniversary of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
What are the Key Achievements of NEP 2020?
- Mother Tongue-Based Education & Curriculum Reform: The 5+3+3+4 structure and NCF-SE (National Curriculum Framework for School Education) promote experiential, competency-based learning with mother tongue as the medium of instruction in early years.
- Inclusivity: Over 1.15 lakh students from SEDG (Socially and Economically Disadvantaged Groups) and 7.58 lakh girls have enrolled in residential schools.
- The PRASHAST App supports disability screening.
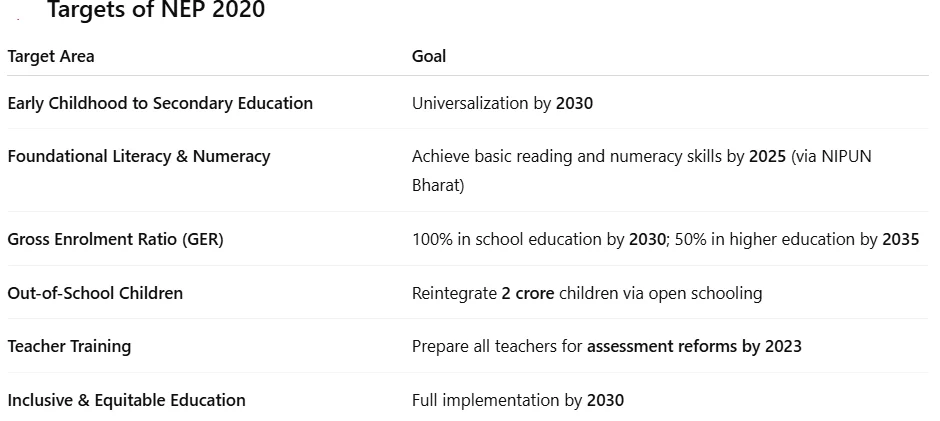
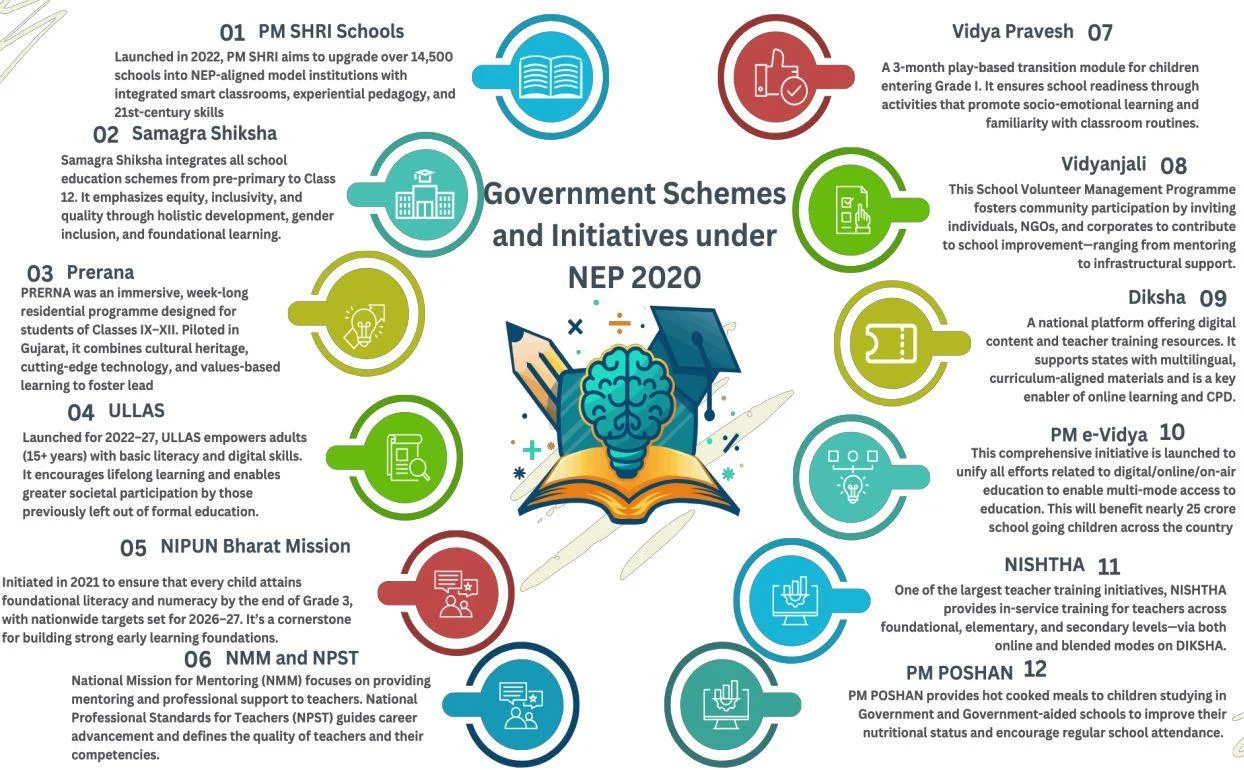
- Foundational Literacy & Numeracy (FLN): NIPUN Bharat and Vidya Pravesh have reached over 4.2 crore students across 8.9 lakh schools.
