Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement
Why in News?
The Ministry of Earth Sciences has set up a 12 member panel to implement a new law to safeguard its interests in international ocean waters, aligning with the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement (High Seas Treaty) agreement.
What is the Biodiversity Beyond National Jurisdiction (BBNJ) Agreement ?
- About: The BBJN Agreement or High Seas Treaty is a legal framework under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) to safeguard the ecological health of oceans.
- Adopted in 2023, it aims to curb pollution, conserve biodiversity, and ensure sustainable use of marine resources in waters beyond national boundaries.
- Scope of the Treaty:
- Establish Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) like national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to regulate activities and conserve ocean ecosystems.
- Regulates extractive activities such as seabed mining & ensures fair distribution of benefits from marine resources and organisms.
- Make EIAs mandatory for major oceanic projects that may harm the high seas, even if carried out within national waters.
- Support developing nations in accessing marine technologies and resources while ensuring conservation.
- Signing and Ratification: As of August 2025, over 140 countries have signed the treaty and 55 have ratified it.
- India has signed the BBNJ Agreement in 2024 but has not yet ratified it.
- Signing shows intent, while ratification legally binds a country to the treaty, with the process differing across nations.
High Seas
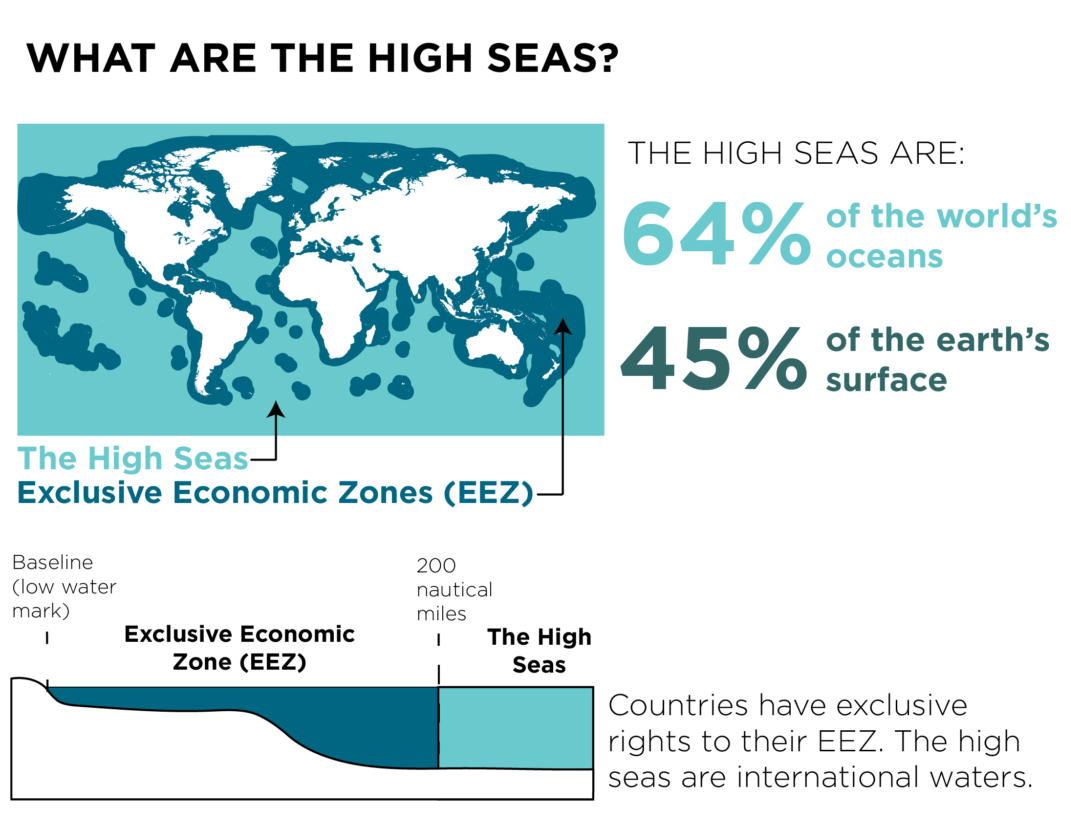
- About: High seas refer to regions beyond the national jurisdiction of any country.
