Startup India Revolution
For Prelims: Startup India, Digital India, Aadhaar, UPI, BharatNet, Fund of Funds for Startups, iDEX, ADITI, Intellectual Property Rights, Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, Skill India.
For Mains: Role of Startup India in transformation of Indian economy, associated challenges and way forward.
Why in News?
The Startup India initiative has been instrumental in transforming India’s innovation ecosystem, fostering the growth of numerous startups.
- According to the Future Unicorn Report 2025, 11 new startups have joined India's unicorn club in 2025.
How has Startup India Transformed India’s Innovation Ecosystem?
- Building the Innovation Stack: Digital India, Aadhaar , UPI, and BharatNet have built a digital public infrastructure that lowers startup barriers, expands access, cuts costs, and drives an inclusive innovation ecosystem.
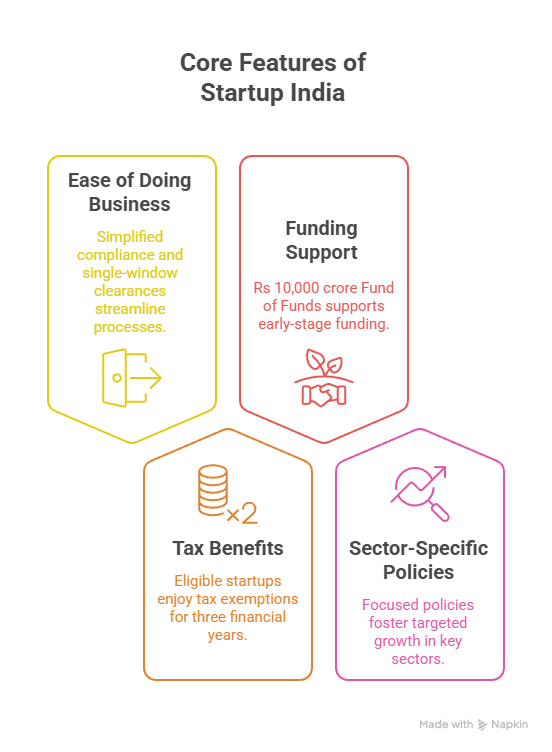
- Fund of Funds for Startups and credit guarantee schemes provided critical capital support for early-stage startups e.g., Fashinza (B2B marketplace streamlining the apparel and fashion supply chain).
- Ease of Doing Business reforms like single-window clearances and online systems have streamlined approvals, significantly reducing the time and cost of starting a business.
- These reforms created a layered innovation ecosystem, or innovation stack, enabling startups to scale rapidly.
- Unicorn Surge: By mid-2025, India had 118 unicorns (4 in 2014), with firms like Zomato, PhonePe, Razorpay, Ola, Meesho, and Delhivery solving local challenges and going global.
- A unicorn is a privately held startup company with a valuation of over USD 1 billion.
- Diversified Startup Ecosystem:
- FinTech: UPI established India as a global leader in digital payments.
- SpaceTech: Post-2020 reforms enabled private players like Skyroot Aerospace and Agnikul Cosmos; India now has 300+ startups in space.
- DefenceTech: Over 600 startups under iDEX and schemes like ADITI are driving indigenisation in defence manufacturing.
- Startup Dividend: Startups have generated over 12 lakh direct jobs and millions of indirect roles, while reducing import dependence and boosting exports, strengthening India’s global economic standing.
What is the Startup India Initiative?
- About: Launched in 2016, the Startup India initiative supports entrepreneurs by fostering a strong innovation ecosystem through tax benefits, simplified compliance, and funding access to drive economic growth and employment.
Core Features:
- Flagship Schemes Under Startup India:
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS) offers financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, and product trials.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS) facilitates collateral-free loans to startups to ensure access to credit.
- Startup Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) provides startups with assistance in patent filing, trademark registration, and Intellectual Property Rights (IPRs) protection at reduced costs.