- Teacher Training: 4 lakh+ teachers trained under NISHTHA via digital platforms like DIKSHA, and PM e-Vidya.
- Multidisciplinary & Holistic Higher Education: NEP 2020 promotes Multidisciplinary Education and Research Universities (MERUs) to provide world-class education.
- Introduction of Academic Bank of Credits (ABC) enables flexible learning and credit transfer and emphasis on Multiple Entry and Exit systems.
- 72% of schools have internet access. Initiatives like Vidyanjali, DIKSHA, PM e-Vidya, e-Jaadui Pitara (AI-powered play-based learning), and AI Bots (e.g., Katha Sakhi, Teacher Tara) are enhancing education delivery.
- Common Testing: CUET, introduced in 2022, has become a key gateway for undergraduate admissions.
What is the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020?
- About: The National Education Policy 2020 aims to address issues of quality, equity, access, and affordability across all levels of education. It replaced the 34-year-old NEP of 1986.
- It is based on the recommendations of the Dr. K. Kasturirangan Committee.
- Key Initiatives:
What are the Key Challenges Related to the NEP 2020?
- Lack of Consensus: NEP implementation varies across states, with opposition from states like Tamil Nadu and West Bengal over provisions like the three-language formula, mother tongue instruction, and common entrance tests.
- Infrastructure & Financial Constraints: There are shortages of qualified teachers, poor digital infrastructure, particularly in rural areas, and inadequate Anganwadi preparedness for quality Balvatika (pre-primary) education.
- Public spending on education remains below NEP’s 6% of GDP target, with budgetary allocations falling short of supporting the policy’s ambitious reforms.
- Regulatory & Linguistic Barriers: The establishment of the Higher Education Commission of India (HECI), intended as a successor to the UGC (University Grants Commission), and the rollout of the National Curriculum Framework for Teacher Education have both experienced delays.
- Additionally, translating educational content into diverse Indian languages and the shortage of regionally fluent teachers pose major implementation challenges.
- Resistance & Weak Monitoring: Institutional resistance to pedagogical reforms and apprehensions about over-centralisation (e.g., CUET) hamper adoption.
- Also, the lack of robust data systems and uneven implementation hinder effective monitoring and evaluation of NEP 2020 outcomes.
What Steps are Needed to Strengthen the Implementation of NEP 2020?
- Enhance Research & Innovation: Invest in research at the technology-pedagogy interface for evidence-based, context-specific innovations.
- Digital Infrastructure Gap: There is an urgent need to upgrade school-level ICT infrastructure, as only 57.2% schools have functional computers and 53.9% have internet access (UDISE+ 2023–24).
- Teacher Training: Enhance capacity-building for tech integration, promoting creativity, critical thinking, and ethical reasoning.
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Foster cooperation among educators, technologists, social scientists, and policymakers to steer future-ready learning ecosystems.
Conclusion
NEP 2020 provides a transformative vision for a 21st-century education system. Notable progress includes Foundational Literacy & Numeracy (FLN), digital access, and higher education reforms. However, federal disagreements, infrastructure gaps, and regulatory delays remain key challenges. With strategic investment, inter-governmental coordination, and innovation, NEP’s goals of a flexible, inclusive, and future-ready education ecosystem can be achieved.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key features of National Education Policy (NEP 2020). Critically analyze the impact of NEP 2020 on federalism. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. National Education Policy 2020 is in conformity with the Sustainable Development Goal-4 (2030). It intends to restructure and reorient the education system in India. Critically examine the statement. (2020)

 2020.webp)