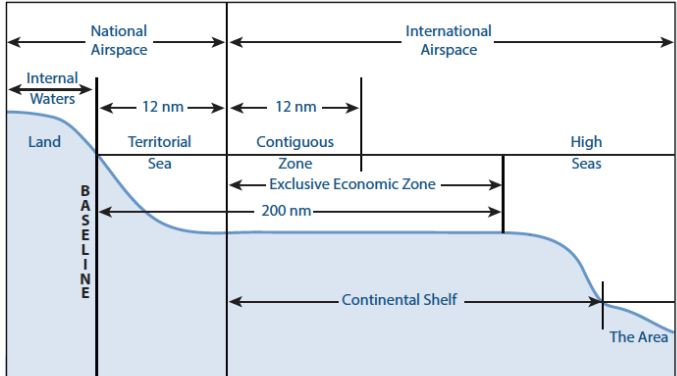
- Generally, national jurisdictions extend up to 200 nautical miles (370 km) from a country's coastline, known as the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
- No country has jurisdiction or responsibility for resource management in these waters.
- Only about 1% of the high seas are currently protected.
- Significance: The high seas cover 64% of oceans and 50% of Earth’s surface & are vital for marine biodiversity, climate regulation, carbon absorption, solar energy storage, and heat distribution.
- They provide key resources like seafood, raw materials, genetic resources, and medicinal compounds.
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS)
- UNCLOS, also called Law of the Sea, is an international treaty adopted and signed in 1982, replacing the 1958 Geneva Conventions.
- It provides the legal framework for marine and maritime activities.
- It divides ocean space into 5 zones- Internal Waters, Territorial Sea, Contiguous Zone, Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ), and High Seas.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Rim Association for Regional Cooperation (IOR-ARC)’, consider the following statements: (2015)
- It was established very recently in response to incidents of piracy and accidents of oil spills.
- It is an alliance meant for maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/ are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. With respect to the South China sea, maritime territorial disputes and rising tension affirm the need for safeguarding maritime security to ensure freedom of navigation and overflight throughout the region. In this context, discuss the bilateral issues between India and China. (2014)
Environment Audit Rules, 2025
Why in News?
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has notified the Environment Audit Rules, 2025 under the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, to establish a comprehensive framework for environmental accountability across India.
What are the Key Features of the Environment Audit Rules, 2025?
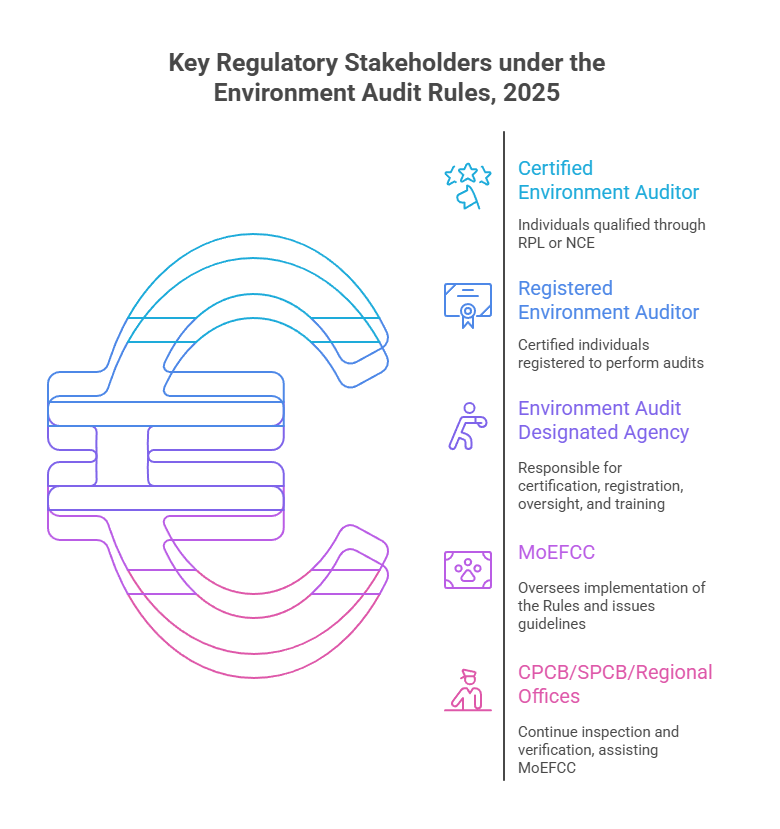
- Certification and Registration of Environmental Auditors: Environment Auditors (EAs) are to be Certified and Registered by the MoEFCC-notified Environment Audit Designated Agency (EADA). EADA is responsible for:
- Certification, registration, and oversight of auditors.