- Key Achievements:
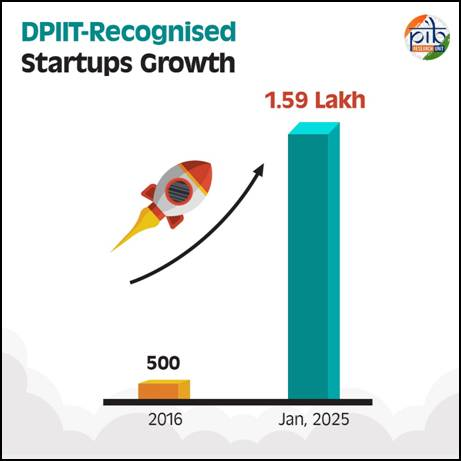
- Growth in Startups: The number of DPIIT-recognized startups surged from 500 in 2016 to 1.59 lakh in 2025.
- Startup Ecosystem: India has emerged as the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, home to 100+ unicorns.
- Job Creation: Over 16.6 lakh direct jobs were generated by startups as of October 31, 2024.
- Women Empowerment: 73,151 recognized startups have at least one woman director, reflecting progress in gender inclusivity.
What are the Key Challenges Facing India’s Startup Ecosystem?
- Funding Constraints: Startups in Tier-II and Tier-III cities struggle with funding, which dropped from Rs 2,202 crore in July 2024 to Rs 630 crore in August 2024.
- Regulatory Complexity: India’s complex regulatory environment poses challenges for startups, with debates under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 on app-based cab classification and compliance under the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 increasing legal and administrative burdens.
- Growth Challenges: Despite strong initial growth, about 90% of startups fail within five years due to scaling difficulties, operational inefficiencies, and obstacles in entering new markets.
- Market Saturation: Intense edtech competition has caused market saturation, shrinking margins, and unsustainable cash burn, with the post-pandemic downturn highlighting consolidation risks.
What Measures are Needed to Strengthen India’s Startup Ecosystem?
- Enhanced Tax Benefits: Extend tax incentives from 3 to 5 years, with additional breaks for deep-tech startups and those addressing national priorities, following global examples like Israel’s 12% corporate tax for tech firms.
- Boosting Market Access: Require a fixed percentage of government procurement to come from startups, creating substantial market opportunities for them.
- Decentralized Startup Ecosystem: Develop tier-2 and tier-3 cities as startup hubs by improving infrastructure and offering incentives, using a hub-and-spoke model where larger cities support surrounding smaller cities.
- Skill Development: Expand sector-specific skill programs under Skill India, focusing on emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT to create a future-ready startup workforce.
Conclusion
India’s startup story is a civilizational reset of confidence. The journey from Startup India to Unicorn Nation captures the essence of a new India: bold, innovative, and globally ambitious. Startup India has transformed India from a job-seeker to a job-creator economy, driving innovation, unicorn growth, and employment across sectors like FinTech, SpaceTech, and DefenceTech, supported by tax incentives, funding, skill development, and decentralized ecosystems for long-term success.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. While the unicorn boom showcases success, India's startup ecosystem faces significant challenges in funding and regulation. Discuss the measures needed to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth. |
UPSC Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Scientific research in Indian universities is declining, because a career in science is not as attractive as are business professions, engineering or administration, and the universities are becoming consumer-oriented. Critically comment. (2014)
Mitigating Flood and Landslide Risks
For Prelims: Monsoon, Himalayas, Cloudbursts, Moraines, Glacial Lake Outburst Floods.
For Mains: Factors Contributing to Flood and Landslide Vulnerability in Hilly Areas and Measures for Mitigation.
Why in News?
The current monsoon has brought unusually intense rainfall to hilly states such as Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh, exacerbating the incidence of landslides and pushing river systems to perilous levels, thereby heightening risks to both lives and infrastructure.
What Factors Increase the Vulnerability of Hilly Regions to Floods and Landslides?
- Steep Slopes and Gravity: Water flows down steep slopes much faster than on flat land, preventing infiltration. This causes water to quickly accumulate in streams and rivers, leading to rapid-onset flash floods.
- For instance, landslides in Mandi, Kullu, Dharali, Tharali, and Jammu.
- Geology and Soil Type: Many young mountain ranges (like the Himalayas) are geologically active and made of fractured, weak, or weathered rocks that are easily dislodged.
- Mountain soils are often thin and lack deep root systems, making them prone to being washed away.
- Frequent landslides in Darjeeling and Sikkim are due to weak rock formations and fragile soils.
- Mountain soils are often thin and lack deep root systems, making them prone to being washed away.
