2nd Edition of the NER District SDG Index | 08 Jul 2025
Why in News?
NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) has launched the 2nd edition of the North Eastern Region (NER) District Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index for 2023-24, building on the first edition launched in 2021.
What is the NER District SDG Index?
- About: The NER District SDG Index is a composite tool designed to monitor district-level progress on selected SDG indicators. Developed collaboratively by NITI Aayog, the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (MoDoNER), and with technical support from United Nations Development Programme (UNDP).
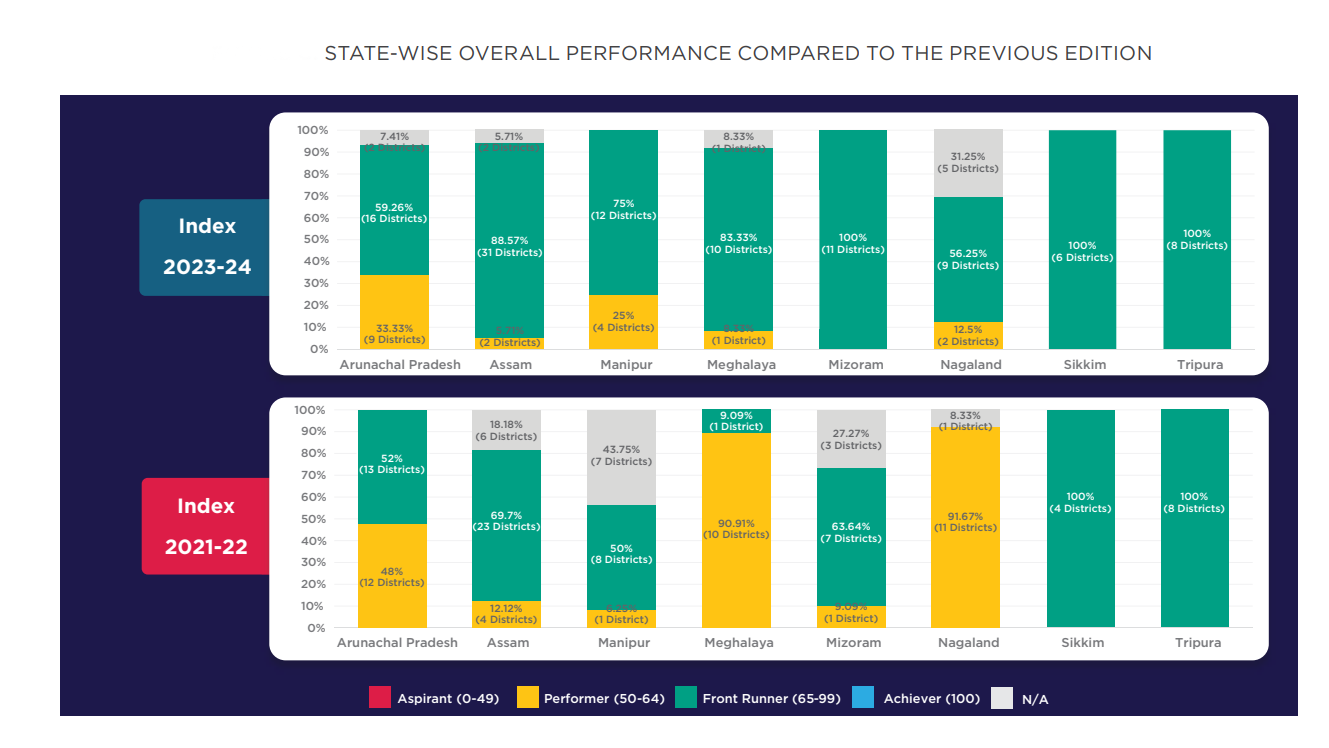
- The index covers all 121 out of 131 (92%) districts across the eight Northeastern states.
- Based on NITI Aayog’s national SDG Index methodology, the districts are ranked into four categories based on their composite scores: Achiever (Score = 100), Front Runner (Score 65–99), Performer (Score 50–64), and Aspirant (Score < 50).
- Key Findings of the NER District SDG Index 2023-24: In the 2023-24 edition, 85% of NER districts are in the Front Runner category (score 65–99), up from 62% in the previous edition, indicating significant improvement in overall district performance.
- All districts in Mizoram, Sikkim and Tripura have achieved Front Runner status, with no districts falling in the Aspirant or Achiever categories.