- Monitoring performance and providing training.
- Taking disciplinary action when required.
- Registered Environment Auditors (REAs): Audits will be conducted by Registered Environment Auditors (REAs).
- REAs will be assigned projects randomly to ensure impartiality.
- REAs will undertake activities including sampling, analysis, compensation calculation, and audits under various environmental and forest-related legislations.
- Two-Tiered System of Compliance:
- Oversight and Monitoring: A Steering Committee, led by an Additional Secretary from MoEFCC, will oversee the implementation of these rules.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Which of the following can be threats to the biodiversity of a geographical area? (2012)
- Global warming
- Fragmentation of habitat
- Invasion of alien species
- Promotion of vegetarianism
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q2. Biodiversity forms the basis for human existence in the following ways: (2011)
- Soil formation
- Prevention of soil erosion
- Recycling of waste
- Pollination of crops
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Bioproducts
Why in News?
The Department of Biotechnology (DBT), under its BioE3 Policy, is setting up 16 biomanufacturing hubs across India to boost domestic production of bioproducts such as APIs, biofuel enzymes, reagents for biofertilizers.
- These hubs, also known as National Bio-Enablers or Mulankur, are specialized facilities supporting indigenous production of bioproducts and fostering innovation across sectors like health, agriculture, energy, environment, and AI-driven biomanufacturing.
What are Bioproducts?
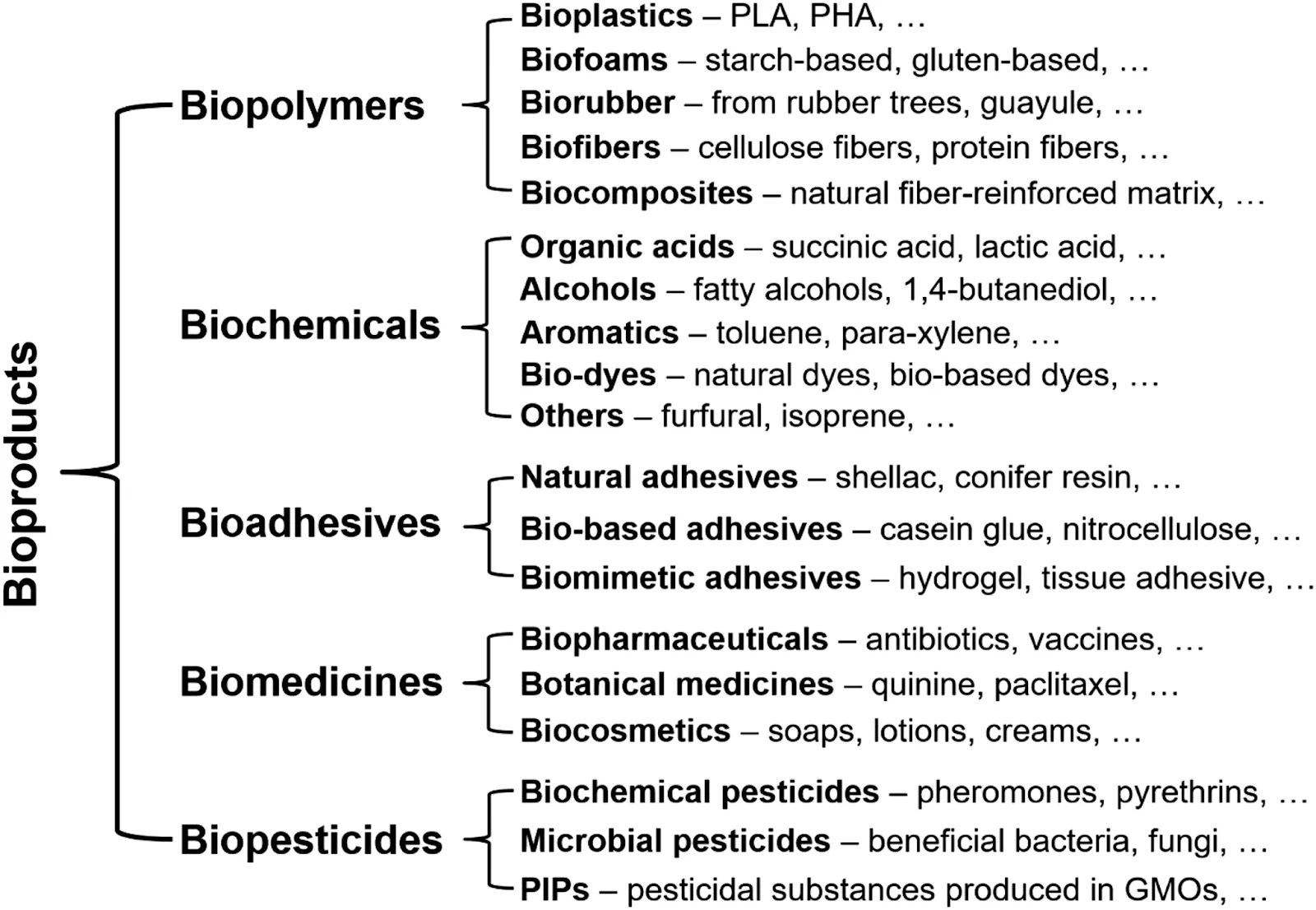
- About: Bioproducts are fuels, materials, and chemicals derived from renewable biomass such as crops, trees, algae, and agricultural waste.