- Hydrological Factors: A valley funnels rainfall into a narrow stream or river, and the steep gradient with high energy flow gives water strong erosive power, which erodes riverbanks and slopes, making floods worse.
- For instance, Alaknanda and Mandakini river valleys in Uttarakhand frequently witness flash floods.
- Trigger Factors: Continuous rain or intense cloudbursts saturate soil, reduce friction, and trigger landslides, flash floods, and debris flows.
- Sudden temperature rise or rain on snow causes snowmelt, releasing large water volumes, saturating the ground, and flooding streams.
- E.g., For the season (June-September 2025), the northwestern region has received more than 30% surplus rainfall.
- Human-Induced Factors: Road cutting, construction on steep slopes, blocked natural drainage, unsustainable agriculture, and overgrazing destabilize slopes, increasing the risk of landslide.
- The Joshimath land subsidence (2023), linked to unregulated construction, highlights human-induced vulnerability.
How does Climate Change Increase Flood and Landslide Vulnerability?
- Increased Extreme Rainfall Events: A warmer atmosphere holds more moisture (≈7% per 1°C), causing intense rainfall and cloudbursts, which trigger flash floods as the ground cannot absorb water fast enough, overwhelming streams and rivers.
- Climate change disrupts monsoon patterns, causing droughts followed by intense rain, where dry, hardened soil reduces absorption, increasing runoff, flood, and erosion risk.
- Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs): Rising temperatures cause glacier retreat and the formation of unstable lakes dammed by moraines, which can breach in GLOF events, releasing massive water and debris, leading to catastrophic flooding downstream.
- The 2023 South Lhonak GLOF (Sikkim) destroyed the Rs 16,000 crore Chungthang hydropower project, caused silting in the Teesta river, and increased downstream flood risk.
- Permafrost Thaw: In high-altitude hilly regions, rising temperatures thaw permafrost, causing slope destabilization, rockfalls, and landslides, which add debris to rivers and increase flood risks.
- Increased Wildfires: Climate change makes hilly areas hotter and drier, increasing wildfires that destroy vegetation, create water-repellent soil, and cause fast-moving debris flows when rain hits.
- For instance, the India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2023 showed that Uttarakhand alone recorded 5,351 forest fire incidents between November 2022 and June 2023.
NDMA Guidelines on Flood Management
- Structural Measures
- Diversion of Flood Water: Use natural/artificial channels to reduce river water levels.
- Catchment Area Treatment/Afforestation: Watershed management, soil conservation, check dams, detention basins to reduce flood peaks
- Embankments/Levees/Walls: Prevent overflow; effective on Yamuna near Delhi.
- Drainage Improvement: Restore natural drainage blocked by roads/canals/railways.
- Channel Improvement/Desilting/Dredging: Increase discharge capacity, selective desilting at outfalls/confluences.
- Reservoirs/Dams/Water Storages: Store excess floodwater.
- Non-Structural Measures
- Flood Management Plans (FMPs): Mandatory for all government departments/agencies.
- Flood Forecasting & Warning: Based on real-time discharge & rainfall data from CWC and IMD.
- Flood Proofing: Raised platforms, utility installations, double-storey shelters for safety.
- Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM): Manage water at basin/watershed scale.
- Flood Plain Zoning: Regulate land use; map areas as extremely or partially affected zones.
NDMA Guidelines on Landslides
- Landslide Hazard Zonation: Landslide Hazard Zonation maps should be prepared at macro (1:50,000/25,000) and meso (1:10,000) scales, using advanced tools like UAVs, Terrestrial Laser Scanners, and high-resolution EO data.
- Early Warning System (LEWS): An effective LEWS must include rainfall threshold-based modelling, wireless instrumentation, and real-time monitoring for both rainfall- and earthquake-triggered landslides.
- Capacity Building & Training: Capacity building requires a Nationwide Training Need Assessment (TNA) in Landslide Risk Management, the use of new technologies in training, and a focus on grassroots communities.
- Mountain Zone Regulations & Policies: The strategy recommends formulating and enforcing land-use policies, updating building regulations, revising BIS codes, and including hazard zoning provisions in town and country planning laws to ensure safety in landslide-prone areas.
What Measures can be Adopted to Mitigate the Vulnerability of Regions to Floods and Landslides?