- Mizoram has the highest-scoring district in the entire NER (Hnahthial at 81.43) and Arunachal Pradesh has the lowest-scoring district in the entire region (Longding at 58.71).
- Sikkim has the narrowest range (5.5 points) in terms of the score of the highest and lowest district, showing the most consistent performance across its districts.
- Importance of NER District SDG Index: The NER District SDG Index facilitates evidence-based planning and resource allocation.
- The Index helps identify development gaps, guide targeted interventions, ensure efficient resource deployment, and support the localisation of SDGs through a cooperative federalism approach.
- It aligns national development programmes with local needs for more focused and effective outcomes.
- This initiative brings together states, NITI Aayog, and MoDoNER to foster sustainable and inclusive development in the region, aligning with India’s broader Viksit Bharat @2047 vision.
- The Index helps identify development gaps, guide targeted interventions, ensure efficient resource deployment, and support the localisation of SDGs through a cooperative federalism approach.
NITI Aayog’s National SDG Index
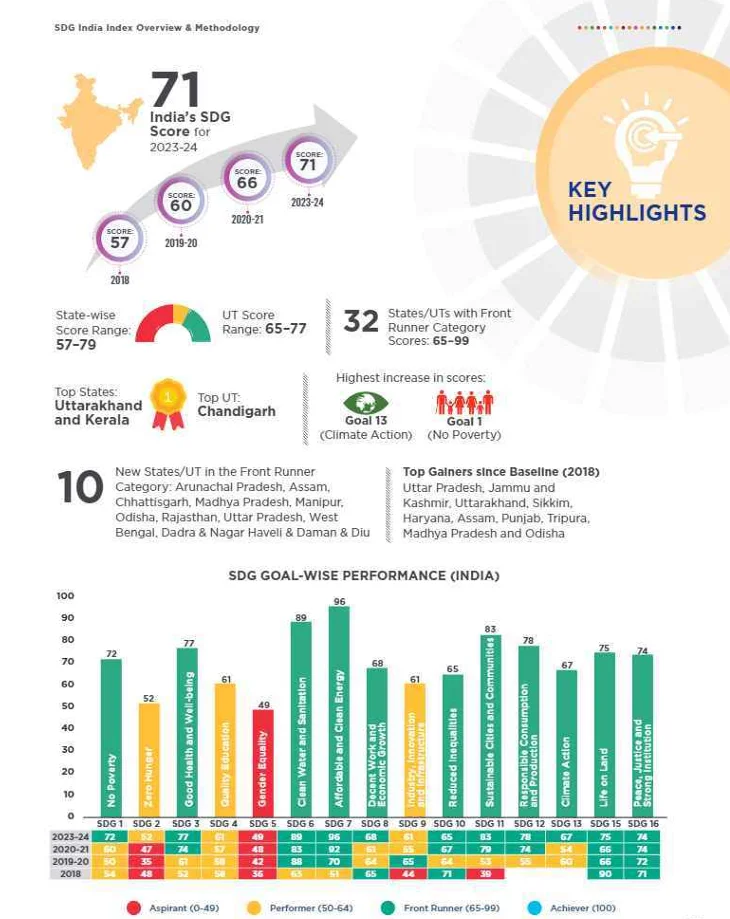
- About: It tracks states’ and UTs’ progress on 16 Sustainable Development Goals using 113 indicators aligned to the National Indicator Framework. The SDG Goal 14 (Life Below Water) has not been included in the calculation of the Composite Score for the Index as it solely pertains to the nine coastal States.
- States/UTs are categorised as Aspirants (0–49), Performers (50–64), Front-Runners (65–99), and Achievers (100), with scores reflecting progress toward India’s 2030 SDG targets and vision of Viksit Bharat @2047.
- SDG India Index for 2023-24: India’s SDG score rose to 71 (from 66 in 2020-21 and 57 in 2018), driven by gains in poverty reduction, economic growth, and climate action.
- Top Performers: Kerala and Uttarakhand topped with scores of 79.
- Lowest Performers: Bihar (57) and Jharkhand (62).
- Top Performing Goals: Goal 13 (Climate Action) score rose from 54 to 67, and Goal 1 (No Poverty) improved from 60 to 72.
- Goals 1, 8, and 13 are now in the Front Runner category (score between 65–99).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Sustainable development is described as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In this perspective, inherently the concept of sustainable development is intertwined with which of the following concepts? (2010)
(a) Social justice and empowerment
(b) Inclusive Growth
(c) Globalization
(d) Carrying capacity
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).” Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)