- Eg: Biofuels (ethanol, biogas), bioplastics, bio-based cosmetics, and plant-derived medicines.
- Types of Bioproducts:
- Production Methods: Generated using fermentation, pyrolysis, enzymatic conversion, or chemical synthesis.
- They are made from soybeans, sugarcane, algae, mycelium, etc., and often use agri-forestry residues, reducing stress on food crops. Eg: Sunflower residue converted into biofuel.
- Significance:
- Reduce fossil fuel dependence and help mitigate air pollution, deforestation, and biodiversity loss.
- Promote climate-resilient development through biotechnological innovation.
- Extend beyond laboratories to support sustainability via biodegradable packaging and eco-friendly products, while also generating rural employment and fostering green jobs.
- Biodegradability: Not all bioproducts are biodegradable, it varies by use (e.g., bio-based paint is not biodegradable).
Did You Know?
- Despite being the world’s 3rd largest pharmaceutical producer (volume) and the largest supplier of generic drugs, India relies heavily on imports for key bioproducts.
- Nearly 70% of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are sourced from China, with India being 100% dependent on China for 45 out of 58 critical APIs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than resistance to pests, what are the prospects for which genetically engineered plants have been created? (2012)
- To enable them to withstand drought
- To increase the nutritive value of the produce
- To enable them to grow and do photosynthesis in spaceships and space stations
- To increase their shelf life
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Sample Registration System (SRS) Statistical Report 2023
The Sample Registration System (SRS) Statistical Report 2023 highlights significant demographic shifts in fertility, mortality in India.
- Total Fertility Rate (TFR): TFR fell to 1.9 in 2023, below the replacement level fertility of 2.1.
- Highest TFR: Bihar (2.8), Lowest TFR: Delhi (1.2).
- TFR is the average number of children a woman is expected to have during her reproductive years (15-49 years).
- Replacement level TFR is the average number of children required per woman for one generation to replace itself.
- Crude Birth Rate (CBR): CBR declined from 19.1 (2022) to 18.4 (2023).
- CBR indicates the number of live births occurring during the year, per 1000 population.
- Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB): SRB for India in 2021–23 was 917 girls per 1,000 boys.
- Highest: Chhattisgarh (974). Lowest: Uttarakhand (868).
- Mortality Trends: The Crude Death Rate (CDR) was 6.4 in 2023, while the Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) stood at 25 in 2023.
About SRS
- The SRS conducted by the Office of the Registrar General of India, is a large-scale demographic survey that collects population data by age, sex, and marital status.
- It measures indicators like CBR, TFR, Age-Specific Fertility Rate (ASFR), General Fertility Rate (GFR), and related statistics at national and sub-national levels.