- Environmental Measures: Afforestation and Reforestation with native trees and Van Panchayats empower communities to bind soil, absorb rainwater, and protect forests.
- Contour trenching, terrace farming, and check dams slow runoff, allow infiltration, trap sediment, and reduce erosive power.
- Engineering Measures: Rock bolts, soil nails, retaining walls, and debris flow barriers/screens stabilize slopes and prevent rocks and debris from reaching roads or settlements.
- Channel improvement, diversion channels, and sediment traps increase river capacity, redirect excess water, and capture silt and debris to reduce flood risk.
- Urban flood resilience can be enhanced through proper drainage, sponge city models, and rainwater harvesting.
- Policy Measures: Enforce carrying capacity studies, stringent land use planning, and hazard zone identification to restrict construction on steep slopes, riverbeds, and floodplains, relocate vulnerable settlements, and implement stringent building codes.
- Develop robust early warning systems integrating weather forecasts, rainfall data, and river levels, and support them with community sirens and drills to ensure timely evacuation to safe zones.
- Economic & Financial Measures: Establish dedicated disaster risk reduction budgets for states and districts.
- Shift to Parametric Insurance Models for quick payouts based on rainfall/flood-level triggers (avoiding lengthy claims).
Conclusion
Hilly regions are inherently vulnerable due to steep slopes and fragile geology. However, human activities like unsustainable construction and deforestation have severely amplified this risk. Effective mitigation requires an integrated approach, aligning with the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction (2015–30), by combining stringent land-use policies, ecological restoration, engineering solutions, and community-based early warning systems.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Critically analyse how geological fragility and human activities contribute to hydrometeorological disasters in Hilly Areas. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Differentiate the causes of landslides in the Himalayan region and Western Ghats. (2021)
Q. The Himalayas are highly prone to landslides.” Discuss the causes and suggest suitable measures of mitigation. (2016)
Bima Sugam: Unified Digital Marketplace for Insurance
Why in News?
- The Bima Sugam India Federation (BSIF) has launched Bima Sugam, a digital platform envisioned as the world’s largest integrated online insurance marketplace.
What are Key Facts Regarding Bima Sugam?
- About: Bima Sugam is a unified digital marketplace for all insurance needs-life, health, and general, where users can buy, renew, manage, and claim policies on a single platform.
- It will securely store policy documents and function like UPI, creating a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for insurance.
- It forms part of IRDAI’s Bima Trinity-Bima Vistaar, Bima Vahak, and Bima Sugam, and is supported by the Life Insurance Council and the General Insurance Council.
- Coverage:
- Life Insurance: Term plans, savings (participating & non-participating), annuity, pension, ULIPs.
- Health Insurance: Comprehensive medical and wellness products.
- Motor Insurance: Third-party liability and own-damage policies.
- Travel & Personal Accident Insurance for individuals/families.
- Commercial Insurance: Property, marine, agricultural, industry-specific products.
- Unique Feature: Bima Sugam differs from private distributors by offering end-to-end policy services and claim settlement at low cost, unlike private firms that only sell policies and earn high commissions.
- Significance: It is the first step in building Digital Public Infrastructure for insurance, supporting ‘Insurance for All by 2047’ under Viksit Bharat 2047.
- It ensures transparency, low-cost access, a centralised database, and fosters innovation with quicker adoption of new products.
Bima Trinity
- Bima Sugam: Unified digital platform for buying, servicing, and settling insurance policies.
- Bima Vistar: Bundled policy covering life, health, property, and accidents with quick claim payouts.
- Bima Vaahaks: Women-led grassroots network promoting insurance awareness and Bima Vistar adoption.
Insurance Sector in India
- India is the 10th largest insurance market globally and is projected to become the 6th largest by 2032, surpassing Germany, Canada, Italy, and South Korea.
- Insurance Density increased from USD 92 in FY23 to USD 95 in FY24, calculated as the per capita premium (ratio of premium to population).
- The insurance penetration declined from 4% in FY23 to 3.7% in FY24 (global average 7%). Insurance penetration is measured as the percentage of insurance premium to GDP.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. In India, under cyber insurance for individuals, which of the following benefits are generally covered, in addition to payment for the loss of funds and other benefits? (2020)
- Cost of restoration of the computer system in case of malware disrupting access to one’s computer
- Cost of a new computer if some miscreant wilfully damages it, if proved so
- Cost of hiring a specialized consultant to minimize the loss in case of cyber extortion
- Cost of defence in the Court of Law if any third party files a suit
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
‘Snapback Mechanism’ & Iran Nuclear Deal (JCPOA)
Iran’s Foreign Minister is set to discuss the country's nuclear program with the UK, France, and Germany to avert the reimposition of international sanctions under the ‘snapback mechanism’, which were lifted under the 2015 JCPOA.
- The E3 (Britain, France, Germany) have invoked the 30-day snapback mechanism to reimpose UN sanctions, unless Iran restores UN nuclear inspector access to its nuclear sites and re-engages with the US.
- Snapback Mechanism: It allows any Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) participant, to reimpose UN sanctions if Iran commits “significant non-performance.”
- In such a case, the issue can be referred to the JCPOA Joint Commission, coordinated by the European Union (EU), and addressed through its Dispute Resolution Mechanism (DRM).
- Iran’s Cooperation with IAEA: Earlier, Iran agreed to resume cooperation with the IAEA, including nuclear site inspections, following a tense period in June when Israeli and U.S. strikes on Iranian facilities led to a temporary suspension of inspections over security concerns.
JCPOA
- The Iran nuclear agreement (formally known as JCPOA), signed in July 2015 between Iran and the P5+1 (China, France, Russia, UK, US, Germany).
- It required Iran to dismantle much of its nuclear program and allow extensive international inspections in exchange for sanctions relief.
- The U.S. withdrew from the JCPOA in May 2018 under President Trump, despite Iran's compliance with the agreement.
- The Trump administration's 'maximum pressure' policy aimed to force Iran into renegotiating the deal, a request Iran rejected.
|
Read More: Iran Nuclear Deal |
2nd Anniversary PM Vishwakarma Yojana
The Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises (MSME) organised a ‘PM Vishwakarma and National SC-ST Hub Mega Conclave’ in Bodh Gaya, Bihar to mark the 2nd anniversary of the PM Vishwakarma Scheme.
PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- About: Launched on 17th September 2023, it is a Central Sector Scheme offering comprehensive support to traditional artisans and craftspeople involved in manual and tool-based work.
- Implementation: The scheme will be jointly implemented by the Union Ministries of MSME, Skill Development, and Finance.
- Eligibility: The applicant must be an artisan or craftsperson in one of the 18 traditional trades in the unorganized sector, self-employed, above 18 years, and actively working at the time of registration.
- The 18 eligible trades include Carpenter, Boat Maker, Armourer, Blacksmith, Locksmith, Goldsmith, Potter among others.
- Exclusion: Beneficiaries who have availed loans under similar credit-based schemes of the Centre or State for self-employment or business development in the past 5 years.
- Achievements: Over two years, 23 lakh people received free skill training, 8 lakh toolkits were provided, and ₹4,100 crore in collateral-free loans were disbursed.
|
Read More: PM Vishwakarma Scheme |
Aquamonitrix: Portable Ion Chromatography
A portable ion chromatograph, Aquamonitrix, has been developed to enable on-site analysis of nitrate and nitrite ions, benefiting both environmental monitoring and classroom teaching.
- Ion chromatography is a laboratory technique used to separate and measure ions (charged particles) in a sample.
- The technique involves passing a liquid sample through a long column that separates ions based on their individual properties.
Aquamonitrix
- About: It is a portable ion chromatograph developed by Australian scientists.
- It is small, battery-operated, and nearly ten times cheaper than traditional lab-based equipment.
- Working Mechanism: Soil water is collected using a vacuum pump, filtered, and injected into the Aquamonitrix unit, where a sodium chloride solution carries the sample.
- The unit's UV light detector displays distinct peaks for nitrate and nitrite ions, avoiding interference from other ions.
- Applications:
- Education: Aquamonitrix serves as an effective teaching tool, bridging the gap between classroom learning and real-world applications in chemistry.
- Environmental Monitoring: Aquamonitrix can be used to monitor nitrate and nitrite pollution in soil and water.
- Agriculture: It helps optimize fertilizer use and prevents overuse.
- Water Safety: The device can be used to test drinking water quality on-site.
|
Read More: Nitrogen Pollution |