|
Read More: Human Development Report 2025 |
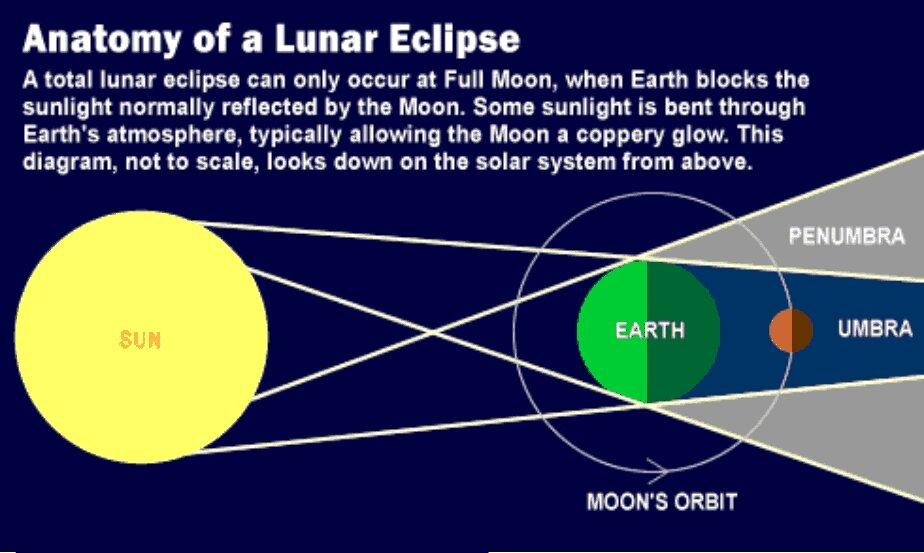
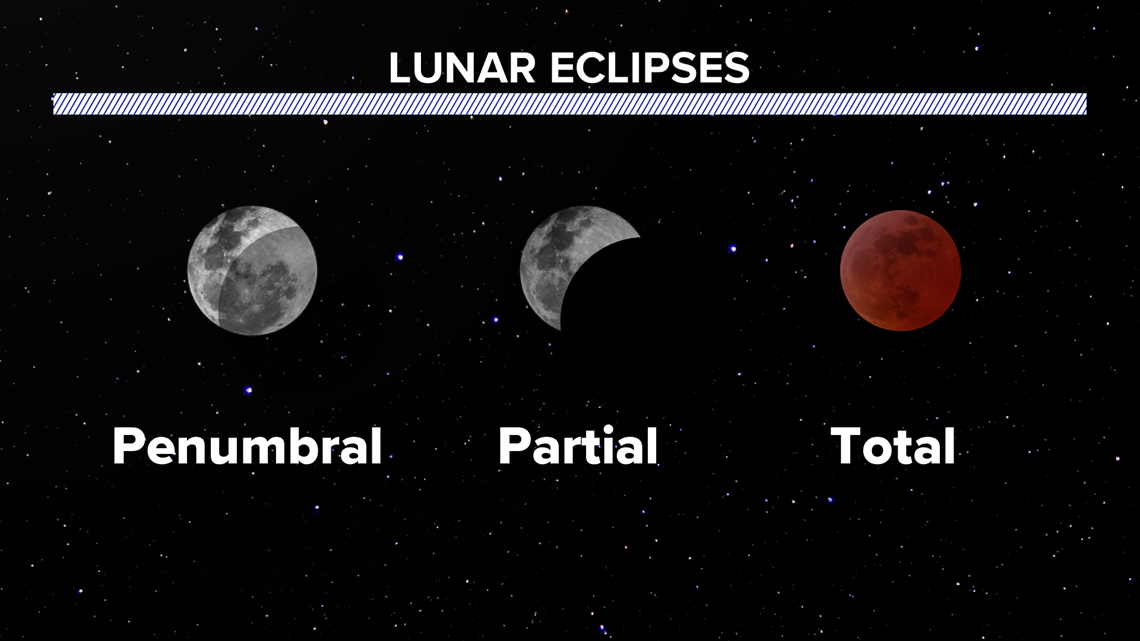
Total Lunar Eclipse and ‘Blood Moon’
A total lunar eclipse is set to occur on the night of 7th September 2025. At this time, the moon will be completely covered by the Earth's shadow, turning copper red (Blood Moon).
Total Lunar Eclipse
- About: A total lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes entirely through Earth’s umbra (darkest part of its shadow), with the Earth, Sun, and Moon perfectly aligned, completely blocking direct sunlight.
Blood Moon
- A Blood Moon refers to the reddish or coppery appearance of the Moon and occurs only during total lunar eclipses, which take place two to three times a year.
- During total lunar eclipses, the Earth blocks direct sunlight from reaching the Moon.
- However, sunlight passes through Earth’s atmosphere, where it is bent (refraction) and scattered.
- The blue wavelengths of light are scattered away, while the red and orange wavelengths pass through and fall on the Moon’s surface.
- This gives the Moon its distinctive deep red or reddish-orange colour.
|
Read More: Types of Eclipses |